Microsatellites are currently exploited as markers for paternity testing. A sample paternity test is shown in the following table in which ten microsatellite markers were used to test samples from a mother, her child, and an alleged father. The name of the microsatellite locus is given in the left-hand column, and the genotype of each individual is recorded as the number of repeats he or she carries at that locus. For example, at locus D9S302, the mother carries 30 repeats on one of her chromosomes and 31 on the other. In cases where an individual carries the same number of repeats on both chromosomes, only a single number is recorded. (Some of the numbers are followed by a decimal point, for example, 20.2, to indicate a partial repeat in addition to the complete repeats.) Assuming that these markers are inherited in a simple Mendelian fashion, can the alleged father be excluded as the source of the sperm that produced the child? Why or why not? Explain. 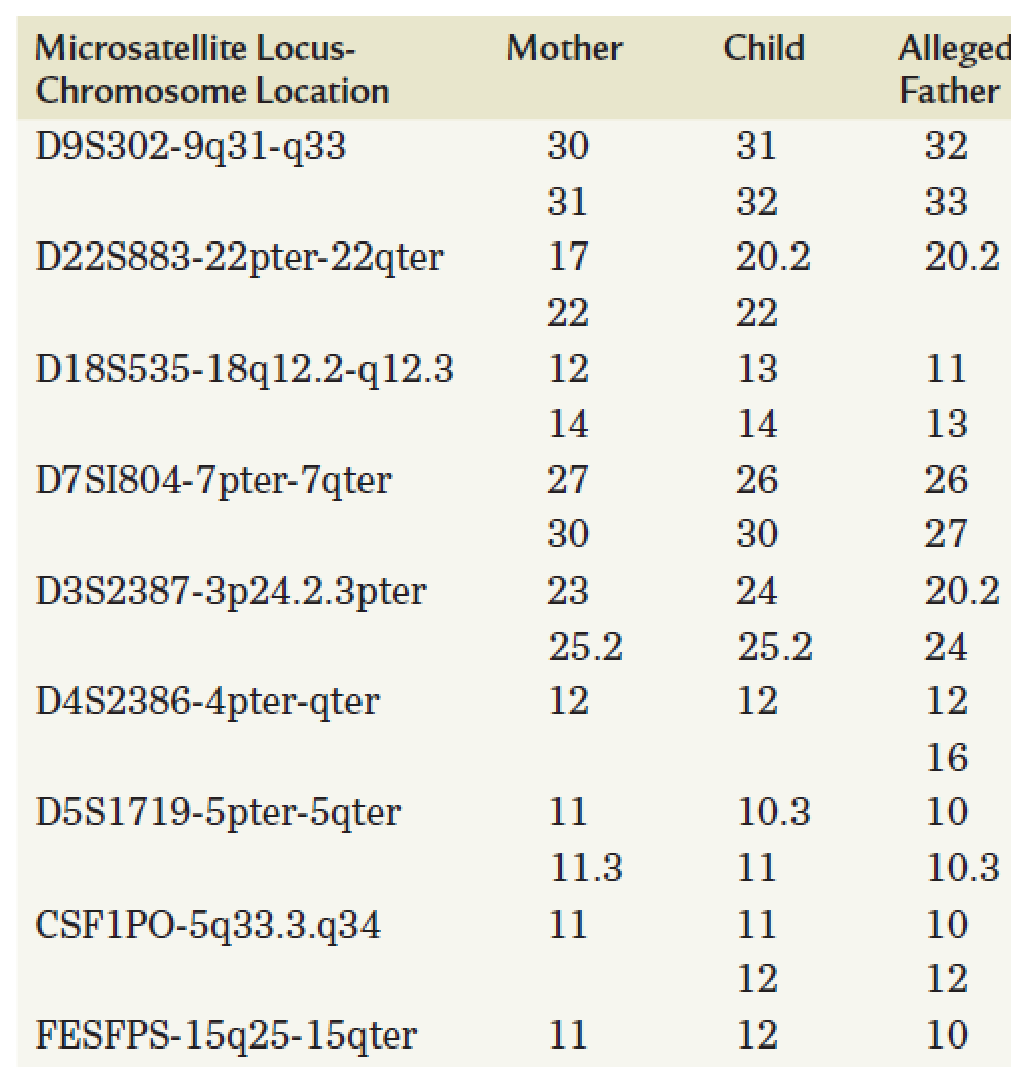
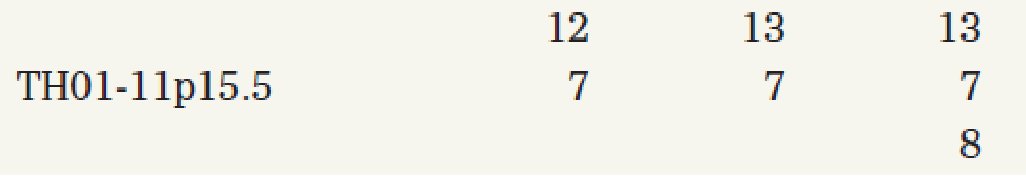
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK CONCEPTS OF GENETICS
- Briefly state the physical meaning of the electrocapillary equation (Lippman equation).arrow_forwardExplain in a small summary how: What genetic information can be obtained from a Punnet square? What genetic information cannot be determined from a Punnet square? Why might a Punnet Square be beneficial to understanding genetics/inheritance?arrow_forwardIn a small summary write down:arrow_forward
- Not part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNoggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage





