
Chebyshev’s Theorem How can you determine whether a distribution is approximately normal? A statistical theorem called Chebyshev’s theorem states that the minimum percent of data between plus and minus K standard deviations from the mean (K > 1) in any distribution can be found by the formula
Minimum percent =
Thus, for example, between ±2 standard deviations from the mean there will always be a minimum of 75% of data. This minimum percent applies to any distribution For K = 2,
Minimum percent
Likewise, between ±3 standard deviations from the mean there will always be a minimum of 89% of the data. For K = 3,
Minimum percent
The following table lists the minimum percent of data in any distribution and the actual percent of data in the normal distribution between ±1.1, ± 1.5, ± 2.0, and ±2.5 standard deviations from the mean. The minimum percents of data m any distribution were calculated by using Chebyshev’s theorem. The actual percents of data for the normal distribution were calculated by using the area given in the standard normal, or z, table.
| K = 1.1 | K = 1.5 | K = 2 | K = 2.5 | |
| Minimum (for any distribution) | 17.4% | 55.6% | 75% | 84% |
| Normal distribution | 72.9% | 86.6% | 95.4% | 98.8% |
| Given distribution |
The third row of the chart has been left blank for you to fill in the percents when you reach part (e).
Consider the following 30 pieces of data obtained from a quiz.
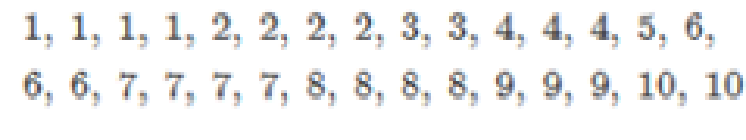
- a. Determine the mean of the set of scores.
- b. Determine the standard deviation of the set of scores.
- c. Determine the values that correspond to 1.1, 1.5, 2, and 2.5 standard deviations above the mean. Then determine the values that correspond to 1.1, 1.5, 2, and 2. 5 standard deviations below the mean.
- d. By observing the 30 pieces of data, determine the actual percent of quiz scores between
±1.1 standard deviations from the mean.
±1.5 standard deviations from the mean.
±2 tandard deviations from the mean.
±2.5 standard deviations from the mean.
- e. Place the percents found in part (d) in the third row of the chart.
- f. Compare the percents in the third row of the chart with the minimum percents in the first row and the normal percents in the second row, and then make a judgment as to whether this set of 30 scores is approximately
normally distributed .
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
A Survey of Mathematics with Applications (10th Edition) - Standalone book
- Question 4 An article in Quality Progress (May 2011, pp. 42-48) describes the use of factorial experiments to improve a silver powder production process. This product is used in conductive pastes to manufacture a wide variety of products ranging from silicon wafers to elastic membrane switches. Powder density (g/cm²) and surface area (cm/g) are the two critical characteristics of this product. The experiments involved three factors: reaction temperature, ammonium percentage, stirring rate. Each of these factors had two levels, and the design was replicated twice. The design is shown in Table 3. A222222222222233 Stir Rate (RPM) Ammonium (%) Table 3: Silver Powder Experiment from Exercise 13.23 Temperature (°C) Density Surface Area 100 8 14.68 0.40 100 8 15.18 0.43 30 100 8 15.12 0.42 30 100 17.48 0.41 150 7.54 0.69 150 8 6.66 0.67 30 150 8 12.46 0.52 30 150 8 12.62 0.36 100 40 10.95 0.58 100 40 17.68 0.43 30 100 40 12.65 0.57 30 100 40 15.96 0.54 150 40 8.03 0.68 150 40 8.84 0.75 30 150…arrow_forwardGiven sets X and Y and Z, can you prove that (X-(Y u Z)) u (Y-(X u Z)) is a subset of (X u Y) - (X intersection Y)arrow_forward4. A car travels in a straight line for one hour. Its velocity, v, in miles per hour at six minute intervals is shown in the table. For each problem, approximate the distance the car traveled (in miles) using the given method, on the provided interval, and with the given number of rectangles or trapezoids, n. Time (min) 0 6 12 18|24|30|36|42|48|54|60 Speed (mph) 0 10 20 40 60 50 40 30 40 40 65 a.) Left Rectangles, [0, 30] n=5 b.) Right Rectangles, [24, 42] n=3 c.) Midpoint Rectangles, [24, 60] n=3 d.) Trapezoids, [0, 24] n=4arrow_forward
- Given the functions A and B, can you prove that if B ◦ A is bijective, then A is injective and B is surjectivearrow_forward- + ++ Table 2: Crack Experiment for Exercise 2 A B C D Treatment Combination (1) Replicate I II 7.037 6.376 14.707 15.219 |++++ 1 བྱ॰༤༠སྦྱོ སྦྱོཋཏྟཱུ a b ab 11.635 12.089 17.273 17.815 с ас 10.403 10.151 4.368 4.098 bc abc 9.360 9.253 13.440 12.923 d 8.561 8.951 ad 16.867 17.052 bd 13.876 13.658 abd 19.824 19.639 cd 11.846 12.337 acd 6.125 5.904 bcd 11.190 10.935 abcd 15.653 15.053 Question 3 Continuation of Exercise 2. One of the variables in the experiment described in Exercise 2, heat treatment method (C), is a categorical variable. Assume that the remaining factors are continuous. (a) Write two regression models for predicting crack length, one for each level of the heat treatment method variable. What differences, if any, do you notice in these two equations? (b) Generate appropriate response surface contour plots for the two regression models in part (a). (c) What set of conditions would you recommend for the factors A, B, and D if you use heat treatment method C = +? (d) Repeat…arrow_forwardTerry has a square plot of land measuring 500 meters by 500 meters. She divided the land into 25 100-m by 100-m plots and created three raster maps showing the type of mineral, fruit tree, and energy available on each plot. Use the maps below to shade the blank maps according to each problem.arrow_forward
- The bracket BCD is hinged at C and attached to a control cable at B. Let F₁ = 275 N and F2 = 275 N. F1 B a=0.18 m C A 0.4 m -0.4 m- 0.24 m Determine the reaction at C. The reaction at C N Z F2 Darrow_forwardQuestion 2 A nickel-titanium alloy is used to make components for jet turbine aircraft engines. Cracking is a potentially serious problem in the final part because it can lead to nonrecoverable failure. A test is run at the parts producer to determine the effect of four factors on cracks. The four factors are: pouring temperature (A), titanium content (B), heat treatment method (C), amount of grain refiner used (D). Two replicates of a 24 design are run, and the length of crack (in mm x10-2) induced in a sample coupon subjected to a standard test is measured. The data are shown in Table 2. 1 (a) Estimate the factor effects. Which factor effects appear to be large? (b) Conduct an analysis of variance. Do any of the factors affect cracking? Use a = 0.05. (c) Write down a regression model that can be used to predict crack length as a function of the significant main effects and interactions you have identified in part (b). (d) Analyze the residuals from this experiment. (e) Is there an…arrow_forwardShow the stepsarrow_forward
- The correct answer is C,i know that we need to use stokes theorem and parametrize the equations then write the equation F with respect to the curve but i cant seem to find a way to do it, the integral should be from 0 to 2pi but i might be wrongcould you show me the steps to get to 18piarrow_forwardA 10-ft boom is acted upon by the 810-lb force as shown in the figure. D 6 ft 6 ft E B 7 ft C 6 ft 4 ft W Determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at the ball-and-socket joint at A. The tension in cable BD is lb. The tension in cable BE is lb. The reaction at A is ( lb) i + Ib) j. (Include a minus sign if necessary.)arrow_forwardthe correct answer is A could you show me whyarrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

