
Concept explainers
In addition to the key words, you should also be able to define each of the following terms:
Linear relationship
Pearson
Monotonic relationship
Spearman correlation
Statistical significance of a
Regression
Third-variable problem
Directionality problem
Multiple regression
To define:
Each of the following terms: Scatter plot, linear relationships, Pearson correlation, monotonic relationship, Spearman correlation, Statistical significance of a correlation, regression, third variable problem, directionality problem, multiple regressions.
Explanation of Solution
Explanations:
Scatter Plot: It is a 2D graph between 2 variables X and Y obtained by plotting X on horizontal and Y on vertical axes. The scatter plot is mainly done to study the extent of correlation between 2 variables. If a large correlation exists then the points scatter in a line and if there's no such correlation then they are scattered randomly.
Linear Relationship: In a linear relationship the relationship between 2 variables can be represented with a line. The linear relationship can be positive or negative depending on the fact that if X increase then Y increases too and it is positive. It is negative when X increases but Y decreases. Linear relationships can be determined using scatter plots between 2 variables. There ca be no relationship too in that case the points scattered randomly. Graphical representation of positive linear relation: 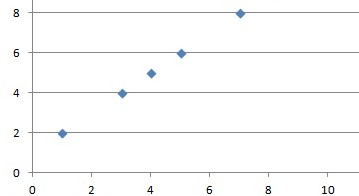
Pearson correlation:
Pearson product correlation coefficient is a measure of linear association between 2 variables X and Y. It has a value between -1 and +1 and is denoted by r.
r consists of a ratio comparing the covariance( X and Y) (numerator) with the variance of X and Y separately (in the denominator).
The formula:
Monotonic relationship: It is the degree to which the relationship is one directional. So as one value increases the other also increases and as one decreases other also decreases. Spearman correlation measures this value.
Spearman Correlation: This is distribution free alternative to Pearson r value. It measures strength and direction of monotonic relationship and used mostly for ordinal observations.
The formula is:
In this case ranks are calculated for each data X and Y and their difference is taken represented as d in the formula. It can also take values in (-1,+1)range. A high positive value like 0.9 indicates a strong positive correlation and vice versa. So here as X increases so does Y (Just like r).
Statistical Significance of a correlation: Correlation is tested using t statistic.
The formula is provided as
to test whether the linear relationship is strong enough to model the relationship in the population. The hypothesis tests decide if the population correlation
Regression: It is a set of statistical processes for establishing or estimating the relationship among variables. Regression analysis helps to understand how changes in independent variable results in changes in dependent variable. It is widely used for prediction and forecasting. It helps in understanding which independent variables are related to the dependent variable and what is the form of the relationship. In other words it can be used to establish causal relationship.
Third variable problem: In context of experimental design third variable can be confounded variable resulting in relationship between 2 variables. Example can be cities with higher churches have higher crime rate but more churches do not lead to more crime so a 3rd variable population lead to more churches and more crime.
Directionality problem: It's a problem with 2 variables when the cause and effect is not known. It's known that there exists a relationship between X and Y however whether X is due to Y or vice versa is not known. For that apart from correlational study experimental study are required to be conducted. So an example can be there's a strong correlation between amount of violence seen on Tv and amount of aggressive behavior by children but its not known whether amount of violence seen on TV is due to aggressive behavior or vice versa.
Multiple regressions: The general purpose of the multiple regressions is to establish a relationship between several predictor variables and a dependent variable. Notation ally if Y is a dependent variable and Xs are several predictors then f is a function or line of least square which is estimated in multiple regressions.
It is widely used in social and natural sciences. Educators might be interested in predictors for success in high school or psychologist might be interested in personality best predicting social adjustments.
For example Price of the house sold can be dependent variable and size of house, number of bedrooms, locality, average income in respective neighborhoods, and appeal of the house can be predictors. The other example can be Salary being dependent and amount of responsibility, number of people to supervise etc. are independent.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
RESEARCH METHODS F/ BEHAV.(LL)-W/MINTAP
- You want to compare the average number of tines on the antlers of male deer in two nearby metro parks. A sample of 30 deer from the first park shows an average of 5 tines with a population standard deviation of 3. A sample of 35 deer from the second park shows an average of 6 tines with a population standard deviation of 3.2. Find a 95 percent confidence interval for the difference in average number of tines for all male deer in the two metro parks (second park minus first park).Do the parks’ deer populations differ in average size of deer antlers?arrow_forwardSuppose that you want to increase the confidence level of a particular confidence interval from 80 percent to 95 percent without changing the width of the confidence interval. Can you do it?arrow_forwardA random sample of 1,117 U.S. college students finds that 729 go home at least once each term. Find a 98 percent confidence interval for the proportion of all U.S. college students who go home at least once each term.arrow_forward
- Suppose that you make two confidence intervals with the same data set — one with a 95 percent confidence level and the other with a 99.7 percent confidence level. Which interval is wider?Is a wide confidence interval a good thing?arrow_forwardIs it true that a 95 percent confidence interval means you’re 95 percent confident that the sample statistic is in the interval?arrow_forwardTines can range from 2 to upwards of 50 or more on a male deer. You want to estimate the average number of tines on the antlers of male deer in a nearby metro park. A sample of 30 deer has an average of 5 tines, with a population standard deviation of 3. Find a 95 percent confidence interval for the average number of tines for all male deer in this metro park.Find a 98 percent confidence interval for the average number of tines for all male deer in this metro park.arrow_forward
- Based on a sample of 100 participants, the average weight loss the first month under a new (competing) weight-loss plan is 11.4 pounds with a population standard deviation of 5.1 pounds. The average weight loss for the first month for 100 people on the old (standard) weight-loss plan is 12.8 pounds, with population standard deviation of 4.8 pounds. Find a 90 percent confidence interval for the difference in weight loss for the two plans( old minus new) Whats the margin of error for your calculated confidence interval?arrow_forwardA 95 percent confidence interval for the average miles per gallon for all cars of a certain type is 32.1, plus or minus 1.8. The interval is based on a sample of 40 randomly selected cars. What units represent the margin of error?Suppose that you want to decrease the margin of error, but you want to keep 95 percent confidence. What should you do?arrow_forward3. (i) Below is the R code for performing a X2 test on a 2×3 matrix of categorical variables called TestMatrix: chisq.test(Test Matrix) (a) Assuming we have a significant result for this procedure, provide the R code (including any required packages) for an appropriate post hoc test. (b) If we were to apply this technique to a 2 × 2 case, how would we adapt the code in order to perform the correct test? (ii) What procedure can we use if we want to test for association when we have ordinal variables? What code do we use in R to do this? What package does this command belong to? (iii) The following code contains the initial steps for a scenario where we are looking to investigate the relationship between age and whether someone owns a car by using frequencies. There are two issues with the code - please state these. Row3<-c(75,15) Row4<-c(50,-10) MortgageMatrix<-matrix(c(Row1, Row4), byrow=T, nrow=2, MortgageMatrix dimnames=list(c("Yes", "No"), c("40 or older","<40")))…arrow_forward
- Describe the situation in which Fisher’s exact test would be used?(ii) When do we use Yates’ continuity correction (with respect to contingencytables)?[2 Marks] 2. Investigate, checking the relevant assumptions, whether there is an associationbetween age group and home ownership based on the sample dataset for atown below:Home Owner: Yes NoUnder 40 39 12140 and over 181 59Calculate and evaluate the effect size.arrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forwardNeed help with the following statistic problems.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning





