
Concept explainers
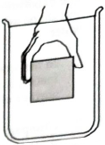
A cubical block is observed to float in a beaker of water. The block is then held near the center of the beaker as shown and released.
- Describe the motion of the block after it is released.
- In the space provided, draw, a free−body diagram for the block at the instant that it is released. Show the forces that the water exerts on each of the surfaces of the block separately.

Make sure the label for each force indicates:
- the type of force,
- the object exerting the force is exerted, and
- the object exerting the force.
Did you use the relationship between pressure and depth to compare the magnitudes ofany of the vertical forces? If so, how?
Did you use information about the motion of the block to compare the magnitudes of any of the vertical forces? If so, how?

Is this vector sum the net force on the block? (Recall that the net force is defined as the vector sum of all forces acting on an object.)
Is the magnitude of the sum of the forces exerted on the block by the water greater than, less than, or equal to the weight of the block? Explain.
(1)
To Explain: The motion of the block after it is released in the center of the block.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
According to Newton’s second law of motion, anybody under influence of a net force accelerates along the direction of the net force. For an object inside a fluid, the forces along the vertical direction are the upward buoyant force and the downward force of gravity. The object moves along the direction of the dominating force. If the two forces are equal, the object stays at rest.
It is given that the block floats in water, which means when the block is released in the center of the beaker, the upward buoyant force dominates and the block moves in the upward direction. So, after release, the block accelerates towards the surface of the water. After reaching the surface, the block comes to rest at the equilibrium position.
Conclusion:
After releasing, the block accelerates towards the surface of the water.
(2)
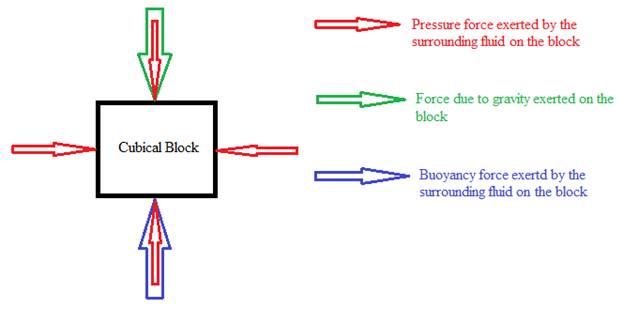
To Draw: A free body diagram of the fully submersed block.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
By Archimedes’ principle, the buoyant force (acts upwards) on an object in a fluid is equal to the weight of the water which is displaced by the object. The other forces that act on the object are the downward force due to gravity and the pressure force exerted by the surrounding fluid on the surface of the object. The pressure force exists due to the weight of the water column that lies above the object and acts equally from all directions due to the properties of an incompressible fluid.
The free-body diagram for the block at the instant it is released is given below.
(3)
To rank: The magnitudes of the vertical forces in the free body diagram.
If the relationship between pressure and depth is used to compare the magnitudes of vertical forces.
If the information about the motion of the block is used to compare the magnitudes of forces.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
If an object is in water, the water above the object exerts pressure on the surface of the object. Due to the properties of the fluid, this pressure is exerted on the object from all directions. The magnitude of this pressure is given by
According to Newton’s second law of motion, anybody under influence of a net force accelerates along the direction of the net force. For an object inside a fluid, the forces along the vertical direction are the upward buoyant force and the downward force of gravity. The object moves along the direction of the dominating force. If the two forces are equal, the object stays at rest.
The different vertical forces that act on the block in the free body diagram are the upward buoyant force (
Since the block floats on the water, following Newton’s second law, it can be said that the upward buoyant force is larger than the downward force of gravity.
So,
But since the pressure force acts equally from all the directions, it does not initiate any motion and cannot be compared with the other forces on the basis of Newton’s second law.
As the block is in a beaker, the depth of the block inside the water is quite negligible. But the atmospheric pressure term is very large as compared to any other vertical force
Conclusion:
The relationship between pressure and depth is used.
The information about the motion of the block is used.
(4)
To draw: The vector sum of all the forces on the block and explain it.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
According to Newton’s second law of motion, anybody under influence of a net force accelerates along the direction of the net force. For an object in a fluid, the forces along the vertical direction are the upward buoyant force and the downward force of gravity. The object moves along the direction of the dominating force. If the two forces are equal, the object stays at rest. One other force that acts on the object is the pressure force due to the weight of the water column above the object. But this force acts equally from all directions. So, the resultant of this force on the object is zero.
The arrow in the box below represents the vector sum of all the forces exerted by the surrounding water on the block.
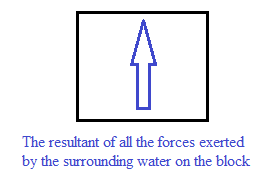
The direction of this force can be determined by the fact that the vector sum of the pressure forces exerted by the surrounding water is zero. So, the only force exerted by the surrounding water that remains is the upward buoyant force.
This force is not the vector sum of the net forces on the block. Because this force is only the vector sum of the forces exerted by the fluid on the block. The one other force that acts on the block is the force due to gravity (weight of the block). The vector sum of these two forces is the net force on the block.
As the block tends to move in the upward direction after release, the net force on the block must be in the upward direction. i.e. the magnitude of all the forces exerted on the block by the water is greater than the weight of the block.
Conclusion:
The net force exerted by the water on the block is in the upward direction.
This force is not equal to the vector sum of all the forces on the block.
The buoyant force on the block is greater than the weight of the block.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- 11. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which brings the car of mass (m) on the left to a halt? I m II III m m ע ע ע brick wall 0.5v 2m 2v 0.5m A. I B. II C. III D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them)arrow_forwardHow can you tell which vowel is being produced here ( “ee,” “ah,” or “oo”)? Also, how would you be able to tell for the other vowels?arrow_forwardYou want to fabricate a soft microfluidic chip like the one below. How would you go about fabricating this chip knowing that you are targeting a channel with a square cross-sectional profile of 200 μm by 200 μm. What materials and steps would you use and why? Disregard the process to form the inlet and outlet. Square Cross Sectionarrow_forward
- 1. What are the key steps involved in the fabrication of a semiconductor device. 2. You are hired by a chip manufacturing company, and you are asked to prepare a silicon wafer with the pattern below. Describe the process you would use. High Aspect Ratio Trenches Undoped Si Wafer P-doped Si 3. You would like to deposit material within a high aspect ratio trench. What approach would you use and why? 4. A person is setting up a small clean room space to carry out an outreach activity to educate high school students about patterning using photolithography. They obtained a positive photoresist, a used spin coater, a high energy light lamp for exposure and ordered a plastic transparency mask with a pattern on it to reduce cost. Upon trying this set up multiple times they find that the full resist gets developed, and they are unable to transfer the pattern onto the resist. Help them troubleshoot and find out why pattern of transfer has not been successful. 5. You are given a composite…arrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardAn electromagnetic wave is traveling through vacuum in the positive x direction. Its electric field vector is given by E=E0sin(kx−ωt)j^,where j^ is the unit vector in the y direction. If B0 is the amplitude of the magnetic field vector, find the complete expression for the magnetic field vector B→ of the wave. What is the Poynting vector S(x,t), that is, the power per unit area associated with the electromagnetic wave described in the problem introduction? Give your answer in terms of some or all of the variables E0, B0, k, x, ω, t, and μ0. Specify the direction of the Poynting vector using the unit vectors i^, j^, and k^ as appropriate. Please explain all stepsarrow_forward
- Another worker is performing a task with an RWL of only 9 kg and is lifting 18 kg, giving him an LI of 2.0 (high risk). Questions:What is the primary issue according to NIOSH?Name two factors of the RWL that could be improved to reduce risk.If the horizontal distance is reduced from 50 cm to 30 cm, how does the HM change and what effect would it have?arrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for z1z2∗. Find r and θ for z1/z2∗? Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1z2∗ Please explain all steps, Thank youarrow_forwardAn ac series circuit consists of a voltage source of frequency 60 Hz and voltage amplitude V, a 505-Ω resistor, and a capacitor of capacitance 7.2 μF. What must be the source voltage amplitude V for the average electrical power consumed in the resistor to be 236 W? There is no inductance in the circuit.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





