
Concept explainers
Find the total resistance and the current flow in each branch for the circuit.
Answer to Problem 19P
The total resistance is
The current flows through the branch
The current flows through the branch
The current flows through the branch
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The supply voltage is
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
Formula used:
Formula to calculate the total resistance in a parallel circuit,
Here,
Formula to calculate the voltage across the resistor
Here,
Rearrange the equation for the current flow through the resistance
Formula to calculate the voltage across the resistor
Here,
Rearrange the equation for the current flow through the resistance
Formula to calculate the voltage across the resistor
Here,
Rearrange the equation for the current flow through the resistance
Formula to calculate the total current drawn by the circuit,
Calculation:
Refer to Figure problem 12.19 in the textbook, and redraw it as Figure 1, with the two light bulbs represents the resistors
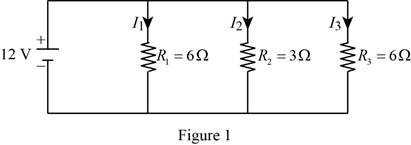
Substitute
Reduce the equation as,
The voltage drop across the each light bulb and the resistor is equal to the
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Hence,
The total resistance is
The current flows through the branch
The current flows through the branch
The current flows through the branch
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- What are the total earned work hours at completion for the column forms?arrow_forward6000 units have been installed to date with 9,000 units to install. Labor costs are $23,300.00 to date. What is the unit cost for labor to date?arrow_forwardThe base rate for labor is $15/hr. The labor burden is 35% and 3% for small tools for the labor. There are 1000 units to install. Records indicate that trade workers can install 10 units per hour, per trade worker. The owners need 15% overhead and profit to pay bills, pay interest on loan and provide some profit to the partners. What is the minimum bid assuming no risk avoidance factor?arrow_forward
- 5. (20 Points) Consider a channel width change in the same 7-foot wide rectangular in Problem 4. The horizontal channel narrows as depicted below. The flow rate is 90 cfs, and the energy loss (headloss) through the transition is 0.05 feet. The water depth at the entrance to the transition is initially 4'. 1 b₁ TOTAL ENERGY LINE V² 129 У1 I b₂ TOP VIEW 2 PROFILE VIEW h₁ = 0.05 EGL Y₂ = ? a) b) c) 2 Determine the width, b₂ that will cause a choke at location 2. Determine the water depth at the downstream end of the channel transition (y₂) section if b₂ = 5 feet. Calculate the change in water level after the transition. Plot the specific energy diagram showing all key points. Provide printout in homework. d) What will occur if b₂ = = 1.5 ft.?arrow_forward4. (20 Points) A transition section has been proposed to raise the bed level a height Dz in a 7-foot wide rectangular channel. The design flow rate in the channel is 90 cfs, and the energy loss (headloss) through the transition is 0.05 feet. The water depth at the entrance to the transition section is initially 4 feet. b₁ = b = b2 1 TOTAL ENERGY LINE V² 129 Ут TOP VIEW 2 hloss = 0.05 " EGL Y₂ = ? PROFILE VIEW a) Determine the minimum bed level rise, Dz, which will choke the flow. b) If the step height, Dz = 1 ft, determine the water depth (y2) at the downstream end of the channel transition section. Calculate the amount the water level drops or rises over the step. c) Plot the specific energy diagram showing all key points. Provide printout in Bework. d) What will occur if Dz = 3.0 ft.?. Crest Front Viewarrow_forward1. (20 Points) Determine the critical depth in the trapezoidal drainage ditch shown below. The slope of the ditch is 0.0016, the side slopes are 1V:2.5H, the bottom width is b = 14', and the design discharge is 500 cfs. At this discharge the depth is y = 4.25'. Also, determine the flow regime and calculate the Froude number. Ye= ? Z barrow_forward
 Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285852225Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning
Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285852225Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337402415Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning
Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337402415Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





