
Beta:
Beta 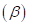 is the covariance of a security with the market upon the variance of the market. Beta
is the covariance of a security with the market upon the variance of the market. Beta 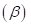 measures the change in percentage in the excess return of a particular security for 1% change in the excess return of a market portfolio or a benchmark portfolio. The beta
measures the change in percentage in the excess return of a particular security for 1% change in the excess return of a market portfolio or a benchmark portfolio. The beta 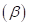 of a market portfolio is always 1. However, the securities may have either higher or lower betas as compared to the beta of the market portfolio. The primary reason for this difference is the sensitivity of the individual industries to the economy.
of a market portfolio is always 1. However, the securities may have either higher or lower betas as compared to the beta of the market portfolio. The primary reason for this difference is the sensitivity of the individual industries to the economy.
The beta 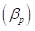 of a portfolio is the weighted average beta of the overall stocks in a portfolio.
of a portfolio is the weighted average beta of the overall stocks in a portfolio.
The beta 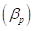 of a portfolio with three stocks, Stock E, Stock C, and Stock K can be calculated using the formula given below.
of a portfolio with three stocks, Stock E, Stock C, and Stock K can be calculated using the formula given below.
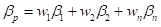
Where,
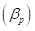 is the beta of a portfolio.
is the beta of a portfolio.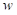 is the weight of a stock.
is the weight of a stock.
To determine:
The beta of the portfolio.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF CORPORATE FINANCE
- Derek plans to retire on his 65th birthday. However, he plans to work part-time until he turns 72.00. During these years of part-time work, he will neither make deposits to nor take withdrawals from his retirement account. Exactly one year after the day he turns 72.0 when he fully retires, he will wants to have $3,104,476.00 in his retirement account. He he will make contributions to his retirement account from his 26th birthday to his 65th birthday. To reach his goal, what must the contributions be? Assume a 8.00% interest rate. Submit Answer format: Currency: Round to: 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardBanking and finance sector ma job kaise payearrow_forward1. Bond X is worth $91 today. The bond will mature in one year and pay $100 or $84 with probabilities 0.75 and 0.25, respectively. Assuming the bond pays no cash flows during the year, which of the following is closest to the expected return on the bond? 5% 0% 0% 5% 0% 2. At the beginning of the year, a mutual fund has a NAV of $20. At the end of the year, the NAV is $21 and the fund has received no dividends or other distributions throughout the year. The return on the fund’s benchmark over the same period of time was 10%. Suppose the fund incurred expenses of $2 per fund share during the year. What was the return on the fund’s underlying portfolio before any expenses that affected NAV? Did this before-expense return beat the fund’s benchmark? 15%; Yes, the fund’s underlying portfolio beat its benchmark 15%; No, the fund’s underlying portfolio beat its benchmark 0%; No, the fund’s underlying portfolio beat its benchmark 20%; Yes, the fund’s underlying portfolio beat its benchmark…arrow_forward
- 1. Which of the following assets is most likely to trade over the counter but still have high liquidity? a. A short-term Treasury bond b. A long-term corporate bond c. A short-term corporate bond d. A large-cap stock e. A small-cap stock 2. Assume you purchased 600 shares of XYZ common stock on margin at $35 per share from your broker. If the initial margin is 60%, the amount you borrowed from the broker is closest to _________. a. $8,500 b. $21,000 c. $29,500 d. $12,500 e. $16,000 3. You invest $1,550 in security A with a beta of 1.4 and $1,350 in security B with a beta of 0.4. The beta of this portfolio is closest to _____________ . a. 0.95 b. 0.90 c. 1.35 d. 1.05 e. 1.15 4. Which of the following orders is most likely to increase the difference between the highest bid price and the lowest ask price? a. A large market order b. A large limit order c. A small limit order d. A small market order e. There will be no major difference between these 5. Bond X is worth $91 today.…arrow_forward1. At the beginning of the year, a mutual fund has a NAV of $20. At the end of the year, the NAV is $21 and the fund has received no dividends or other distributions throughout the year. The return on the fund’s benchmark over the same period of time was 10%. What was the return to investors in the fund? Did the fund’s return to investors beat the benchmark return? a. 5%; No, the fund did not beat its benchmark b. 10%; No, the fund did not beat its benchmark c. 15%; No, the fund did not beat its benchmark d. 20%; Yes, the fund beat its benchmark e. None of the above 2. You are advising a pension fund that is required to have a portfolio risk of 5%. Which of the following would be the portfolio optimization problem for constructing their fund? a. Maximize return subject to a constraint that portfolio volatility is 5% b. Not enough information c. Maximize the Sharpe ratio with no additional constraints d. Minimize the risk needed to get their long-term return target e. None of the…arrow_forwardHow the Synthesizing Qualitative Research Methodology in Case Study Research can be used in case of the collapse of Circuit City? What cause the Circuit City Failed to Adapt to E-commerce? Why DMAIC, a data-driven problem-solving method, and Lean Six Sigma did not save Circuit City?arrow_forward
- How was the poor strategic decisions lead to economic downturns of Circuit City Company? What are the sequence of key events and problems that contribute to its collapse. Could you please explain each one them? How Lean Six Sigma businesses can reduce waste, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction?arrow_forwardSuppose you deposit $9500 into an savings account earning 5% annual interest compounded continuously. To pay for all your music downloads, each year you withdraw $1000 in a continuous way. Let A(t) represent the amount of money in your savings account t years after your initial deposit. (A) Write the DE model for the time rate of change of money in the account. Also state the initial condition. dA dt A(0) (B) Solve the IVP to find the amount of money in the account as a function of time. A(t)= (C) When will your money run out? t = yearsarrow_forwardWhat support comment would be for the Creating Problem Statements and Applicable Research Questions for Sears collapse? Could explain and show the problem is happening from the perspective of the leader who has the problem in Sears company? How Sear problem would be soved? What are other elements of the problem, could you give some assumptions about the problem, or give recommendations to mitigate the problem?arrow_forward
- An S corporation earns 59.10 per share before taxes. The corporate tax rate is 39%, the personal tax rate on dividends is 15%, and the personal tax rate on non-dividend income is 36%. What is the total amount of earnings after - taxes? a. $3.28 b. $3.93 c. $2.62 d. $4.59arrow_forwardYou want to buy a new sports car from Muscle Motors for $36,000. The contract is in the form of an annuity due for 60 months at an APR of 8.00 percent. What will your monthly payment be?arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer this question: Net sales Windswept, Incorporated 2024 Income Statement Cost of goods sold Depreciation ($ in millions) Earnings before interest and taxes Interest paid Taxable income Taxes Net income $ 14,150 8,150 515 $ 5,485 108 $ 5,377 1,129 $ 4,248 Windswept, Incorporated 2023 and 2024 Balance Sheets ($ in millions) 2023 2024 2023 2024 Cash Accounts received $ 300 $ 330 Accounts payable $ 1,980 $1,955 1,190 1,090 Long-term debt 1,110 1,430 Inventory 2,120 1,795 Common stock 3,440 3,080 Total $ 3,610 $ 3,215 Retained earnings 690 940 Net fixed assets 3,610 Total assets $ 7,220 4,190 $ 7,405 Total liabilities & equity $ 7,220 $ 7,405 What is the fixed asset turnover for 2024?arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





