
Draw the shear and bending moment diagrams for the girders of given frame.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The uniformly distributed load acting along the girder DEF (w) is 30 kN/m.
The horizontal distance of the point AB and BC
The vertical distance of the members AD, BE, and CF
Calculation:
The span length and loads for the two girders of the frame DE and EF are same; therefore the approximate shear and bending moment diagrams for the girders will also be the same.
Consider the girder DE.
Determine the span for the middle portion of the girder using the relation.
Substitute 6 m for L.
Determine the span for the two end portion of the girder using the relation.
Substitute 6 m for L.
Draw the statically determinate girder portion as in Figure (1).
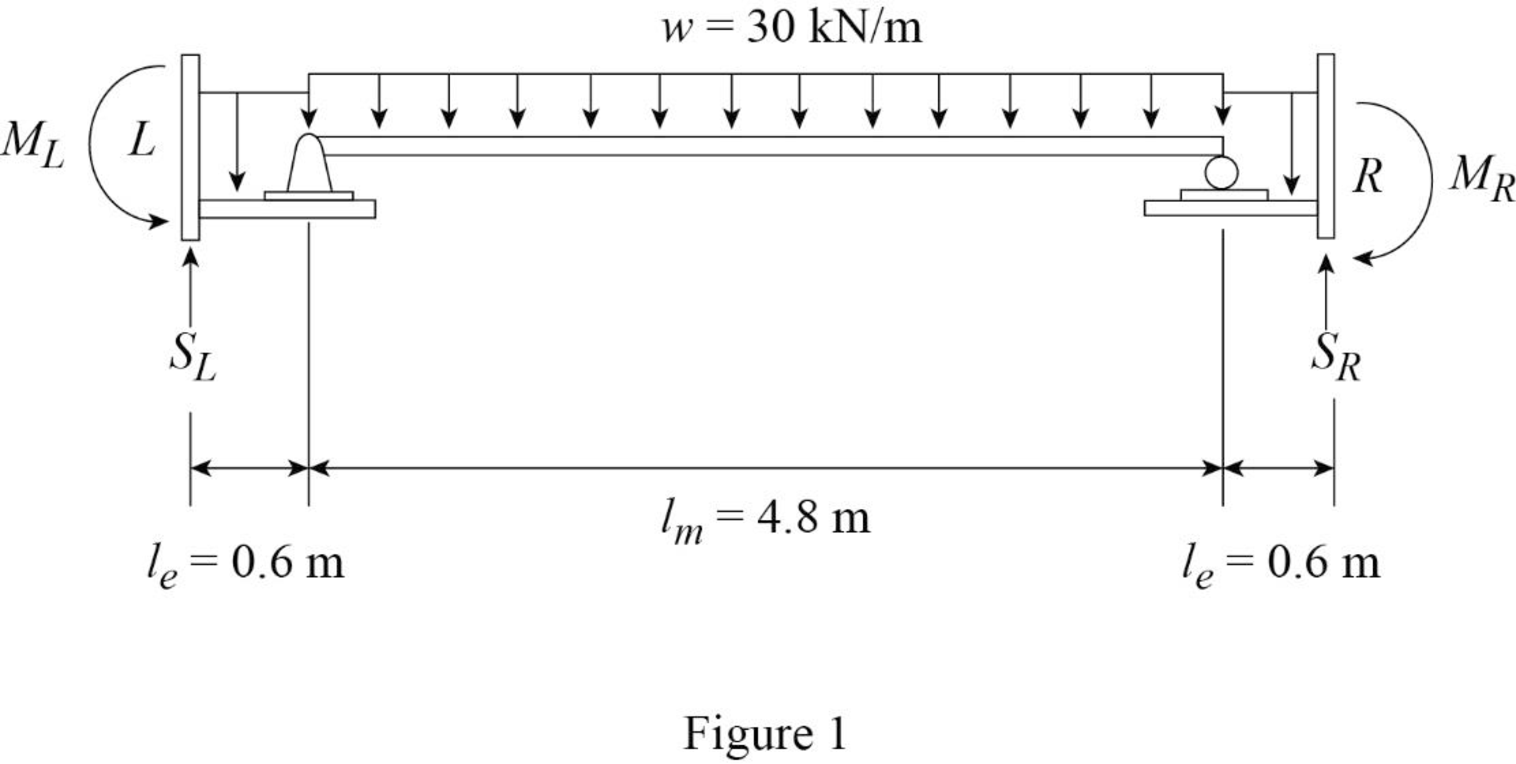
Consider the equilibrium of the simply supported middle portion of the girder.
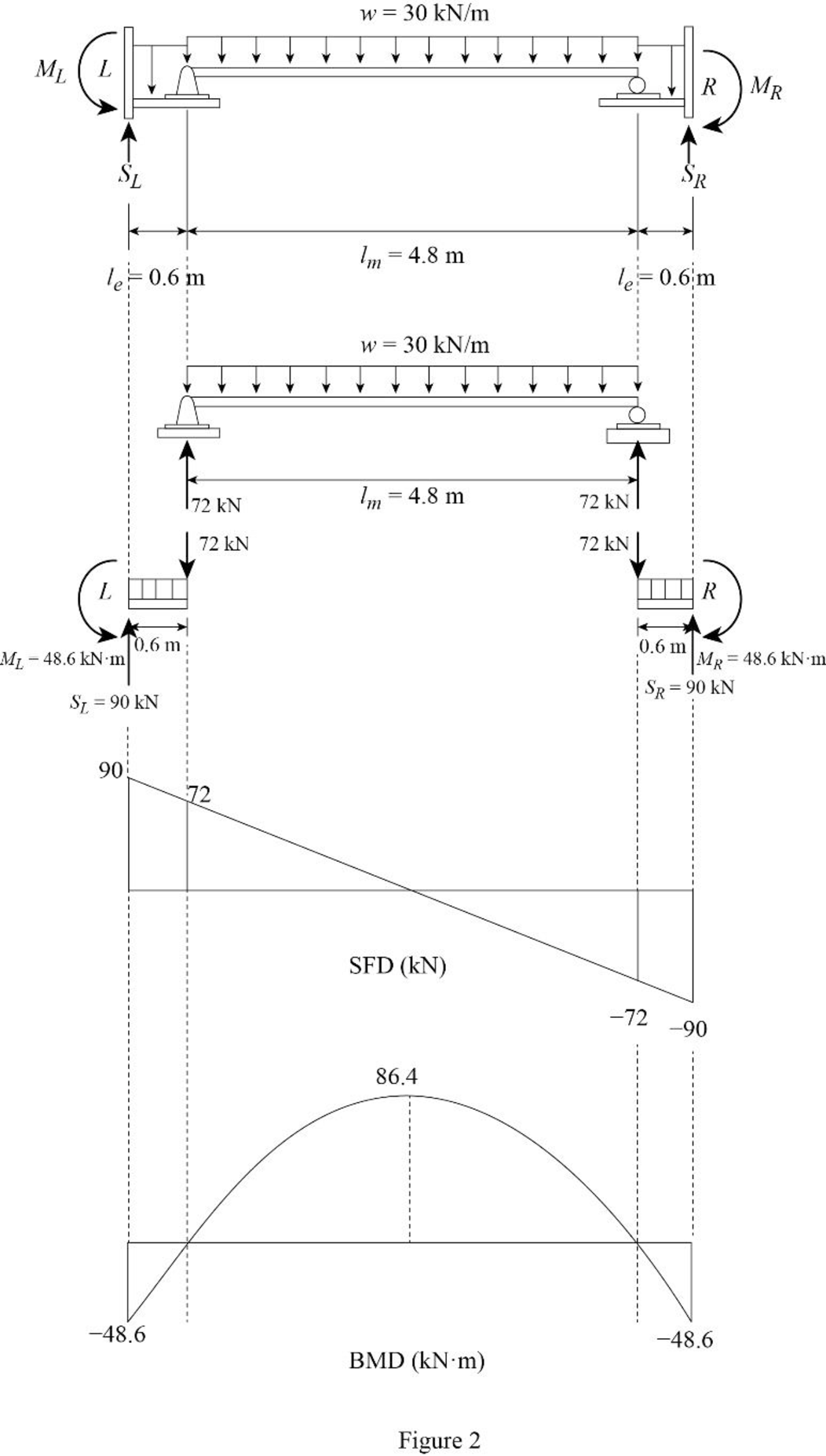
Determine the vertical reactions at the end portion using the relation.
Substitute 30 kN/m for w and 4.8 m for
Consider the equilibrium conditions of the end portions of the girder.
Consider upward direction is positive and counter clockwise moment is positive.
Determine the support reaction at the left end.
Apply the equations of equilibrium to the left end portion.
Substitute 30 kN/m for w, 0.6 m for
Determine the moment at the left end.
Take moment about left end is equal to zero.
Substitute 30 kN/m for w, 0.6 m for
Consider upward direction is positive and clockwise moment is positive.
Determine the support reaction at the right end.
Apply the equations of equilibrium to the right end portion.
Substitute 30 kN/m for w, 0.6 m for
Determine the moment at the right end.
Take moment about right end is equal to zero.
Substitute 30 kN/m for w, 0.6 m for
Determine the maximum bending moment at the middle of the girder using the relation.
Substitute 30 kN/m for w and 4.8 m for
Draw the shear force and bending moment diagram as in Figure (2).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Structural Analysis, Si Edition (mindtap Course List)
- Problem 2 (A is fixed and C is a pin) Find the reactions and A and C. 10 k- 6 ft 6 ft B A 2 k/ft 15 ftarrow_forward6. A lake with no outlet is fed by a river with a constant flow of 1200 ft3/s. Water evaporates from the surface at a constant rate of 13 ft3/s per square mile of surface area. The surface area varies with the depth h (in feet) as A (square miles) = 4.5 + 5.5h. What is the equilibrium depth of the lake? Below what river discharge (volume flow rate) will the lake dry up?arrow_forwardProblem 5 (A, B, C and D are fixed). Find the reactions at A and D 8 k B 15 ft A -20 ft C 10 ft Darrow_forward
- Problem 4 (A, B, E, D and F are all pin connected and C is fixed) Find the reactions at A, D and F 8 m B 6m E 12 kN D F 4 marrow_forwardProblem 1 (A, C and D are pins) Find the reactions and A, C and D. D 6 m B 12 kN/m 8 m A C 6 marrow_forwardUniform Grade of Pipe Station of Point A is 9+50.00. Elevation Point A = 250.75.Station of Point B is 13+75.00. Elevation Point B = 244.10 1) Calculate flowline of pipe elevations at every 50 ft. interval (Half Station). 2) Tabulate station and elevation for each station like shown on example 3) Draw Sketcharrow_forward
- quantity surveyingarrow_forwardNote: Please accurately answer it!. I'll give it a thumbs up or down based on the answer quality and precision. Question: What is the group name of Sample B in problem 3 from the image?. By also using the ASTM flow chart!. This unit is soil mechanics btwarrow_forwardPick the rural location of a project site in Victoria, and its catchment area-not bigger than 25 sqkm, and given the below information, determine the rainfall intensity for ARI = 5, 50, 100 year storm event. Show all the details of the procedure. Each student must propose different length of streams and elevations. Use fig below as a sample only. Pt. E-ht. 95.0 200m 600m PLD-M. 91.0 300m Pt. C-93.0 300m PL.B-ht. 92.0 PL.F-ht. 96.0 500m Pt. A-M. 91.00 To be deemed satisfactory the solution must include: Q.F1.1.Choice of catchment location Q.F1.2. A sketch displaying length of stream and elevation Q.F1.3. Catchment's IFD obtained from the Buro of Metheorology for specified ARI Q.F1.4.Calculation of the time of concentration-this must include a detailed determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.5.Use must be made of the Bransby-Williams method for the determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.6.The graphical display of the estimation of intensities for ARI 5,50, 100 must be shown.arrow_forward
