
(a):
Cumulative distribution of income.
(a):
Explanation of Solution
The economic development is achieved when the economic price increases per head of the population in the economy. The unequal distribution of the economic price between the people in the economy causes the income inequality in the economy. The income inequality is the situation in the economy in which the major part of the income will be earned by a smaller proportion of the population and vice versa.
The cumulative share of income can be easily calculated by adding the share of income with each preceding level's cumulative share of income. Here, in this case, the percentage share of income for A for the lowest fifth is 17.7 percent. Since there are no preceding levels, the cumulative share would remain the same as 17.7 percent. The percentage share of income for the second lowest fifth is 19.9 percent. Thus, the cumulative share of the second lowest fifth will be summation of the percentage share of both lowest fifth and second lowest fifth, which can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the cumulative share of income for the second lowest fifth is calculated to be 37.6 percent. Similarly, the cumulative share of income can be calculated, and the table can be completed as follows:
| A | B | |||
| Percentage of families | Percentage share | Cumulative share | Percentage share | Cumulative share |
| Lowest fifth | 17.7% | 17.7% | 9.0% | 9.0% |
| Second lowest fifth | 19.9 | 37.6 | 14.2 | 23.2 |
| Middle fifth | 20.4 | 58.0 | 17.5 | 40.7 |
| Second highest fifth | 20.7 | 78.7 | 21.9 | 62.6 |
| Highest fifth | 21.3 | 100.0 | 37.4 | 100.0 |
Income Inequality: The income inequality is the situation where most of the
(b):
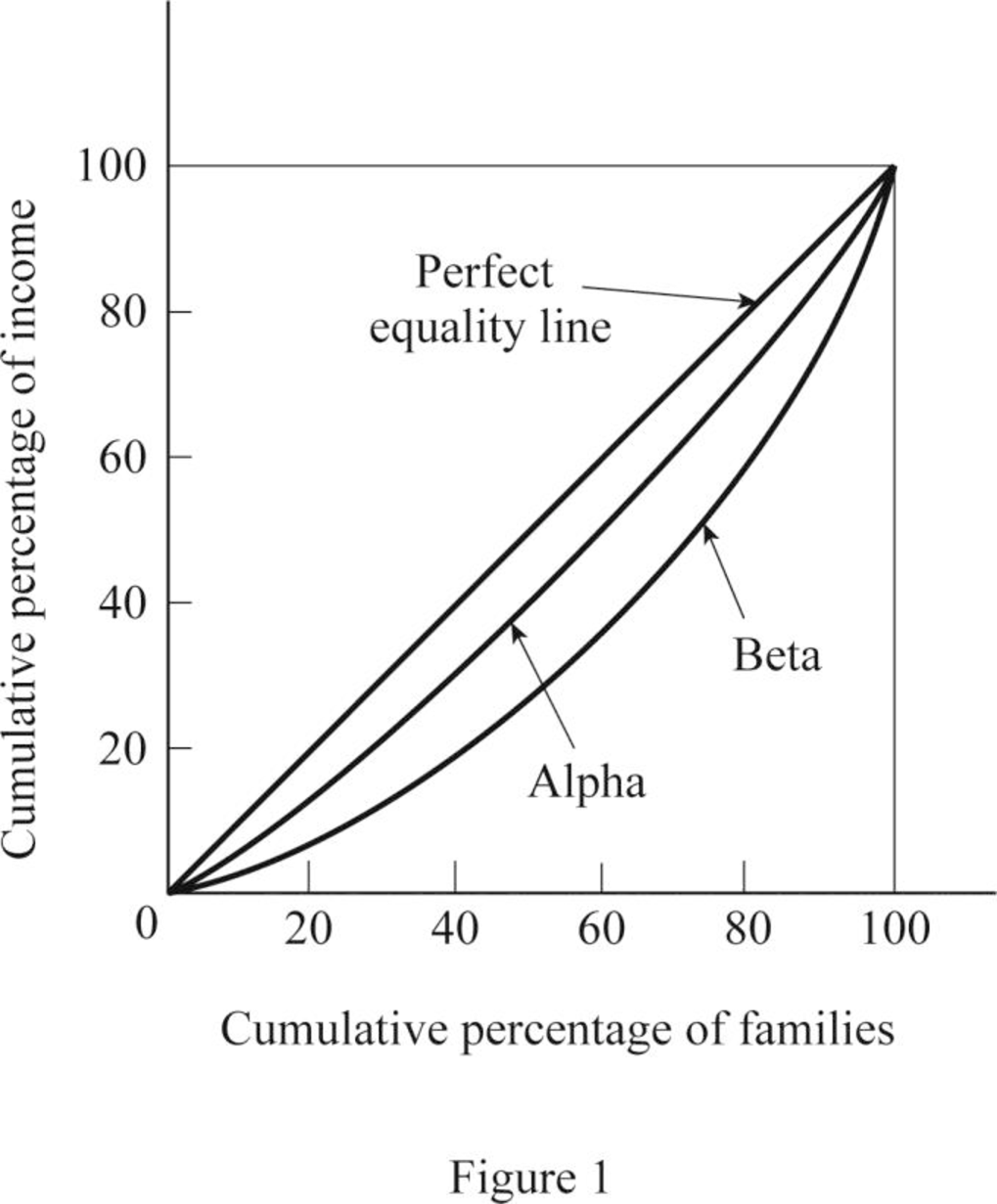
Lorenz curve of the economy.
(b):
Explanation of Solution
The Lorenz curve is the graphical illustration of the distribution of wealth in the economy. It is drawn on the cumulative percentage of income against the cumulative percentage of the population. Thus, it shows the cumulative shares of income received by the family. Thus, based on the table above, the Lorenz curve can be constructed as follows:
(c):
Country with more equal distribution of income.
(c):
Explanation of Solution
From the Lorenz curve diagram, it can be identified that the line that lies more close to the line of equality has more equal distribution of income. From the diagram, it is identified that Lorenz curve of Country A is closest to the line of equality and thus, Country A has more equal income distribution.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Microeconomics For Today (MindTap Course List)
- You are the manager of a large automobile dealership who wants to learn more about the effective- ness of various discounts offered to customers over the past 14 months. Following are the average negotiated prices for each month and the quantities sold of a basic model (adjusted for various options) over this period of time. 1. Graph this information on a scatter plot. Estimate the demand equation. What do the regression results indicate about the desirability of discounting the price? Explain. Month Price Quantity Jan. 12,500 15 Feb. 12,200 17 Mar. 11,900 16 Apr. 12,000 18 May 11,800 20 June 12,500 18 July 11,700 22 Aug. 12,100 15 Sept. 11,400 22 Oct. 11,400 25 Nov. 11,200 24 Dec. 11,000 30 Jan. 10,800 25 Feb. 10,000 28 2. What other factors besides price might be included in this equation? Do you foresee any difficulty in obtaining these additional data or incorporating them in the regression analysis?arrow_forwardsimple steps on how it should look like on excelarrow_forwardConsider options on a stock that does not pay dividends.The stock price is $100 per share, and the risk-free interest rate is 10%.Thestock moves randomly with u=1.25and d=1/u Use Excel to calculate the premium of a10-year call with a strike of $100.arrow_forward
- Please solve this, no words or explanations.arrow_forward17. Given that C=$700+0.8Y, I=$300, G=$600, what is Y if Y=C+I+G?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write explanation in paragraphs and if you use currency use USD currency: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write it all in paragraphs: 2. Give an overview of the equation of exchange (EoE) as used by Classical Theory. Now,carefully explain each variable in the EoE. What is meant by the “quantity theory of money”and how is it different from or the same as the equation of exchange?arrow_forwardZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwharrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all:arrow_forward


 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





