
Concept explainers
Using the accompanying diagram, do the following:
a. Draw a tree diagram for the scissors.
b. Prepare an MRP plan for scissors. Lead times are one day for each component and final scissor assembly, but two days for the plastic grips. Six hundred pairs of scissors are needed on day 6. Note: There are 200 straight blades and 350 bent blades on hand, and 40 top blade assemblies on hand.
Use lot-for-lot ordering for all items.
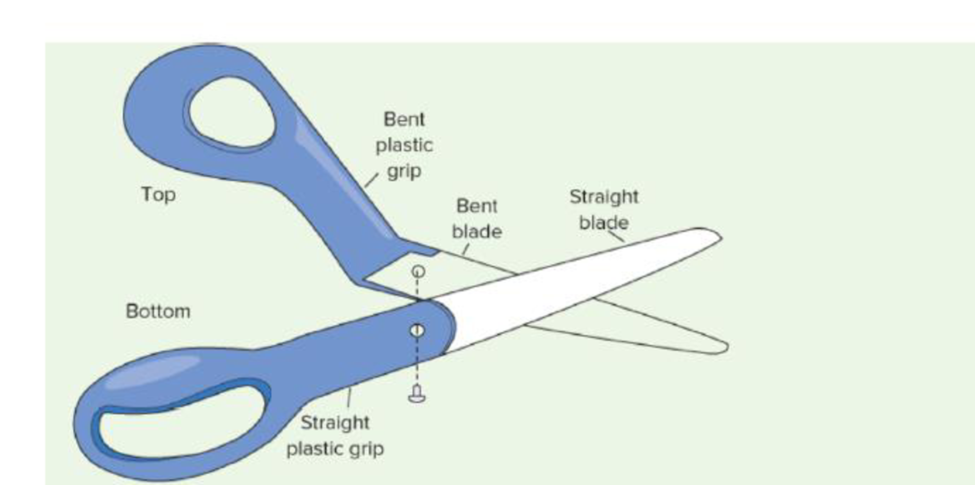
a)
To prepare: Tree diagram for the scissors.
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Lead-time is one day for all the components except plastic grips, which has the lead-time of 2 days. 600 pairs of scissors are needed on day 6. There are 350 bent blades, 200 straight blades, and 40 top blade assemblies on hand. Lot size is lot-for-lot ordering for all items.
In addition to that, following diagram is given:
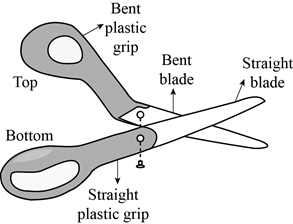
Prepare tree diagram for the scissors using given diagram:
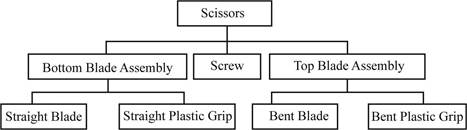
b)
To prepare: A Material requirement planning for scissors.
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Lead-time is one day for all the components except plastic grips, which has the lead-time of 2 days. 600 pairs of scissors are needed on day 6. There are 350 bent blades, 200 straight blades, and 40 top blade assemblies on hand. Lot size is lot-for-lot ordering for all items.
In addition to that, following diagram is given:

Develop material requirement planning for scissors:
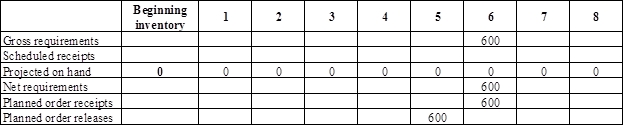
- It is given that 600 pairs of scissors are needed on day 6.
- Beginning inventory is 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 600 units in week 6 (600-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 600 units in the beginning of Week 6. Hence, they need to order for 600 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 5.
Develop material requirement planning for bottom blade assembly:
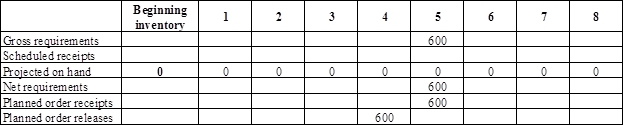
- Scissor is the parent for bottom blade assembly. Hence, the planned order release of the scissor would be the gross requirement of the bottom blade assembly. As number of units required is 1 for bottom blade assembly, the planned order release row of scissor should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of bottom blade assembly.
- Beginning inventory is 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 600 units in week 5(600-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 600 units in the beginning of Week 5. Hence, they need to order for 600 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
Develop material requirement planning for top blade assembly:
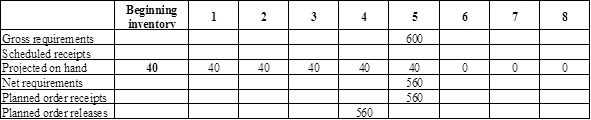
- Scissor is the parent for top blade assembly. Hence, the planned order release of the scissor would be the gross requirement of the top blade assembly. As number of units required is 1 for top blade assembly, the planned order release row of scissor should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of top blade assembly.
- Beginning inventory is 40 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 560 units in week 5 (600-40).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 560 units in the beginning of Week 5. Hence, they need to order for 560 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop material requirement planning for screw:

- Scissor is the parent for screw. Hence, the planned order release of the scissor would be the gross requirement of the screw. As number of units required is 1 for screw, the planned order release row of scissor should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of screw.
- Beginning inventory is 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 600 units in week 5 (600-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 600 units in the beginning of Week 5. Hence, they need to order for 600 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
Develop material requirement planning for straight blade:
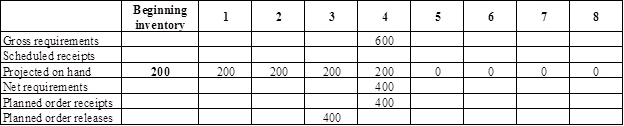
- Bottom blade assembly is the parent for straight blade. Hence, the planned order release of the bottom blade assembly would be the gross requirement of the straight blade. As number of units required is 1 for straight blade, the planned order release row of bottom blade assembly should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of straight blade.
- Beginning inventory is 200 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 400 units in week 4(600-200).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 400 units in the beginning of Week 4. Hence, they need to order for 400 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 5 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop material requirement planning for straight plastic grip:
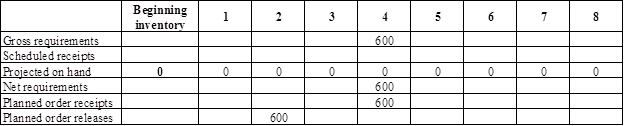
- Bottom blade assembly is the parent for straight blade. Hence, the planned order release of the bottom blade assembly would be the gross requirement of the straight blade. As number of units required is 1 for straight blade, the planned order release row of bottom blade assembly should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of straight blade.
- Beginning inventory is 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 600 units in week 4 (600-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. Company requires 600 units in the beginning of Week 4. Hence, they need to order for 600 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) before two weeks (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
Develop material requirement planning for bent blade:
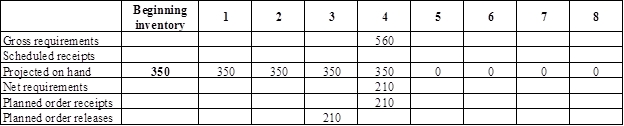
- Top blade assembly is the parent for bent blade. Hence, the planned order release of the top blade assembly would be the gross requirement of the bent blade. As number of units required is 1 for bent blade, the planned order release row of top blade assembly should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of bent blade.
- Beginning inventory is 350 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 210 units in week 4 (560-350).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 210 units in the beginning of Week 4. Hence, they need to order for 210 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 5 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop material requirement planning for bent plastic grip:
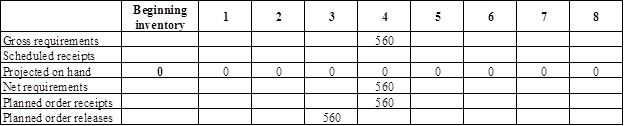
- Top blade assembly is the parent for bent plastic grip. Hence, the planned order release of the top blade assembly would be the gross requirement of the bent plastic grip. As number of units required is 1 for bent plastic grip, the planned order release row of top blade assembly should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of bent plastic grip.
- Beginning inventory is 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 560 units in week 4 (560-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 560 units in the beginning of Week 4. Hence, they need to order for 560 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT W/ CNCT+
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Principles Of Taxation For Business And Investment Planning 2020 Edition
FUNDAMENTALS OF CORPORATE FINANCE
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forwardSam's Pet Hotel operates 51 weeks per year, 6 days per week, and uses a continuous review inventory system. It purchases kitty litter for $11.00 per bag. The following information is available about these bags: > Demand 95 bags/week > Order cost $52.00/order > Annual holding cost = 25 percent of cost > Desired cycle-service level = 80 percent >Lead time 4 weeks (24 working days) > Standard deviation of weekly demand = 15 bags > Current on-hand inventory is 320 bags, with no open orders or backorders. a. Suppose that the weekly demand forecast of 95 bags is incorrect and actual demand averages only 75 bags per week. How much higher will total costs be, owing to the distorted EOQ caused by this forecast error? The costs will be $ higher owing to the error in EOQ. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardSam's Pet Hotel operates 50 weeks per year, 6 days per week, and uses a continuous review inventory system. It purchases kitty litter for $10.50 per bag. The following information is available about these bags: > Demand = 95 bags/week > Order cost = $55.00/order > Annual holding cost = 35 percent of cost > Desired cycle-service level = 80 percent > Lead time = 4 weeks (24 working days) > Standard deviation of weekly demand = 15 bags > Current on-hand inventory is 320 bags, with no open orders or backorders. a. Suppose that the weekly demand forecast of 95 bags is incorrect and actual demand averages only 75 bags per week. How much higher will total costs be, owing to the distorted EOQ caused by this forecast error? The costs will be $ 10.64 higher owing to the error in EOQ. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.) b. Suppose that actual demand is 75 bags but that ordering costs are cut to only $13.00 by using the internet to automate order placing. However, the buyer does…arrow_forward
- BUS-660 Topic 4: Intege... W Midterm Exam - BUS-66... webassign.net b Answered: The binding c... × W Topic 4 Assignment - BU... how to get more chegg... b My Questions | bartleby + macbook screenshot - G... C Consider the following m... As discussed in Section 8.3, the Markowitz model uses the variance of the portfolio as the measure of risk. However, variance includes deviations both below and above the mean return. Semivariance includes only deviations below the mean and is considered by many to be a better measure of risk. (a) Develop a model that minimizes semivariance for the Hauck Financial data given in the file HauckData with a required return of 10%. Assume that the five planning scenarios in the Hauck Financial Services model are equally likely to occur. Hint: Modify model (8.10)-(8.19). Define a variable d for each 5 - scenario and let d≥ Ŕ – R¸ with d¸ ≥ 0. Then make the objective function: Min 1 5 Σας Let Min s.t. 15 FS = proportion of portfolio invested in the foreign…arrow_forwardOn a daily basis, the van is dispatched from Maplewood Hospital to pickup blood and platelet donations made at its local donation centers. The distances in miles between all locations may be found in the table below. Click the icon to view mileage data for Vampire Van. a. The van travels from the Hospital (A) to (B) to (C) to (D) to (E) and then returns to the Hospital (A). What is the total number of miles that the van must travel using this route? Route ABCDEA requires a total distance of miles. (Enter your response rounded to one decimal place.) More Info Maplewood City Center Westbrook Hospital (A) Donation Site (B) Donation Site (C) Municipal Park Donation Site (D) Valley Hills Donation Site (E) Maplewood 3.1 5.3 3.2 4.4 Hospital (A) City Center 3.1 6.7 2.2 4.3 Donation Site (B) Westbrook 5.3 Donation Site (C) 19 6.7 | 6.2 2.5 Municipal Park 3.2 2.2 6.2 | 4.6 Donation Site (D) Valley Hills 4.4 4.3 2.5 4.6 Donation Site (E) - ☑arrow_forwardThe Harvey Motorcycle Company produces three models: the Tiger, a sure-footed dirt bike; the LX2000, a nimble cafe racer; and the Golden, a large interstate tourer. The month's master production schedule calls for the production of 32 Goldens, 31 LX2000s, and 38 Tigers per 10-hour shift. What average cycle time is required for the assembly line to achieve the production quota in 10 hours? 0.099 hours per motorcycle. (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places.) If mixed-model scheduling is used, how many of each model will be produced before the production cycle is repeated? The greatest common divisor of the production requirements is Therefore, the Harvey Motorcycle Company will produce Goldens, LX2000s, and Tigers. (Enter your responses as integers.)arrow_forward
- The Harvey Motorcycle Company produces three models: the Tiger, a sure-footed dirt bike; the LX2000, a nimble cafe racer; and the Golden, a large interstate tourer. The month's master production schedule calls for the production of 32 Goldens, 31 LX2000s, and 38 Tigers per 10-hour shift. What average cycle time is required for the assembly line to achieve the production quota in 10 hours? hours per motorcycle. (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places.)arrow_forwardThe binding constraints for this problem are the second and third constraints are binding. Min x1 + 2x2 s.t. x1 + x2 ≤ 300 2x1 + x2 ≥ 400 2x1 + 5x2 ≥750 X1, X220 (a) Keeping the second objective function coefficient fixed at 2, over what range can the first objective function coefficient vary before there is a change in the optimal solution point? The first objective coefficient can from a low of to a high of (b) Keeping the first objective function coefficient fixed at 1, over what range can the second objective function coefficient vary before there is a change in the optimal solution point? The second objective coefficient can from a low of to a high of (c) If the objective function becomes Min 1.5x₁ + 2x2, what will be the optimal values of x1 and x2? x1 = X2 = What is the value of the objective function at the minimum? (d) If the objective function becomes Min 7x₁ + 6x2, what constraints will be binding? (Select all that apply.) First Constraint Second Constraint Third Constraint…arrow_forward[-16.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES CAMMIMS16 4.E.008. 0/1 Submissions Used A linear programming computer package is needed. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER The Clark County Sheriff's Department schedules police officers for 8-hour shifts. The beginning times for the shifts are 8:00 a.m., noon, 4:00 p.m., 8:00 p.m., midnight, and 4:00 a.m. An officer beginning a shift at one of these times works for the next 8 hours. During normal weekday operations, the number of officers needed varies depending on the time of day. The department staffing guidelines require the following minimum number of officers on duty: Time of Day 8:00 A.M. Noon Noon - 4:00 P.M. Minimum Officers Time of Day on Duty 4 7 4:00 P.M. - 8:00 P.M. 11 8:00 P.M. Midnight 6 Midnight 4:00 A.M. 4:00 A.M. -8:00 A.M. 3 7 Determine the number of police officers that should be scheduled to begin the 8-hour shifts at each of the six times (8:00 a.m., noon, 4:00 p.m., 8:00 p.m., midnight, and 4:00 a.m.) to minimize the total number…arrow_forward
 Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning




