
Concept explainers
Figure 12-15 shows three situations in which the same horizontal rod is supported by a hinge on a wall at one end and a cord at its other end. Without written calculation, rank the situations according to the magnitudes of (a) the force on the rod from the cord, (b) the vertical force on the rod from the hinge, and (c) the horizontal force on the rod from the hinge, greatest first.
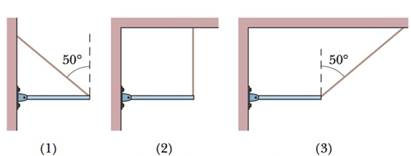
Figure 12-15 Question 1.
To rank:
a) The situations according to the magnitudes of the force on the rod from the cord.
b) The situations according to the magnitudes of the vertical force on the rod from the hinge.
c) The situations according to the magnitudes of the horizontal force on the rod form the hinge.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution:
a) Magnitudes of force on the rod from the cord in case (1) and (3) is same and greater than that in case (2).
b) Magnitudes of the vertical force on the rod from the hinge is same for all 3 cases.
c) Magnitudes of the horizontal force on the rod form the hinge is same in cases (1) and (3) and is zero in case (2)
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
We can use the concept of balancing of forces and torque at equilibrium to rank the situations according to the magnitude of the forces.
2) Formulae:
At equilibrium,
i.
ii.
3) Given:
i. The figure of rod-cable system.
ii. The angle made by the cord with the vertical direction in case 1 and 3 is 500
4) Calculation:
a) We consider the hinge point as the point of rotation. The torques acting on the rod are due to tension in the string and the weight of the rod. In all the three cases, the rod is in static equilibrium, hence:
The weight of the rod is acting at its centre and is the same in magnitude. Hence the torque equation tells us that torque due to tension, it is same in all the cases.
But the cord is making an angle with the vertical in cases (1) and (3). Hence we understand that the torque due to vertical component of the tension (T cos 50o) is the same. Since it is a component of the total tension, we know that the total tension is greater than the components in cases (1) and (3).Thus, for cases (1) and (3) the tension in the string is same and it will be greater than this in case (2).
b) We consider the hinge point as the point of rotation. In all the three cases, the rod is in static equilibrium. So the torques acting on the rod due to the tension in the string and the weight of the rod are balanced and the forces are also balanced.
Thus the vertical force from the hinge on the rod is same in all the three cases.
c) The forces acting on the rod in the horizontal direction are the force from hinge and the horizontal component of tension in the cord. In cases (1) and (3), the tension in the string is the same. Hence their corresponding horizontal components are also the same.
Thus, the horizontal force on the rod from the hinge is the same in cases (1) and (3). In case (2), there is no horizontal component of tension, hence the horizontal force from the hinge is also zero.
Conclusion:
The rod is in static equilibrium in all three cases. From the balancing conditions for torque and forces, we can determine the magnitudes of the forces acting on the rod.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
FUND PHYS 10TH EXT WILEY PLUS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- as a hiker in glacier national park, you need to keep the bears from getting at your food supply. You find a campground that is near an outcropping of ice. Part of the outcropping forms a feta=51.5* slopeup that leads to a verticle cliff. You decide that this is an idea place to hang your food supply out of bear reach. You put all of your food into a burlap sack, tie a rope to the sack, and then tie a bag full of rocks to the other end of the rope to act as an anchor. You currently have 18.5 kg of food left for the rest of your trip, so you put 18.5 kg of rocks in the anchor bag to balance it out. what happens when you lower the food bag over the edge and let go of the anchor bag? Determine the acceleration magnitude a of the two-bag system when you let go of the anchor bag?arrow_forward2. A thin Nichrome wire is used in an experiment to test Ohm's law using a power supply ranging from 0 to 12 V in steps of 2 V. Why isn't the graph of I vs V linear? 1. Nichrome wire does obey Ohm's law. Explain how that can that be true given the results abovearrow_forward1. The average KE and temperature in Kelvin of the molecules of a gas are related by the equation KE = 3/2 KT where k is the Boltzmann constant 1.38 x 10 m² kg s². The diagram shows the energy levels for a Hydrogen atom. Energy/eV 0.00 -1.51 3.39 13.58 Use this information to show that Hydrogen at room temperature will not emit light. 2. When hydrogen burns in oxygen 241.8 kJ of energy are released per mole. Show that this reaction can produce light.arrow_forward
- 3. By using the fact that around any closed loop the sum of the EMFS = the sum of the PDs. Write equations for the two loops shown in the cct below. 40 ΔΩ I₂ 4V (loop1 20 (loop2) 2v I+12 Use these equations to show that the current flowing through the 20 resistor is 0.75Aarrow_forward5. A potential divider circuit is made by stretching a 1 m long wire with a resistance of 0.1 per cm from A to B as shown. 8V A 100cm B sliding contact 5Ω A varying PD is achieved across the 5 Q resistor by moving the slider along the resistance wire. Calculate the distance from A when the PD across the 5 Q resistor is 6 V.arrow_forward4. A voltmeter with resistance 10 kQ is used to measure the pd across the 1 kQ resistor in the circuit below. 6V 5ΚΩ 1ΚΩ V Calculate the percentage difference between the value with and without the voltmeter.arrow_forward
- 1. A 9V battery with internal resistance 5 2 is connected to a 100 2 resistor. Calculate: a. the Power dissipated in the 100 2 resistor b. The heat generated per second inside the battery. C. The rate of converting chemical to electrical energy by the battery. 2. A 230 V kettle is rated at 1800 W. Calculate the resistance of the heating element.arrow_forward2. If each of the resistors in the circuit below has resistance R show that the total resistance between A and B is 5R/11 A Barrow_forward1. At 0°C a steel cable is 1km long and 1cm diameter when it is heated it expands and its resistivity increases. Calculate the change in resistance of the cable as it is heated from 0-20°C The temperature coefficient of resistance a, gives the fractional increase in resistance per °C. So increase in resistance AR = Ra.AT Where R, is the resistance at 0°C For steel a, 0.003 °C The coefficient of linear expansion a- gives the fractional increase in length per °C temperature rise. So increase in Length AL La-AT Where L, is the length at 0°C For steel a₁ = 12 x 10 °C-1 The resistivity of steel at 0°C = 1.2 x 10 Qmarrow_forward
- 1. F E 6V 10 1.1. B a 6V b C C Apply Kirchoff's 1st law to point C for the circuit above Apply Kirchoff's 2nd Law to loops: a. ABCFA b. ABDEA C. FCDEF d. Find values for currents a,b and c Darrow_forward2. The results of the Rutherford experiment can be categorized in 3 statements. Fill in the missing words Most 11. Some III. A few State which result gives evidence that the nucleus is a. heavier than an alpha particle b. very small compared to the size of the atom c. positively charged 3. Using values in the diagram derive an expression for r .0 e marrow_forward3. A 100 W light bulb is connected to 230 V mains supply by a cable with resistance 0.12. Determine the heat loss per second by the cable.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





