
Concept explainers
Entries for selected corporate transactions
Morrow Enterprises Inc. manufactures bathroom fixtures. Morrow Enterprises’ stockholders’ equity accounts, with balances on January 1, 20Y6, are as follows:

The following selected transactions occurred during the year:


Instructions
- 1. Enter the January 1 balances in T accounts for the stockholders’ equity accounts listed. Also prepare T accounts for the following: Paid-In Capital from Sale of
Treasury Stock ; Stock Dividends Distributable; Stock Dividends; Cash Dividends. - 2. Journalize the entries to record the transactions, and post to the eight selected accounts. Assume that the closing entry for revenues and expenses has been made and post net income of $1,125,000 to the
retained earnings account. - 3. Prepare a statement of stockholders’ equity for the year ended December 31, 20Y6. Assume that net income was $1,125,000 for the year ended December 31, 20Y6.
- 4. Prepare the “Stockholders’ Equity” section of the December 31, 20Y6,
balance sheet .
(1) and (2)
Journalize the transactions and post to the eight selected accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Common stock: These are the ordinary shares that a corporation issues to the investors in order to raise funds. In return, the investors receive a share of profit from the profits earned by the corporation in the form of dividend.
Treasury Stock: It refers to the shares that are reacquired by the corporation that are already issued to the stockholders, but reacquisition does not signify retirement.
Par value: It refers to the value of a stock that is stated by the corporation’s charter. It is also known as face value of a stock.
Stated value: It refers to an amount per share, which is assigned by the board of directors to no par value stock.
Issue of common stock for non-cash assets or services: Corporations often issue common stock for the services received from attorneys or consultants as compensation, or for the purchase of non-cash assets such as land, buildings, or equipment.
Record the transactions for Incorporation ME.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 20Y6 | ||||||
| January | 22 | Cash Dividends Payable | 28,000 | |||
| Cash | 28,000 | |||||
| (To record the payment of cash dividends) | ||||||
| April | 10 | Cash | 1,800,000 | |||
| Common Stock | 1,500,000 | |||||
|
Paid-in Capital in Excess of stated value Common Stock | 300,000 | |||||
| (To record issuance of 75,000 shares in excess of stated value) | ||||||
| June | 6 | Cash | 650,000 | |||
|
Treasury stock | 450,000 | |||||
|
Paid-in capital from treasury stock | 200,000 | |||||
| (To record sale of treasury stock for above the cost price of $18 per share) | ||||||
| July | 5 | Stock Dividends (4) | 450,000 | |||
|
Common Stock Dividends Distributable (5) | 360,000 | |||||
|
Paid-in Capital in excess of Stated Value-Common stock (6) | 90,000 | |||||
| (To record the declaration of stock dividends) | ||||||
| August | 15 | Common Stock Dividends Distributable (5) | 360,000 | |||
| Common Stock | 360,000 | |||||
| (To record the distribution of stock dividends) | ||||||
| November | 23 | Treasury stock | 570,000 | |||
| Cash | 570,000 | |||||
| (To record the purchase of 30,000 shares of treasury stock) | ||||||
| December | 28 | Cash Dividends (8) | 43,800 | |||
| Cash Dividends Payable | 43,800 | |||||
| (To record the declaration of cash dividends) | ||||||
| December | 31 | Retained Earnings | 493,800 | |||
| Stock dividends (4) | 450,000 | |||||
| Cash Dividends (8) | 43,800 | |||||
| (To record the closing of stock dividends and cash dividends to retained earnings account) | ||||||
Table (1)
Working note (1)
Calculate treasury stock cost per share.
Working note (2)
Compute number of shares outstanding after the sale of treasury stock on June 6.
Working note (3)
Compute the stock dividends shares.
Working note (4)
Compute the stock dividends amount payable to common stockholders.
Working note (5)
Compute common stock dividends distributable value.
Working note (6)
Compute paid-in capital in excess of par value-common stock.
Working note (7)
Compute number of shares outstanding as on December 28.
Working note (8)
Calculate the amount of cash dividend declared on December 28.
Enter the beginning balance and post the transactions into the stockholders’ equity accounts for Incorporation ME.
Common stock account is a component of stockholder’s equity with a normal credit balance.
| Common stock | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Date | Particulars | Credit |
| January 1 | Balance | $7,500,000 | |||
| April 10 | Cash | $1,500,000 | |||
| August 15 | Stock dividends distributable | $360,000 | |||
| Total | $ 0 | Total | $ 9,360,000 | ||
| December 31 | Balance | $9,360, 000 | |||
Table (2)
Paid-in capital in excess of stated value - Common stock account is a component of stockholder’s equity with a normal credit balance.
| Paid-in capital in excess of stated value - Common stock | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Date | Particulars | Credit |
| January 1 | Balance | $825,000 | |||
| April 10 | Cash | $300,000 | |||
| July 5 | Stock dividends | $90,000 | |||
| Total | $ 0 | Total | $ 1,215,000 | ||
| December 31 | Balance | $ 1,215,000 | |||
Table (3)
Retained earnings are a component of stockholder’s equity with a normal credit balance.
| Retained earnings | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Date | Particulars | Credit |
| December 31 | Cash and stock dividends | $493,800 | January 1 | Balance | $33,600,000 |
| December 31 | Net income | $1,125,000 | |||
| Total | $493,800 | Total | $34,725,000 | ||
| December 31 | Balance | $ 34,231,200 | |||
Table (4)
Treasury stock is a component of stockholder’s equity with a normal debit balance.
| Treasury stock | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Date | Particulars | Credit |
| January 1 | Balance | $450,000 | June 6 | Cash | $450,000 |
| November 23 | Cash | $570,000 | |||
| Total | $ 1,020,000 | Total | $450,000 | ||
| December 31 | Balance | $ 450,000 | |||
Table (5)
Paid-in capital from treasury stock is a component of stockholder’s equity with a normal credit balance.
| Paid-in capital from treasury stock | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Date | Particulars | Credit |
| June 6 | Cash | $200,000 | |||
| Total | $ 0 | Total | $200,000 | ||
| December 31 | Balance | $200,000 | |||
Table (6)
Stock dividend distributable is a contra stockholder’s equity with a normal credit balance.
| Stock dividend distributable | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Date | Particulars | Credit |
| August 15 | Common stock | $360,000 | June 5 | Stock dividend | $360,000 |
| Total | $360,000 | Total | $360,000 | ||
| December 31 | Balance | $0 | |||
Table (7)
Stock dividend is a component of stockholder’s equity with a normal debit balance.
| Stock dividend | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Date | Particulars | Credit |
| July 5 | Stock dividend distributable | $360,000 | December 31 | Retained earnings | $450,000 |
| July 5 | Paid in capital in excess of stated value –Common value | $90,000 | |||
| Total | $450,000 | Total | $450,000 | ||
| December 31 | Balance | $0 | |||
Table (8)
Cash dividend is a component of stockholder’s equity with a normal debit balance.
| Stock dividend | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Date | Particulars | Credit |
| December 28 | Cash dividend payable | $43,800 | December 31 | Retained earnings | $43,800 |
| Total | $43,800 | Total | $43,800 | ||
| December 31 | Balance | $0 | |||
Table (9)
(3)
Prepare the statement of stockholders’ equity for the year ended December 31, 20Y6.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the statement of stockholders’ equity for the year ended December 31, 20Y6.
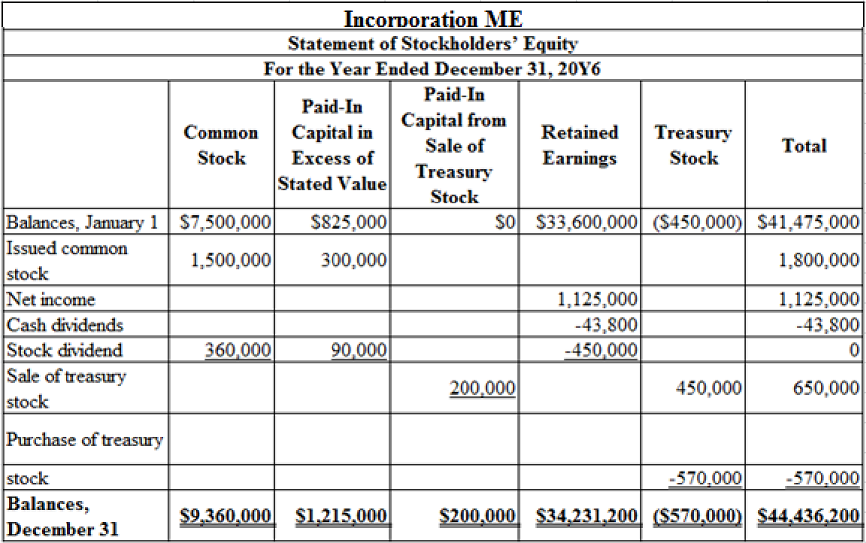
Table (10)
(4)
Prepare the stockholders’ equity section of the December 31, 20Y6, balance sheet.
Explanation of Solution
Stockholders’ equity: It refers to the amount of capital that includes the amount of investment by the stockholders, earnings generated from the normal business operations, and less any dividends paid to the stockholders.
Prepare the stockholders’ equity section of the December 31, 20Y6, balance sheet.
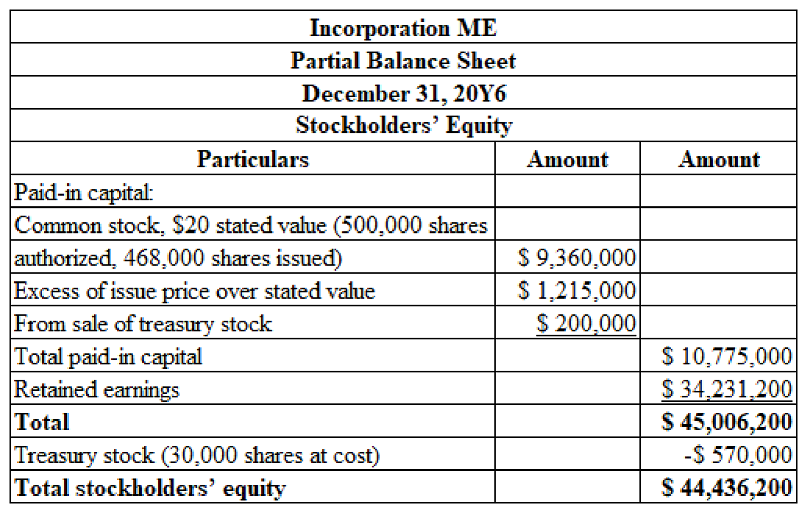
Table (11)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Financial and Managerial Accounting - Workingpapers
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning




