
a.
Journalize the
a.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Journalize the stockholders’ equity transactions in the books of Incorporation TS.
Transaction on January 3:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| January | 3 | Dividends | 362,000 | |||
| Dividends Payable | 362,000 | |||||
| (Record declaration of dividends) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Dividends is a stockholders’ equity account. Since the dividends are declared, stockholders’ equity is decreased, and a decrease in equity account is debited.
- Dividends Payable is a liability account. Since the liability to pay dividends increased, liability increased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute the amount of cash dividends on common stock.
Transaction on February 15:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| February | 15 | Dividends Payable | 382,000 | |||
| Cash | 382,000 | |||||
| (Record payment of cash dividends) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Dividends Payable is a liability account. Since the liability to pay dividends has been paid off, liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because cash is paid as dividends, and a decrease in assets should be credited.
Transaction on April 12:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| April | 12 | 240,000 | ||||
| Cash | 240,000 | |||||
| (Record reacquisition of common stock as treasury stock) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since the issued shares are bought back, the stockholders’ equity decreases, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because cash is paid as dividends, and a decrease in assets should be credited.
Working Notes:
Compute cash paid.
Transaction on May 9:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| May | 9 | Cash | 176,000 | |||
| Treasury Stock | 160,000 | |||||
| Additional Paid-in Capital–Treasury Stock | 16,000 | |||||
| (Record sale of treasury stock) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased because cash is received on sale of reacquired shares, and an increase in assets should be debited.
- Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since reacquired shares of treasury stock are sold, the value of treasury stock is reduced. The treasury stock which was debited previously, is now credited to reduce its balance.
- Additional Paid-In Capital–Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since treasury stock is sold for a price more than its purchase price, equity value is increased. An increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute cash received.
Compute treasury stock value.
Compute additional paid-in capital value.
Transaction on June 1:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| June | 1 | 798,000 | ||||
| Stock Dividends to Be Distributed | 19,000 | |||||
| Additional Paid-in Capital: Stock Dividends | 779,000 | |||||
| (Record declaration of stock dividends) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Retained Earnings is a stockholders’ equity account. Since the dividends are declared, stockholders’ equity is decreased, and a decrease in equity account is debited.
- Stock Dividends to Be Distributed is a stockholders’ equity account. Since common stock is declared to be distributed as stock dividends at par value, equity value is increased. An increase in equity is credited.
- Additional Paid-in Capital: Stock Dividends is a stockholders’ equity account. Since the stock is issued in excess of par value, equity value is increased. An increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute the number of shares to be distributed as stock dividends.
Compute amount of retained earnings distributable for stock dividends (Refer to Equation (1) for stock dividend shares value).
Compute the amount of stock dividends to be distributed (Refer to Equation (1) for stock dividend shares value).
Compute additional paid-in capital (Refer to Equations (2) and (3) for retained earnings and stock dividends to be distributed value).
Transaction on June 30:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| June | 30 | Stock Dividends to Be Distributed | 19,000 | |||
| Common Stock | 19,000 | |||||
| (Record distribution of stock dividends) | ||||||
Table (6)
Description:
- Stock Dividends to Be Distributed is a stockholders’ equity account. Since common stock is issued due to declaration of stock dividends, the value is transferred to common stock, the equity value is decreased. A decrease in equity is debited.
- Common Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since common stock is issued, equity value is increased. An increase in equity is credited.
Note: Refer to Equation (3) for value and computation of stock dividends distributable value.
Transaction on August 4:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| August | 4 | Cash | 22,200 | |||
| Additional Paid-in Capital–Treasury Stock | 1,800 | |||||
| Treasury Stock | 24,000 | |||||
| (Record sale of treasury stock) | ||||||
Table (7)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased because cash is received on sale of reacquired shares, and an increase in assets should be debited.
- Additional Paid-In Capital–Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since treasury stock is sold for a price less than its purchase price, equity value is decreased. A decrease in equity is debited.
- Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since reacquired shares of treasury stock are sold, the value of treasury stock is reduced. The treasury stock which was debited previously, is now credited to reduce its balance.
Working Notes:
Compute cash received.
Compute treasury stock value.
Compute additional paid-in capital value.
Transaction on December 31 (closing net income):
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Income Summary | 1,928,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings | 1,928,000 | |||||
| (Record net income being closed to Retained Earnings account) | ||||||
Table (8)
Description:
- Income Summary is a temporary account used to close the net balance of revenue and expense accounts. Since the net income is closed to Retained Earnings account, the Retained Earnings is credited and Income Summary account is debited.
- Retained Earnings is a stockholders’ equity account. Since revenues are transferred to the account, the value increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Transaction on December 31 (closing dividends):
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Income Summary | 381,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings | 381,000 | |||||
| (Record dividends being closed to Retained Earnings account) | ||||||
Table (9)
Description:
- Retained Earnings is a stockholders’ equity account. Since dividends are transferred to the account, the value decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Income Summary is a temporary account used to close the net balance of revenue and expense accounts. Since the dividends (expense) are closed to Retained Earnings account, the Retained Earnings is debited and Income Summary account is credited.
b.
Prepare the stockholders’ equity section of the
b.
Explanation of Solution
Stockholders’ equity section: The section of balance sheet which reports the changes in stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock, during the year is referred to as stockholders’ equity section.
Prepare the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet for Incorporation TS at December 31, 2018.
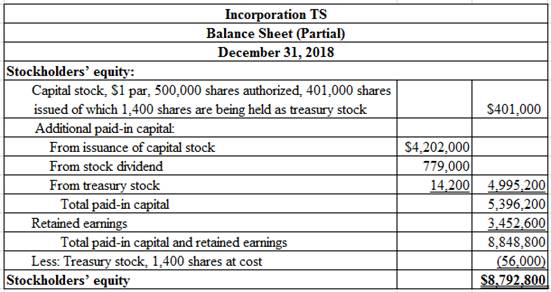
Table (10)
Working Notes:
Compute the number of shares issued as at December 31, 2018.
Compute number of shares in treasury stock.
Refer to transaction on June 1 for value of additional paid-in capital from stock dividend.
Compute additional paid-in capital from treasury stock.
Compute amount of retained earnings (Refer to the working notes of transactions on February 15 and June 1 for value of cash and stock dividends).
| Incorporation TS | ||
| Statement of Retained Earnings | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Retained earnings, January 1, 2018 | $2,704,600 | |
| Add: Net income | 1,928,000 | |
| 4,632,600 | ||
| Less: | ||
| Cash dividends | $382,000 | |
| Stock dividends | 798,000 | (1,180,000) |
| Retained earnings, December 31, 2018 | $3,452,600 | |
Table (11)
Thus, the total stockholders’ equity of Incorporation TS is $8,792,800.
c.
Compute the amount of legal cash dividend per share according to the given condition.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Cash dividends: This is the amount of cash distributed to stockholders by a company out of its earnings, according to their proportion of shares held in the company stock.
Compute the amount of legal cash dividend per share of Incorporation TS in 2018.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Retained earnings, December 31, 2018 | $3,452,600 |
| Less: Restriction of retained earnings for treasury stock | 56,000 |
| Unrestricted retained earnings | 3,396,600 |
| Number of outstanding common shares | ÷ 401,000 shares |
| Maximum legal cash dividend per common share | $8.50 |
Table (12)
Note: Refer to working notes of Part (b) for the value of retained earnings ending balance, and number of outstanding shares at the end of 2018.
Thus, the legal cash dividend per common share of Incorporation TS for the year ended December 31, 2018 is $8.50.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Please give me true answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardRaptors Inc. creates aluminum alloy parts for commercial aircraft. In a recent transaction Raptors leased a high precision lathe machine from Grizzlies Corp. on January 1, 2024. The following information pertains to the leased asset and the lease agreement: Cost of lathe to lessor $140,000 Grizzlies normal selling price for lathe 178,268 Useful life 7 years Estimated value at end of useful life 8,000 Lease provisions Lease term 5 years Payment frequency Annual Start date of lease January 1 Payment timing December 31 Estimated residual value at end of lease (unguaranteed) 20,000 Interest rate implicit in the lease (readily determinable by lessee) 7% Lessee's incremental borrowing rate 8% The lathe machine will revert back to the lessor at end of lease term, title does not transfer to lessee at any time, and there is not a bargain purchase option. Required…arrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forward
- Can you please solve this financial accounting problem without use Ai?arrow_forwardHobbiton Tours Ltd. has the following details related to its defined benefit pension plan as at December 31, 2024: Pension fund assets of $1,900,000 and actuarial obligation of $1,806,317. The actuarial obligation represents the present value of a single benefit payment of $3,200,000 that is due on December 31, 2030, discounted at an interest rate of 10%; i.e. $3,200,000 / 1.106 = $1,806,317. Funding during 2025 was $55,000. The actual value of pension fund assets at the end of 2025 was $2,171,000. As a result of the current services received from employees, the single payment due on December 31, 2030, had increased from $3,200,000 to $3,380,000. Required Compute the current service cost for 2025 and the amount of the accrued benefit obligation at December 31, 2025. Perform this computation for an interest rate of 8%. Derive the pension expense for 2025 under various assumptions about the expected return and discount rate. Complete the following table: Case…arrow_forwardCalculate Debt Ratios and Debt to Equity Ratio for 2016arrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forwardIn 2026, Maple Leafs Co. sells its single machine, which cost $100,000 and has an undepreciated capital cost (UCC) of $25,000 for tax purposes. For financial reporting, the machine has carrying amount of $40,000. The sale price of the machine is $30,000. Aside from the sale of the machine, the company has other income (before taxes) of $600,000, which includes non-taxable dividends of $120,000 dollars received during the year. There are no other permanent or temporary differences. The company faces an income tax rate of 35%. Required Provide the journal entries for the company for 2026.arrow_forwardBlue Jays Corporation started operations on March 1, 2025. It needs to acquire a special piece of equipment for its manufacturing operations. It is evaluating two options as follows. Option 1: Lease the equipment for 5 years. Lease payments would be $11,000 per year, due at the beginning of each fiscal year (March 1). Blue Jays incremental borrowing rate is 5%. There is not a bargain purchase or renewal option. Blue Jays is responsible for all non-lease costs of operating the equipment. Option 2: Purchase the equipment for $50,000 by borrowing the full purchase amount at 5% over 5 years. This price is considered the fair value of the equipment. Payments are due at the end of each fiscal year (February 28). The equipment has a useful life of 5 years and would be depreciated on a straight-line basis. No residual value is expected to exist at the end of 5 years. Required Calculate the present value of the lease payments (Option 1). Calculate the payment that would be…arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





