
Concept explainers
Instructions: Choose one or more of the data sets A-J below, or as assigned by your instructor. The first column is X, or independent, variable and the second column is the Y, or dependent, variable. Use Excel or a statistical package (e.g., MegaStat or Minitab) to obtain the simple regression and required graphs. Write your answers to exercises 12.46 through 12.61 (or those assigned by your instructor) in a concise report, labeling your answers to each question. Insert tables and graphs in your report as appropriate. You may work with a partner if your instructor allows it.
(a) Based on the R2 and ANOVA table for your model, how would you assess the fit? (b) Interpret the p-value for the F statistic. (c) Would you say that your model’s fit is good enough to be of practical value?
DATA SET B Midterm and Final Exam Scores for Business Statistics Students, Fall Semester 2011 (n = 58 students)
a.
Explain how one would assess the fit based on the
Explanation of Solution
Answer will vary.
Here the data set B is taken, in which the midterm exam (X) and final exam score (Y) is given.
Hypotheses:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the slope is zero.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the slope not equal to zero.
Regression:
Suppose
Where,
The total sum of squares is denoted as,
The regression sum of squares is denoted as,
The error sum of squares is denoted as,
From the regression the fitted line is denoted as,
The 95% confidence interval for the slope,
Where,
Software Procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to find R-squared using EXCEL is as follows:
- • Open an EXCEL file.
- • In column A and B, the Midterm Exam Score and Final Exam Score data were entered.
- • Click on data > click on Data analysis.
- • Choose Regression > click OK.
- • Select Input Y range asthe column of Final Exam Score.
- • Select Input X range asthe column of Midterm Exam Score.
- • Select the output range.
- • Click OK.
- Output using EXCEL is given below:
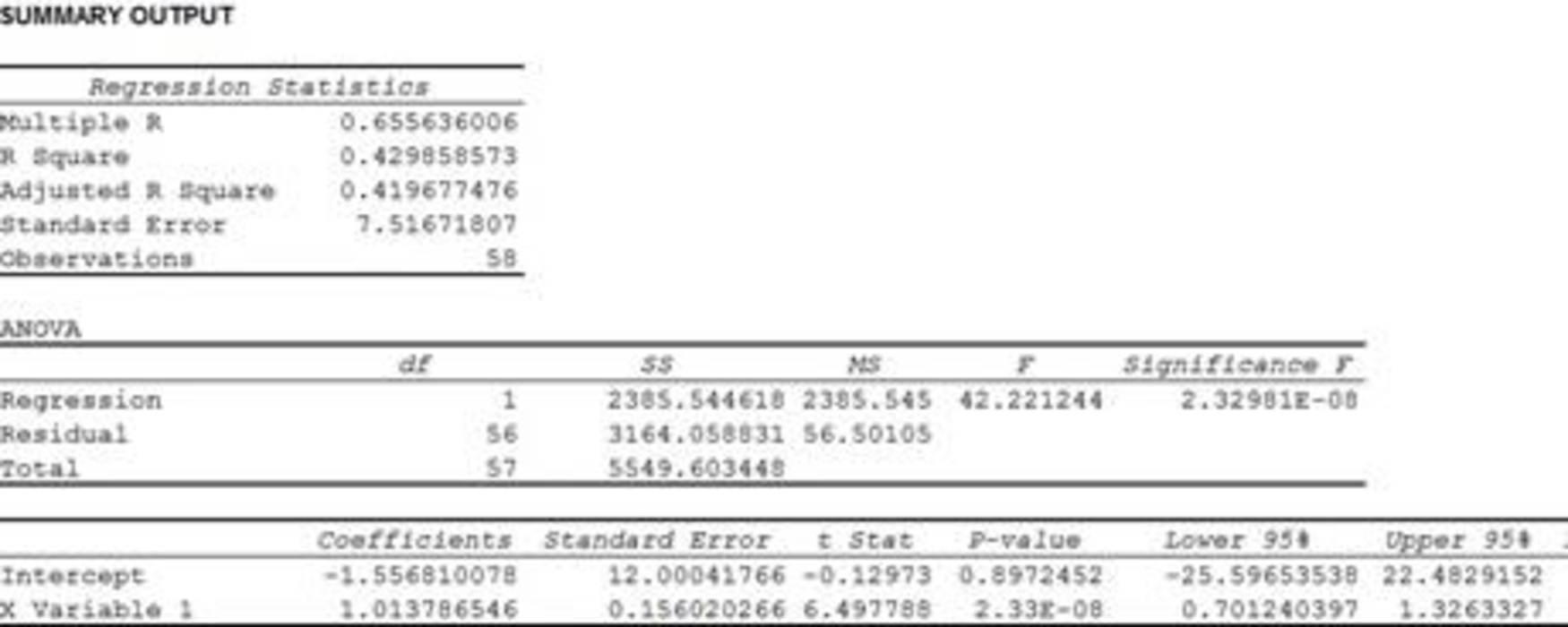
From the output, the R-squared value is 0.429.
The coefficient of determination (
The
b.
Interpret the p-value for the F statistic.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For the F-test of the slope the p-value is 0.000.
Decision rule:
If
If
It is assumed that the level of significance is 0.05.
Conclusion:
Here the p-value is less than the level of significance.
That is,
Hence, by the decision rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, it can be concluded that there is not sufficient evidence to support that the slope is zero.
Hence, the linear model provides significant fit.
c.
Check whether the model’s fit is good enough to be of practical value.
Explanation of Solution
Now, a hypothesis test is needed to check the whether the model provides good fit or not.
Decision rule:
If
If
Critical value:
Here from the output, the sample size,
The degrees of freedom is,
Thus, the degrees of freedom is56.
For two tailed test, the critical value for t-test will be,
It is assumed that the level of significance,
Procedure for critical-value using EXCEL:
Software Procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain critical-value using EXCEL software is as follows:
- • Open an EXCEL file.
- • In cell A1, enter the formula “=F.INV.RT(0.05,1,56)”
- Output using EXCEL software is given below:
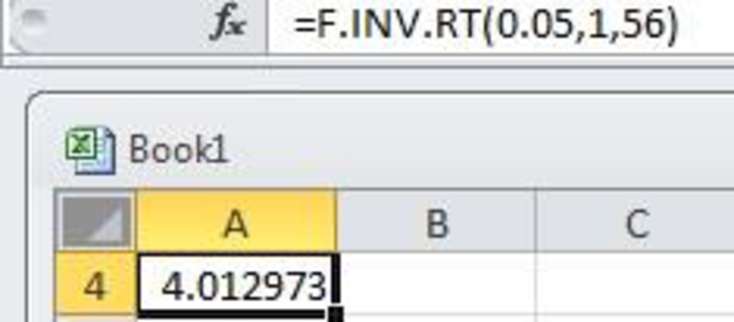
Hence, the critical value will be 4.013.
From the output of part (a), the F-statistic value is 42.22.
The level of significance is 0.05.
Conclusion:
Here the F-statistics is greater than the critical value.
That is,
Hence, by the decision rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, it can be concluded that there is not sufficient evidence to support that the slope is zero.
Hence, linear model provides significant fit.
The coefficient of determination (
Thus, using
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
- Problem 3 In their lab, engineer Daniel and Paulina are desperately trying to perfect time travel. But the problem is that their machine still struggles with power inconsistencies-sometimes generating too little energy, other times too much, causing unstable time jumps. To prevent catastrophic misjumps into the Jurassic era or the far future, they must calibrate the machine's power output. After extensive testing, they found that the time machine's power output follows a normal distribution, with an average energy level of 8.7 gigawatts and a standard deviation of 1.2 gigawatts. The Time Travel Safety Board has set strict guidelines: For a successful time jump, the machine's power must be between 8.5 and 9.5 gigawatts. What is the probability that a randomly selected time jump meets this precision requirement? Daniel suggests that adjusting the mean power output could improve time-travel accuracy. Can adjusting the mean reduce the number of dangerous misjumps? If yes, what should the…arrow_forwardProblem 5 ( Marybeth is also interested in the experiment from Problem 2 (associated with the enhancements for Captain America's shield), so she decides to start a detailed literature review on the subject. Among others, she found a paper where they used a 2"(4-1) fractional factorial design in the factors: (A) shield material, (B) throwing mechanism, (C) edge modification, and (D) handle adjustment. The experimental design used in the paper is shown in the table below. a. Run A B с D 1 (1) -1 -1 -1 1 2 a 1 -1 -1 1 3 bd -1 1 -1 1 4 abd 1 1 -1 1 5 cd -1 -1 1 -1 6 acd 1 -1 1 -1 7 bc -1 1 1 -1 abc 1 1 1 -1 paper? s) What was the generator used in the 2"(4-1) fractional factorial design described in the b. Based on the resolution of this design, what do you think about the generator used in the paper? Do you think it was a good choice, or would you have selected a different one? Explain your answer in detail.arrow_forwardSuppose we wish to test the hypothesis that women with a sister’s history of breast cancer are at higher risk of developing breast cancer themselves. Suppose we assume that the prevalence rate of breast cancer is 3% among 60- to 64-year-old U.S. women, whereas it is 5% among women with a sister history. We propose to interview 400 women 40 to 64 years of age with a sister history of the disease. What is the power of such a study assuming that the level of significance is 10%? I only need help writing the null and alternative hypotheses.arrow_forward
- 4.96 The breaking strengths for 1-foot-square samples of a particular synthetic fabric are approximately normally distributed with a mean of 2,250 pounds per square inch (psi) and a standard deviation of 10.2 psi. Find the probability of selecting a 1-foot-square sample of material at random that on testing would have a breaking strength in excess of 2,265 psi.4.97 Refer to Exercise 4.96. Suppose that a new synthetic fabric has been developed that may have a different mean breaking strength. A random sample of 15 1-foot sections is obtained, and each section is tested for breaking strength. If we assume that the population standard deviation for the new fabric is identical to that for the old fabric, describe the sampling distribution forybased on random samples of 15 1-foot sections of new fabricarrow_forwardUne Entreprise œuvrant dans le domaine du multividéo donne l'opportunité à ses programmeurs-analystes d'évaluer la performance des cadres supérieurs. Voici les résultats obtenues (sur une échelle de 10 à 50) où 50 représentent une excellente performance. 10 programmeurs furent sélectionnés au hazard pour évaluer deux cadres. Un rapport Excel est également fourni. Programmeurs Cadre A Cadre B 1 34 36 2 32 34 3 18 19 33 38 19 21 21 23 7 35 34 8 20 20 9 34 34 10 36 34 Test d'égalité des espérances: observations pairéesarrow_forwardA television news channel samples 25 gas stations from its local area and uses the results to estimate the average gas price for the state. What’s wrong with its margin of error?arrow_forward
- You’re fed up with keeping Fido locked inside, so you conduct a mail survey to find out people’s opinions on the new dog barking ordinance in a certain city. Of the 10,000 people who receive surveys, 1,000 respond, and only 80 are in favor of it. You calculate the margin of error to be 1.2 percent. Explain why this reported margin of error is misleading.arrow_forwardYou find out that the dietary scale you use each day is off by a factor of 2 ounces (over — at least that’s what you say!). The margin of error for your scale was plus or minus 0.5 ounces before you found this out. What’s the margin of error now?arrow_forwardSuppose that Sue and Bill each make a confidence interval out of the same data set, but Sue wants a confidence level of 80 percent compared to Bill’s 90 percent. How do their margins of error compare?arrow_forward
- Suppose that you conduct a study twice, and the second time you use four times as many people as you did the first time. How does the change affect your margin of error? (Assume the other components remain constant.)arrow_forwardOut of a sample of 200 babysitters, 70 percent are girls, and 30 percent are guys. What’s the margin of error for the percentage of female babysitters? Assume 95 percent confidence.What’s the margin of error for the percentage of male babysitters? Assume 95 percent confidence.arrow_forwardYou sample 100 fish in Pond A at the fish hatchery and find that they average 5.5 inches with a standard deviation of 1 inch. Your sample of 100 fish from Pond B has the same mean, but the standard deviation is 2 inches. How do the margins of error compare? (Assume the confidence levels are the same.)arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL





