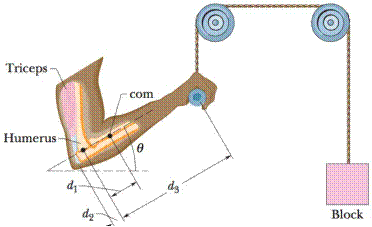
Problem 1Q: Figure 12-15 shows three situations in which the same horizontal rod is supported by a hinge on a... Problem 2Q: In Fig, 12-16, a rigid beam is attached to two posts that are fastened to a floor. A small but heavy... Problem 3Q: Figure 12-17 shows four overhead views of rotating uniform disks that are sliding across a... Problem 4Q: A ladder leans against a frictionless wall but is prevented from falling because of friction between... Problem 5Q: Figure 12-18 shows a mobile of toy penguins hanging from a ceiling. Each crossbar is horizontal, has... Problem 6Q: Figure 12-19 shows an overhead view of a uniform stick on which four forces act. Suppose we choose a... Problem 7Q Problem 8Q: Three piatas hang from the stationary assembly of massless pulleys and cords seen in Fig, 12-21. One... Problem 9Q: In Fig. 12-22, a vertical rend is hinged at its lower end and attached to a cable at its upper end.... Problem 10Q: Figure 12-23 shows a horizontal block that is suspended by two wires, A and B, which are identical... Problem 11Q: The table gives the initial lengths of three reds and the changes in their lengths when forces are... Problem 12Q: A physical therapist gone wild has constructed the stationary assembly of massless pulleys and cords... Problem 1P Problem 2P: An automobile with a mass of 1360 kg has 3.05 m between the front and rear axles. Its center of... Problem 3P: SSM WWWIn Fig. 12-26, a uniform sphere of mass m = 0.85 kg and radius r = 4.2 cm is held in place by... Problem 4P: An archers bow is drawn at its midpoint until the tension in the string is equal to the force... Problem 5P: ILWA rope of negligible mass is stretched horizontally between two supports that are 3.44 m apart.... Problem 6P: A scaffold of mass 60 kg and Length 5.0 m is supported in a horizontal position by a vertical cable... Problem 7P: A 75 kg window cleaner uses a 10 kg ladder that is 5.0 m long. He places one end on the ground 2.5 m... Problem 8P: A physics Brady Bunch, whose weights in newtons are indicated in Fig. 12-27, is balanced on a... Problem 9P: SSMA meter stick balances horizontally on a knife-edge at the 50.0 cm mark. With two 5.00 g coin... Problem 10P: GO The system in Fig. 12-28 is in equilibrium, with the siring in the center exactly horizontal.... Problem 11P: SSMFigure 12-29 shows a diver of weight 580 N standing at the end of a diving board with a length of... Problem 12P: In Fig. 12-30, trying to gel his car out of mud, a man ties one end of a rope around the front... Problem 13P: Figure 12-31 shows the anatomical structures in the lower leg and foot that are involved in standing... Problem 14P: In Fig. 12-32, a horizontal scaffold, of length 2.00 m and uniform mass 50.0 kg, is suspended from a... Problem 15P: ILWForces F1, F2 and F3 act on the structure of Fig. 12-33, shown in an overhead view. We wish to... Problem 16P: A uniform cubical crate is 0.750 m on each side and weighs 500 N. It rests on a floor with one edge... Problem 17P: In Fig. 12-34, a uniform beam of weight 500 N and length 3.0 m is suspended horizontally. On the... Problem 18P: GO In Fig. 12-35, horizontal scaffold 2, with uniform mass m2 = 30.0 kg and length L2= 2.00 m, hangs... Problem 19P: To crack a certain nut in a nutcracker, forces with magnitudes of at least 40 N must act on its... Problem 20P: A bowler holds a bowling ball M = 7.2 kg in the palm of his hand Fig. 12-37. His upper arm is... Problem 21P: ILWThe system in Fig. 12-38 is in equilibrium. A concrete block of mass 225 kg hangs from the end of... Problem 22P: GO In Fig-12-39, a 55 kg rock climber is in a lie-back climb along a fissure, with hands pulling on... Problem 23P: GO In Fig. 12-40, one end of a uniform beam of weight 222 N is hinged to a wall; the other end is... Problem 24P: GO In Fig. 12-41, a climber with a weight of 533.8 N is held by a belay rope connected to her... Problem 25P: SSM WWWIn Fig. 12-42, what magnitude of constant force F applied horizontally at the axle of the... Problem 26P: GO In Fig. 12-43, a climber leans out against a vertical ice wall that has negligible friction.... Problem 27P: GO In Fig. 12-44, a 15 kg block is held in place via a pulley system. The persons upper arm is... Problem 28P: GO In Fig. 12-45, suppose the length L of the uniform bar is 3.00 m and its weight is 200 N. Also,... Problem 29P: A door has a height of 2.1 m along a y axis that extends vertically upward and a width of 0.91 m... Problem 30P: GO In Fig. 12-46, a 50.0 kg uniform square sign, of edge length L = 2.00 m, is hung from a... Problem 31P: GO In Fig. 12-47, a nonuniform bar is suspended at rest in a horizontal position by two massless... Problem 32P: In Fig. 12-48, the driver of a car on a horizontal road makes an emergency stop by applying the... Problem 33P: Figure 12-49a shows a vertical uniform beam of length L that is hinged at its lower end. A... Problem 34P: In Fig. 12-45, a thin horizontal bar AB of negligible weight and length L is hinged to a vertical... Problem 35P: SSM WWWA cubical box is filled with sand and weighs 890 N. We wish to roll the box by pushing... Problem 36P: Figure 12-50 shows a 70 kg climber hanging by only the crimp hold of one hand on the edge of a... Problem 37P: GO In Fig. 12-51, a uniform plank, with a length L of 6.10 m and a weight of 445 N, rests on the... Problem 38P: In Fig, 12-52, uniform beams A and B are attached to a wall with hinges and loosely bolted together... Problem 39P: For the stepladder shown in Fig. 12-53, sides AC and CE are each 2.44 m long and hinged at C. Bar BD... Problem 40P: Figure 12-54a shows a horizontal uniform beam of mass mb and length L that is supported on the left... Problem 41P: A crate, in the form of a cube with edge lengths of 1.2 m, contains a piece of machinery; the center... Problem 42P: In Fig. 12-7 and the associated sample problem, let the coefficient of static friction s between the... Problem 43P: SSM ILWA horizontal aluminum rod 4.8 cm in diameter projects 5.3 cm from a wall. A 1200 kg object is... Problem 44P: Figure 12-55 shows the stressstrain curve for a material. The scale of the stress axis is set by s =... Problem 45P: In Fig. 12-56, a lead brick rests horizontally on cylinders A and B. The areas of the top faces of... Problem 46P: Figure 12-57 shows an approximate plot of stress versus strain for a spider-web thread, out to the... Problem 47P: A tunnel of length L = 150 m, height H = 7.2 m, and width 5.8 m with a flat roof is to be... Problem 48P: Figure 12-59 shows the stress versus strain plot for an aluminum wire that is stretched by a machine... Problem 49P: GO In Fig. 12-60, a 103kg uniform log hangs by two stool wires,A and B, both of radius 1.20 mm.... Problem 50P: GO Figure 12-61 represents an insect caught at the midpoint of a spider-web thread. The thread... Problem 51P: GO Figure 12-62 is an overhead view of a rigid rod that turns about a vertical axle until the... Problem 52P: After a fall, a 95 kg rock climber finds himself dangling from the end of a rope that had been 15 m... Problem 53P: SSMIn Fig 12-63, a rectangular slab of slate rests on a bedrock surface inclined at angle = 26. The... Problem 54P: A uniform ladder whose length is 5.0 m and whose weight is 400 N leans against a frictionless... Problem 55P: SSM In Fig. 12-64, block A mass 10 kg is in equilibrium, but it would slip if block B mass 5.0 kg... Problem 56P: Figure 12-65a shows a uniform ramp between two buildings that allows for motion between the... Problem 57P: GO In Fig. 12-66, a 10 kg sphere is supported on a frictionless plane inclined at angle = 45 from... Problem 58P: In Fig. 12-67a, a uniform 40.0 kg beam is centered over two rollers. Vertical lines across the beam... Problem 59P: SSM In Fig. 12-68, an 817 kg construction bucket is suspended by a cable A that is attached at O to... Problem 60P: In Fig. 12-69, a package of mass m hangs from a short cord that is tied to the wall via cord 1 and... Problem 61P: ILWThe force F in Fig. 12-70 keeps the 6.40 kg block and the pulleys in equilibrium. The pulleys... Problem 62P: A mine elevator is supported by a single steel cable 2.5 cm in diameter. The total mass of the... Problem 63P: Four bricks of length L, identical and uniform, are stacked on top of one another Fig. 12-71 in such... Problem 64P Problem 65P: In Fig. 12-73, a uniform beam with a weight of 60 N and a length of 3.2 m is hinged at its lower... Problem 66P: A uniform beam is 5.0 m long and has a mass of 53 kg. In Fig. 12-74, the beam is supported in a... Problem 67P: A solid copper cube has an edge length of 85.5 cm. How much stress must be applied to the cube to... Problem 68P: A construction worker attempts to lift a uniform beam off the floor and raise it to a vertical... Problem 69P: SSM In Fig. 12-76, a uniform rod of mass m is hinged to a building at its lower end, while its upper... Problem 70P: A 73 kg man stands on a level bridge of length L. He is at distance L/4 from one end. The bridge is... Problem 71P: SSMA uniform cube of side length 8.0 cm rests cm a horizontal floor. The coefficient of static... Problem 72P: The system in Fig. 12-77 is in equilibrium. The angles are 1 = 60 and 2 = 20, and the ball has mass... Problem 73P: SSMA uniform ladder is 10 m long and weighs 200 N. In Fig. 12-78, the ladder leans against a... Problem 74P: A pan balance is made up of a rigid, massless rod with a hanging pan attached at each end. The rod... Problem 75P: The rigid square frame in Fig. 12-79 consists of the four side bars AB, BC, CD, and DA plus two... Problem 76P: A gymnast with mass 46.0 stands on the end of a uniform balance beam as shown in Fig. 12-80. The... Problem 77P: Figure 12-81 shows a 300 kg cylinder that is horizontal. Three steel wires support the cylinder from... Problem 78P: In Fig. 12-82, a uniform beam of length 12.0 m is supported by a horizontal cable and a hinge at... Problem 79P: Four bricks of length L, identical and uniform, are stacked on a table in two ways, as shown in Fig.... Problem 80P: A cylindrical aluminum rod, with an initial length of 0.8000 m and radius 1000.0 m, is clamped in... Problem 81P Problem 82P: If the square beam in Fig. 12-6a and the associated sample problem is of Douglas fir, what must be... Problem 83P: Figure 12-84 shows a stationary arrangement of two crayon boxes and three cords. Box A has a mass of... Problem 84P: A makeshift swing is constructed by makings loop in one end of a rope and tying the other end to a... Problem 85P: Figure 12-85a shows details of a finger in the crimp hold of the climber in Fig. 12-50. A tendon... Problem 86P: A trap door in a ceiling is 0.91 m square, has a mass of 11 kg, and is hinged along one side, with a... Problem 87P: A particle is acted on by forces given, in newtons, by F1=8.40i5.70j and F2=16.0i+4.10j. a What are... Problem 88P: The leaning Tower of Pisa is 59.1 m high and 7.44 m in diameter. The top of the tower is displaced... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University




