
a
Interpretation:
Total annual parts and logistics cost for each supplier.
Concept Introduction:
The lot sizing rule consists of lot-for-lot, Fixed order quantity and Fixed period quantity. Out of all lot sizing rule, lot-for-lot rule results in least inventory because the order is planned and released according to net requirement of that particular week. A fixed order quantity is an inventory system in which a firm orders a fixed lot size i.e. the order quantity remains the same when ordered every time.
a
Explanation of Solution
| Data | Supplier A | Supplier L |
| Procurement cost/ unit, P | $11.80 | $10.85 |
| Tariff cost/ unit, | $0.00 | $0.46 |
| Unit transportation cost, | $0.90 | $1.25 |
| Order cost/ order, | $155 | $195 |
| Holding cost per unit, | $1.45 | $1.10 |
| Lead time, L | 45 | 100 |
The different cost components that are involved in this case are:
Compute these costs for all the three suppliers and select based on the least total cost of the supply chain.
The following formulae will be used:
Total procurement cost = D.P
Total tariff cost =
Total transportation cost =
Annual ordering cost =
Annual carrying cost =
Annual pipeline inventory cost =
Where, D= annual demand, P= procurement cost per unit,
Note the computations done in the following Excel format.
| Total supply chain cost analysis | ||
| Data | Supplier A | Supplier L |
| Procurement cost/ unit, P | $11.80 | $10.85 |
| Tariff cost/ unit, | $0.00 | $0.46 |
| Unit transportation cost, | $0.90 | $1.25 |
| Order cost/ order, | $155 | $195 |
| Holding cost per unit, | $1.45 | $1.10 |
| Lead time, L | 45 | 100 |
| Order quantity | 50000 | 100000 |
| Average number of orders/ year (D/Q) | 20 | 10 |
| Annual demand, D | 1000000 | |
| No. of days in a year, d | 340 | |
| Average daily demand (D/d) | 2941 | |
| Cost calculations | ||
| Total procurement cost | $11,800,000.00 | $10,850,000.00 |
| Total management oversight cost | $0.00 | $460,000.00 |
| Total annual transportation cost | $900,000.00 | $1,250,000.00 |
| Annual order cost | $3,100 | $1,950 |
| Annual holding cost | $36,250.00 | $55,000.00 |
| Average annual pipeline Inventory cost | $191,911.76 | $323,529.41 |
| Total supply chain cost | $12,931,261.76 | $12,940,479.41 |
The following is the formulated excel sheet calculations as shown below:
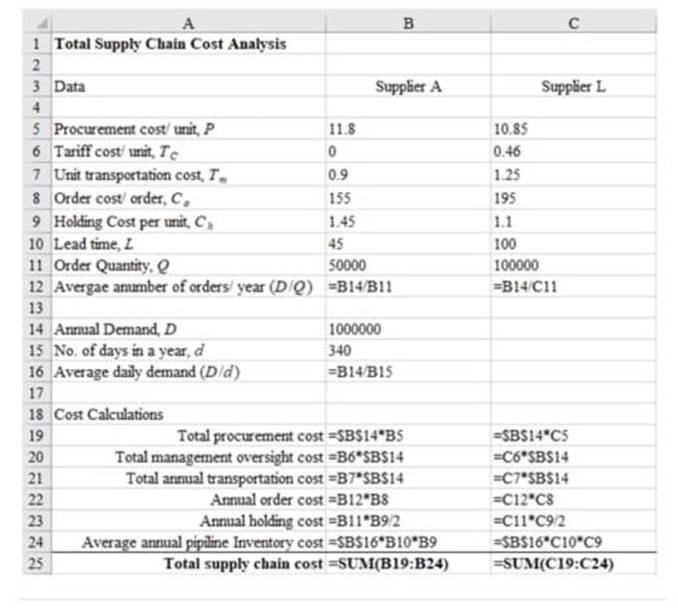
b
Interpretation:
Recommendation on order quantity
Concept Introduction:
The lot sizing rule consists of lot-for-lot, Fixed order quantity and Fixed period quantity. Out of all lot sizing rule, lot-for-lot rule results in least inventory because the order is planned and released according to net requirement of that particular week. A fixed order quantity is an inventory system in which a firm orders a fixed lot size i.e. the order quantity remains the same when ordered every time.
b
Explanation of Solution
Based on the minimum total cost, the correct choice should be the Supplier A with Q = 50,000.
c
Interpretation:
Criteria for choosing supplier and quantity
Concept Introduction:
The lot sizing rule consists of lot-for-lot, Fixed order quantity and Fixed period quantity. Out of all lot sizing rule, lot-for-lot rule results in least inventory because the order is planned and released according to net requirement of that particular week. A fixed order quantity is an inventory system in which a firm orders a fixed lot size i.e. the order quantity remains the same when ordered every time.
c
Explanation of Solution
Following are some of the criteria other than then total cost. The relevant metrics for measurement are also mentioned in the following table.
| Criteria | Metric |
| Quality | Sigma level |
| Reliability | Average service level |
| Capacity | Percentage utilization |
| Delivery adherence | Variability in lead time |
d
Interpretation:
Recommendation for supplier who is not awarded the brake pad order..
Concept Introduction:
The lot sizing rule consists of lot-for-lot, Fixed order quantity and Fixed period quantity. Out of all lot sizing rule, lot-for-lot rule results in least inventory because the order is planned and released according to net requirement of that particular week. A fixed order quantity is an inventory system in which a firm orders a fixed lot size i.e. the order quantity remains the same when ordered every time.
d
Explanation of Solution
Supplier L should be given a target of reducing the procurement cost per unit by, say, 3%. Even with a 3% reduction of procurement cost per unit, it can compete with supplier A based on the total cost. This is shown below.
| Total supply chain cost analysis | ||
| Data | Supplier A | Supplier L |
| Procurement cost/ unit, P | $11.80 | $10.85 |
| Tariff cost/ unit, | $0.00 | $0.46 |
| Unit transportation cost, | $0.90 | $1.25 |
| Order cost/ order, | $155 | $195 |
| Holding cost per unit, | $1.45 | $1.10 |
| Lead time, L | 45 | 100 |
| Order quantity | 50000 | 100000 |
| Average number of orders/ year (D/Q) | 20 | 10 |
| Annual demand, D | 1000000 | |
| No. of days in a year, d | 340 | |
| Average daily demand (D/d) | 2941 | |
| Cost calculations | ||
| Total procurement cost | $11,800,000.00 | $10,524,500.00 |
| Total management oversight cost | $0.00 | $460,000.00 |
| Total annual transportation cost | $900,000.00 | $1,250,000.00 |
| Annual order cost | $3,100 | $1,950 |
| Annual holding cost | $36,250.00 | $55,000.00 |
| Average annual pipeline Inventory cost | $191,911.76 | $323,529.41 |
| Total supply chain cost | $12,931,261.76 | $12,614,979.41 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
OM (with OM Online, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card)
- Do you think there are other methods to achieve efficiency, such as specialization or using technology to alleviate the bottleneck, like patient wait time?arrow_forwardIs it hard to improve efficiency in a process? Why or why not? Give an example of how to improve the efficiency of a process. Please provide a reference in APA formarrow_forwardSimplex Method Three types of paints are manufactured in one machine; Interior paint, Exterior paint and Paint for metal structures. The preparation time for each type of paint is 2, 3 and 4 minutes respectively and the processing time is 3, 2 and 1 minute. The profit contributed by each product is 12, 10 and 15 dollars respectively. The machine availability is 100 minutes and 200 minutes for machine setup. 1. Determine the optimum number of types of paints to be manufactured. 2. Determine the optimal utility value.arrow_forward
- The company LED S.A DE C.V. produces 2 devices for lamps, devices 1 and 2 that require metal parts and electrical parts. The manager wants to determine how many units of each product should be manufactured to maximize the profit for each unit, device 1 requires 2 metal parts and 4 electrical parts, device 2 requires 4 metal parts and 2 electrical parts, the company has 24 units of each material available for batch production, device 1 generates $4 profit and device 2 generates $6 profit. a) Formulate PL model. b) Solve by the graphical method and determine what is the resulting maximum profit. Translated with DeepL.com (free version)arrow_forwardQuestion 3 i. Using the Center of Gravity method, determine the optimal location (X, Y) for the new distribution center. [7 marks] [TOTAL 25 MARKS] Time (sec.) Power steering assembly firm wants to set up an assembly line which must have an output of 60 units per hour. The work elements, task times and their precedence relationships are shown in Table 2: Table 1 Work Element Immediate Predecessor(s) A 30 NONE B 26 A C 50 A D 44 B E 10 с F 20 с G 15 D.E H 30 E,G,F Required: a. Draw the precedence diagram showing the task precedence and their times b. Determine the cycle time associated with the rate of output required. [3 marks] c. What is the theoretical number of work stations required to satisfy this output rate? [3 marks] [4 marks] d. Allocate the tasks to work stations taking into consideration the precedence requirements and using the LOT rule to break ties between feasible tasks. e. Calculate the total idle time [8 marks] [3 marks] f. What is the efficiency of the line and the…arrow_forwardHyundai Motors is considering three sites-A, B, and C-at which to locate a factory to build its new electric car batteries. The goal is to locate at a minimum-cost site, where cost is measured by the annual fixed plus variable costs of production. Hyundai Motors has gathered the following data: Site Annualized Fixed Cost Variable Cost per Battery Produced A $11,000,000 $2,600 B C $2,000 $1,100 $20,000,000 $25,000,000 The firm knows it will produce between 0 and 60,000 batteries at the new plant each year, but, thus far, that is the extent of its knowledge about production plans. a) The value of volume, V, of production above which site C is recommended = batteries (round your response up to the next whole number).arrow_forward
- Hyundai Motors is considering three sites-A, B, and C-at which to locate a factory to build its new electric car batteries. The goal is to locate at a minimum-cost site, where cost is measured by the annual fixed plus variable costs of production. Hyundai Motors has gathered the following data: Site Annualized Fixed Cost Variable Cost per Battery Produced A $11,000,000 $2,500 B C $2,100 $1,050 $20,000,000 $25,000,000 The firm knows it will produce between 0 and 60,000 batteries at the new plant each year, but, thus far, that is the extent of its knowledge about production plans. a) The value of volume, V, of production above which site C is recommended = batteries (round your response up to the next whole number).arrow_forwardThe importance of keeping track of invoices and budgeting in a nursing home kitchen and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of interviewing potential food service aides and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- What role does job analysis and job evaluation play in the compensation decision? Give an example of an organization NO AIarrow_forwardI did the first half correct! Please help me with the second half, not quite sure of the naive approach. Thanks in advance!arrow_forwardBecause my tutor and I didnt get it rightarrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning



