
Concept explainers
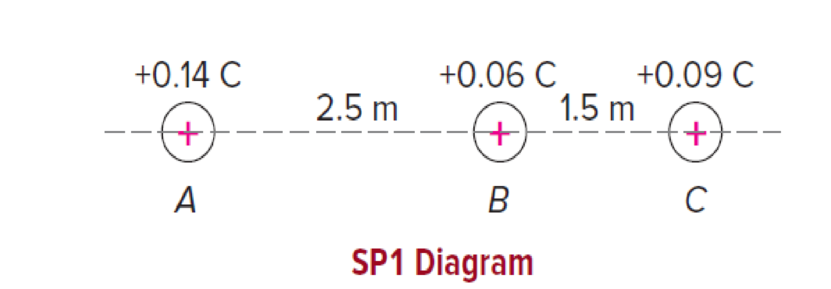
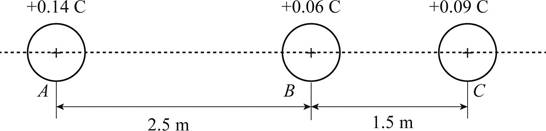
Three positive charges are located along a line, as in the diagram. The 0.14 C charge at points A is 2.5 m to the left of the 0.06 C charge at point B, and the 0.09 C charge at point C is 1.5 m to the right of point B.
a. What is the magnitude of the force exerted on the 0.06 C charge by the 0.14 C charge?
b. What is the magnitude of the force exerted on the 0.06 C charge by the 0.09 C charge?
c. What is the net force exerted on the 0.06 C charge by the other two charges?
d. If we regard the 0.06 C charge as a test charge used to probe the strength of the electric field produced by the other two charges, what are the magnitude and direction of the electric field at point B?
e. If the 0.06 C charge at point B is replaced by a –0.17 C charge, what are the magnitude and direction of the electrostatic force exerted on this new charge? (Use the electric field value to find this force.)
(a)
The magnitude of the force on
Answer to Problem 1SP
The magnitude of the force on
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The distance between the charges at A and B is
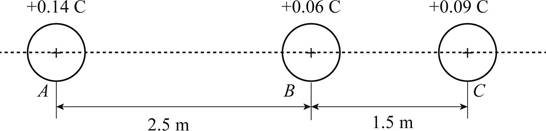
The diagram showing the charges
Write the expression to find the electrostatic force.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the force on
(b)
The magnitude of the force on
Answer to Problem 1SP
The magnitude of the force on
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The distance between the charges at C and B is
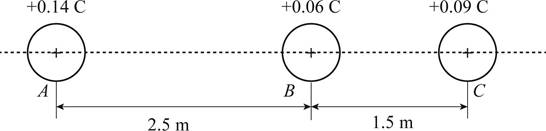
The diagram showing the charges
Write the expression to find the electrostatic force.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the force on
(c)
The net force exerted on the
Answer to Problem 1SP
The net force exerted on the
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The magnitude of the force on
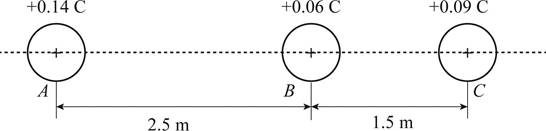
The diagram showing the charges
Write the expression to find the net electrostatic force on charge at B.
Here,
F is the net electrostatic force on charge at B
Consider the right direction to be positive.
Substitute
Since, the net force is negative; the direction of the net force will be in the left direction.
Conclusion:
The net force exerted on the
(d)
The direction and magnitude of the electric field at the point B.
Answer to Problem 1SP
The direction and magnitude of the electric field at point B is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The net force exerted on the
The diagram showing the charges
Write the expression to find the electric field.
Here,
q is the charge
Substitute
The direction of the electric field is in the left direction.
Conclusion:
The direction and magnitude of the electric field at point B is
(e)
The direction and magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted on the new charge if the
Answer to Problem 1SP
The direction and magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted on the new charge if the
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The direction and magnitude of the electric field at point B is
The diagram showing the charges

Write the expression to find the electrostatic force.
Here,
q is the charge
Substitute
The direction of the electrostatic force will be in the right direction.
Conclusion:
The direction and magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted on the new charge if the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
- Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





