
a.
To identify: the sample and the population for each situation.
Then describe a statistic and a parameter.
a.
Answer to Problem 19PPS
The pennies chosen by Theo, Lydia and Peter each represents a sample and the total pennies in the jar, that is,
The mean year of the pennies in the sample is a statistic and the mean year of the pennies in the population is the parameter.
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
There are
The year of pennies in jar:
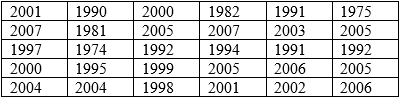
As per problem,
A sample is some portion of a larger group called population.
As per the given information, of the
The pennies chosen by Theo, Lydia and Peter each represents a sample and the total pennies in the jar, that is,
The mean year of the pennies in the sample is the statistic and the mean year of the pennies in the population is the parameter.
b.
To calculate: the mean year and mean absolute deviation of Theo’s pennies.
b.
Answer to Problem 19PPS
The mean year of Theo’s pennies is
The mean absolute deviation is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
There are
The years of Theo’s pennies are:
Formula used :
Step1: Find the mean,
Step2: Find the sum of the absolute values of the difference between each value in the set of data and the mean.
Step3: divide the sum by the number of values in the set of data.
Calculation:
As per the given problem,
The data set:
The number of values in the data set
Step1: To find the mean, add the values in the data and then divide by the number of values in the data set.
Step2: To find the sum of the absolute values, add the difference between each value and the mean.
The sum of absolute values
Step 3: Divide the sum by the number of values
c.
To calculate:the mean year and mean absolute deviation for Lydia’s pennies.
c.
Answer to Problem 19PPS
The mean year of Lydia’s pennies is
The mean absolute deviation is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
There are
The years of Lydia’s pennies are:
Calculation:
As per the given problem,
The data set:
The number of values in the data set
Step1: To find the mean, add the values in the data and then divide by the number of values in the data set.
Step2: To find the sum of the absolute values, add the difference between each value and the mean.
The sum of absolute values
Step 3: Divide the sum by the number of values
d.
To calculate: the mean year and mean absolute deviation for Peter’s pennies.
d.
Answer to Problem 19PPS
The mean year of Peter’s pennies is
The mean absolute deviation is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
There are
The years of Peter’s pennies are:
Calculation:
As per the given problem,
The data set:
The number of values in the data set
Step1: To find the mean, add the values in the data and then divide by the number of values in the data set.
Step2: To find the sum of the absolute values, add the difference between each value and the mean.
The sum of absolute values
Step 3: Divide the sum by the number of values
e.
To calculate: the mean year and mean absolute deviation for all the pennies in the jar.
To compare the samples with the full population.
e.
Answer to Problem 19PPS
The mean year of all the pennies is
The mean absolute deviation is
Peter’s sample is more similar to the full population than that of the others.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
There are
The year of pennies in jar:
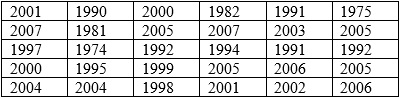
Calculation:
As per the given problem,
The data set:
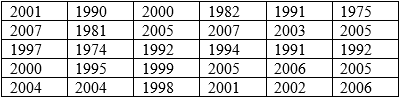
The number of values in the data set
Step1: To find the mean, add the values in the data and then divide by the number of values in the data set.
Step2: To find the sum of the absolute values, add the difference between each value and the mean.
The sum of absolute values
Step 3: Divide the sum by the number of values
As, Peter’s sample (calculate in part (d)) has the minimum difference from the population’s mean year (one year) and mean absolute deviation (
Chapter 12 Solutions
Algebra 1
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Precalculus
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- 13) Let U = {j, k, l, m, n, o, p} be the universal set. Let V = {m, o,p), W = {l,o, k}, and X = {j,k). List the elements of the following sets and the cardinal number of each set. a) W° and n(W) b) (VUW) and n((V U W)') c) VUWUX and n(V U W UX) d) vnWnX and n(V WnX)arrow_forward9) Use the Venn Diagram given below to determine the number elements in each of the following sets. a) n(A). b) n(A° UBC). U B oh a k gy ท W z r e t ་ Carrow_forward10) Find n(K) given that n(T) = 7,n(KT) = 5,n(KUT) = 13.arrow_forward
- 7) Use the Venn Diagram below to determine the sets A, B, and U. A = B = U = Blue Orange white Yellow Black Pink Purple green Grey brown Uarrow_forward8) Use the Venn diagram provided to shade An Bº. A B U Darrow_forward5) Describe the difference between disjoint sets and overlapping sets.arrow_forward
- 12) Suppose U = {a,b,c,d,e) and A = {a, b, c, e) and B = (c,d,e). Determine (An B).arrow_forward1) Use the roster method to list the elements of the set consisting of: a) All positive multiples of 3 that are less than 20. b) Nothing (An empty set).arrow_forward2) Let M = {all postive integers), N = {0,1,2,3... 100), 0= {100,200,300,400,500). Determine if the following statements are true or false and explain your reasoning. a) NCM b) 0 C M c) O and N have at least one element in common d) O≤ N e) o≤o 1arrow_forward
- 4) Which of the following universal sets has W = {12,79, 44, 18) as a subset? Choose one. a) T = {12,9,76,333, 44, 99, 1000, 2} b) V = {44,76, 12, 99, 18,900,79,2} c) Y = {76,90, 800, 44, 99, 55, 22} d) x = {79,66,71, 4, 18, 22,99,2}arrow_forward3) What is the universal set that contains all possible integers from 1 to 8 inclusive? Choose one. a) A = {1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5, 5.5, 6, 6.5, 7, 7.5, 8} b) B={-1,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8} c) C={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8} d) D = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}arrow_forward5) 8.4 6.3 ?arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





