
1.
Calculate the maximum machine annual operating cost of the overhauled AccDril for replacing decision.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the maximum machine annual operating cost of the overhauled AccDril for replacing decision as follows:
Working note (1):
Calculate the difference in the present value of
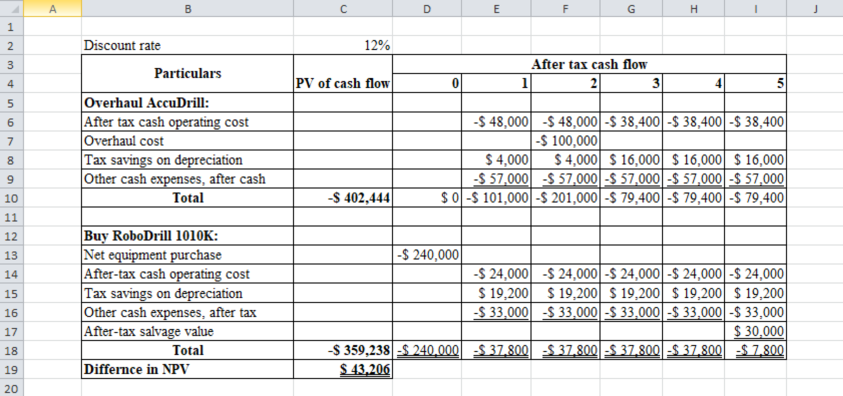
Table (1)
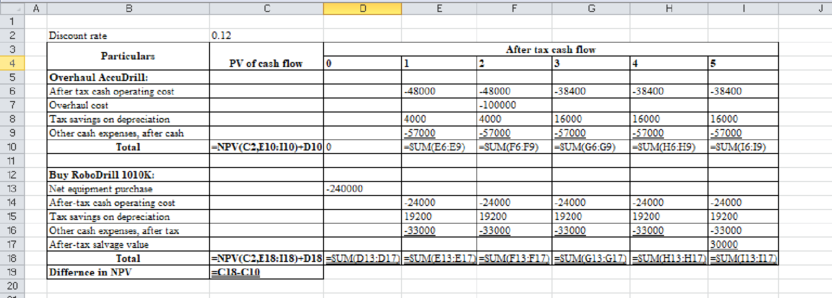
Table (2)
Note: Sum the PV factors from years 3, 4, and 5:
2.
Calculate the maximum amount of annual after-tax operating cost for the new machine in order to change the decision using the Goal seek function in Excel.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the maximum amount of annual after-tax operating cost for the new machine in order to change the decision using the Goal seek function in Excel as follows:
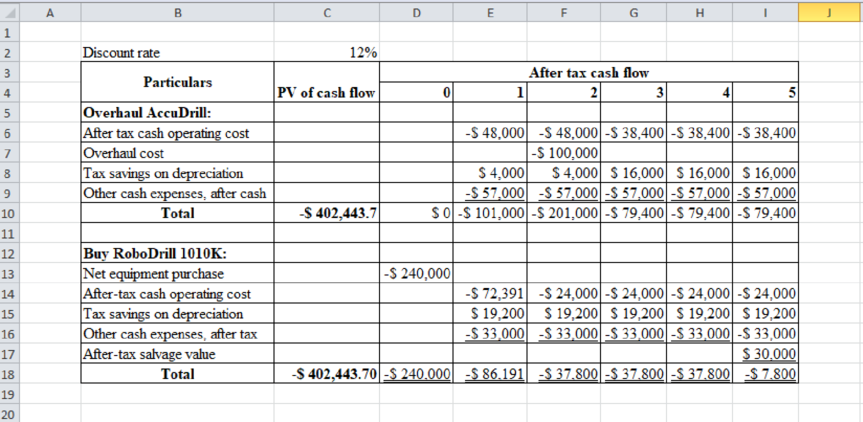
Table (3)
Excel workings:
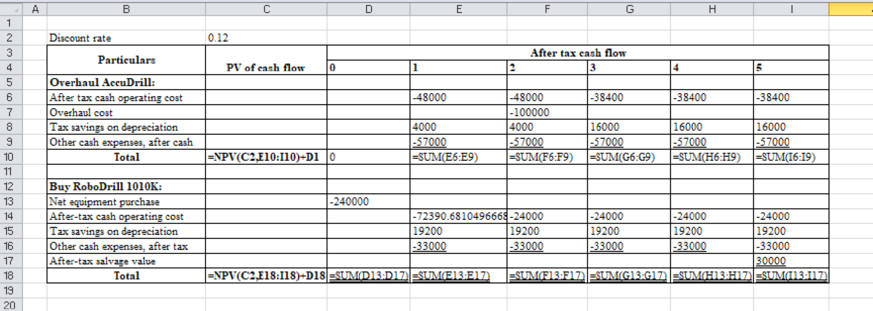
Table (4)
3.
State whether company should invest overhaul now and after 2 years or overhaul Accdrill for 2 years.
3.
Explanation of Solution
State whether company should invest overhaul now and after 2 years or overhaul Accdrill for 2 years as follows:
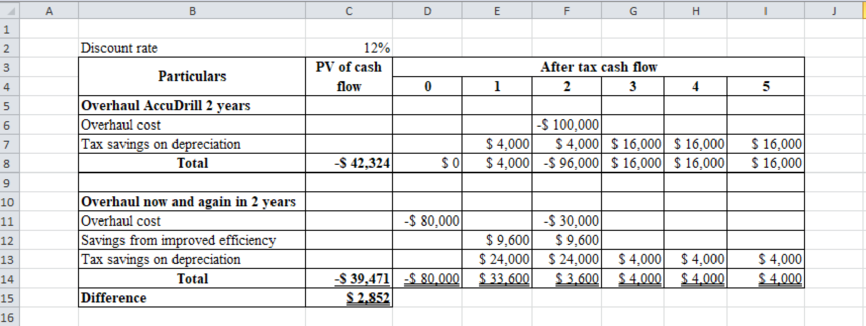
Table (5)
In this case, company can overhaul the machine now, because overhaul now and again in 2 years has favor difference and it has less negative
Excel workings:
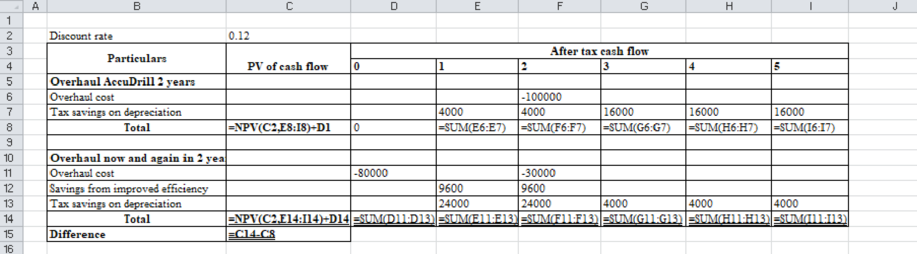
Table (6)
Working note (2):
| Calculate the tax savings on | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Depreciation expense per year (a) | $ 10,000 |
| Income tax rate (b) | 40% |
| Tax savings on depreciation, year 1 and 2 | $ 4,000 |
Table (7)
Working note (3):
| Calculate the tax savings on depreciation, year 3, 4 and 5 | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Book value before overhaul | $ 20,000 |
| Add: Overhaul cost, year3 | $ 100,000 |
| Total amount to be depreciated (c ) | $ 120,000 |
| Number of years (d) | 3 |
| Depreciation expense per year (e ) | $ 40,000 |
| Income tax rate (f) | 40% |
| Tax saving on depreciation, year 3, 4 and 5 | $ 16,000 |
Table (8)
Working note (4):
| Overhaul now and again in two years | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Savings from the improved productivity | $ 16,000 |
| Less: Income taxes on savings @40% | $ 6,400 |
| After tax savings | $ 9,600 |
Table (9)
Working note (5):
| Depreciation tax savings: year 1 and 2 | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Book value at the time of overhaul | $ 40,000 |
| Add: Overhaul cost | $ 80,000 |
| Total amount to be depreciated (h) | $ 120,000 |
| Number of years (i) | 2 |
| Depreciation expense per year (j) | $ 60,000 |
| Tax rate (k) | 40% |
| Tax savings on depreciation | $ 24,000 |
Table (10)
Working note (6):
| Depreciation tax savings: year 3, 4 and 5 | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Overhaul cost (l) | $ 30,000 |
| Number of years (m) | 3 |
| Depreciation expense per year (n) | $ 10,000 |
| Income tax rate (o) | 40% |
| Tax savings on depreciation | $ 4,000 |
Table (11)
4.
State whether company should overhaul now.
4.
Explanation of Solution
State whether company should overhaul now as follows:
The cost difference between the two alternatives is $2,852 that is less that 0.3%
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Cost Management: A Strategic Emphasis
- Lawrence Industries plans to produce 30,000 units next period at a denominator activity of 45,000 direct labor hours. The direct labor wage rate is $16.00 per hour. The company's standards allow 2.2 yards of direct materials for each unit of product; the material costs $8.50 per yard. The company's budget includes a variable manufacturing overhead cost of $3.25 per direct labor hour and fixed manufacturing overhead of $270,000 per period. Using 45,000 direct labor hours as the denominator activity, compute the predetermined overhead rate and break it down into variable and fixed elements.arrow_forwardCan you show me the correct approach to solve this financial accounting problem using suitable standards?arrow_forwardCould you explain the steps for solving this general accounting question accurately?arrow_forward
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardWhat is the company's CM ratio?arrow_forwardJohnson Jewelry uses the perpetual inventory system. On May 12, Johnson sold merchandise for $95,000 to a customer on account with terms 2/10, n/30. The cost of goods sold (COGS) was $37,000. On May 20, Johnson received payment from the customer. Calculate the amount of gross profit.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting question using valid accounting techniques?arrow_forwardLauren's Hardware common stock is currently selling at $48.75 per share. The company follows a 55% dividend payout ratio and has a P/E ratio of 18. There are 75,000 shares of stock outstanding. What is the amount of the annual net income for the firm? solve this Accounting problemarrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





