
(a)
Interpretation:
The appropriate alkene or alkyne from which the given compound can be produced is to be determined along with the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of
The initial addition of borane is a syn, anti-Markovnikov addition via a four-membered cyclic transition state. Boron adds to the less substituted (less hindered) carbon because it is less electronegative than hydrogen. This results in an anti-Markovnikov addition of a water molecule to the double bond.
Answer to Problem 12.53P
The appropriate alkene used to synthesize the given compound is
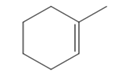
The necessary reagents and special reaction conditions for the synthesis are
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given compound is
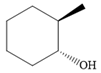
Alcohol with a specific stereochemistry is to be synthesized from an alkene. A reaction involving a carbocation needs to be avoided to prevent unwanted carbocation rearrangements. Also, the OH group must be added to a less substituted carbon, i.e., an anti-Markovnikov addition is needed. Therefore, the reaction needs to be carried out using hydroboration-oxidation.
The appropriate alkene for the synthesis of the given compound would be
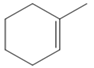
The given compound is synthesized by using the above alkene via hydroboration-oxidation reaction. So the necessary reagents for the reaction are
In the first step, an electrophilic addition of borane across the double bond of the alkene takes place either from above or below the plane of the alkene. So a mixture of enantiomers is obtained after oxidation of the adduct by basic
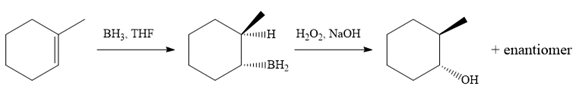
The alkene necessary for the synthesis of the given compound and the reagents and special conditions for the reaction are determined on the basis of the structure of the given compound.
(b)
Interpretation:
The appropriate alkene or alkyne from which the given compound can be produced is to be determined along with the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of alkenes and alkynes is carried out by the hydroboration-oxidation reaction. Alkenes are oxidized to alcohol while alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds. Terminal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding aldehyde, and internal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding ketone by a sterically hindered borane like disiamylborane
The initial addition of borane is a syn, anti-Markovnikov addition via a four-membered cyclic transition state. Boron adds to the less substituted (less hindered) carbon because it is less electronegative than hydrogen. This results in an anti-Markovnikov addition of a water molecule to the double bond.
Answer to Problem 12.53P
The appropriate alkyne used to synthesize the given compound is
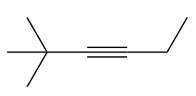
The necessary reagents and special reaction conditions to synthesize the given compound are
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
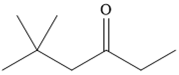
It is a ketone, so the starting compound must be an alkyne. A hydroboration-oxidation reaction can convert an alkyne into a ketone. Since only one molecule of borane is to be added, a bulky reagent like disiamylborane is more appropriate than borane. Also, the dialkylborane part must add to the less hindered carbon of the triple bond. Therefore, the triple bond must be between the carbon bonded to oxygen and the carbon close to the bulky tertiary carbon. Therefore, the alkyne that can be used is

A sterically hindered dialkylborane, like disiamylborane
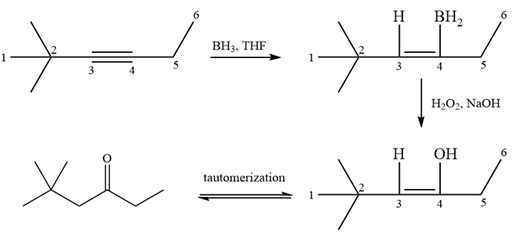
Thus the specific reagents and reaction conditions are
The alkene necessary for the synthesis of the given compound and the reagents and special conditions for the reaction are determined on the basis of the structure of the given compound.
(c)
Interpretation:
The appropriate alkene or alkyne from which the given compound can be produced is to be determined along with the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of alkenes and alkynes is carried out by the hydroboration-oxidation reaction. Alkenes are oxidized to alcohol while alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds. Terminal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding aldehyde, and internal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding ketone by a sterically hindered borane like disiamylborane
The initial addition of borane is a syn, anti-Markovnikov addition via a four-membered cyclic transition state. Boron adds to the less substituted (less hindered) carbon because it is less electronegative than hydrogen. This results in an anti-Markovnikov addition of a water molecule to the double bond.
Answer to Problem 12.53P
The appropriate alkyne used to synthesize the given compound is
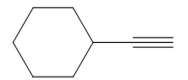
The necessary reagents and special reaction conditions to synthesize the given compound are
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
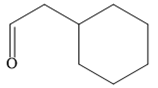
It is an aldehyde, so it can be prepared from a terminal alkyne by hydroboration-oxidation. In the hydroboration reaction, boron is added to the terminal carbon. So the appropriate alkyne for the synthesis of the given compound is
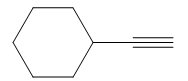
The alkyne is treated with the bulky disiamylborane to prevent the addition of a second molecule and formation of a mixture of products. Subsequent treatment of the adduct by
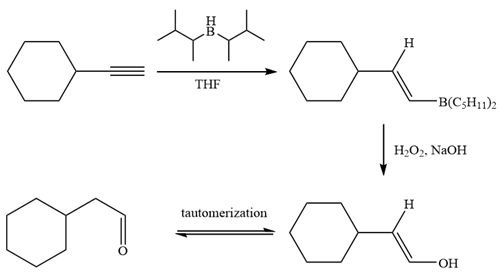
Thus, the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions for the synthesis are
The alkene necessary for the synthesis of the given compound and the reagents and special conditions for the reaction are determined on the basis of the structure of the given compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
The appropriate alkene or alkyne from which the given compound can be produced is to be determined along with the necessary reagents and special reaction conditions.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of alkenes and alkynes is carried out by the hydroboration-oxidation reaction. Alkenes are oxidized to alcohol while alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds. Terminal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding aldehyde, and internal alkynes are oxidized to the corresponding ketone by a sterically hindered borane like disiamylborane
The initial addition of borane is a syn, anti-Markovnikov addition via a four-membered cyclic transition state. Boron adds to the less substituted (less hindered) carbon because it is less electronegative than hydrogen. This results in an anti-Markovnikov addition of a water molecule to the double bond.
Answer to Problem 12.53P
The appropriate alkene used to synthesize the given compound is
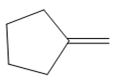
The necessary reagents and special reaction conditions for the synthesis are
Explanation of Solution
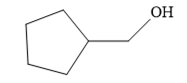
Since the product is an alcohol, an alkene with a methylene substituent on a cyclopentane ring would be appropriate as the starting compound.

Treating this alkene with borane in THF will add
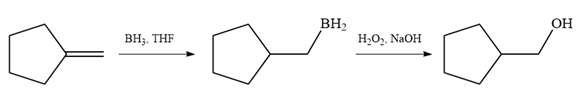
Thus, the necessary reagents for the reaction are
The alkene necessary for the synthesis of the given compound and the reagents and special conditions for the reaction are determined on the basis of the structure of the given compound.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- One method for the analysis of Fe3+, which is used with a variety of sample matrices, is to form the highly colored Fe3+–thioglycolic acid complex. The complex absorbs strongly at 535 nm. Standardizing the method is accomplished using external standards. A 10.00-ppm Fe3+ working standard is prepared by transferring a 10-mL aliquot of a 100.0 ppm stock solution of Fe3+ to a 100-mL volumetric flask and diluting to volume. Calibration standards of 1.00, 2.00, 3.00, 4.00, and 5.00 ppm are prepared by transferring appropriate amounts of the 10.0 ppm working solution into separate 50-mL volumetric flasks, each of which contains 5 mL of thioglycolic acid, 2 mL of 20% w/v ammonium citrate, and 5 mL of 0.22 M NH3. After diluting to volume and mixing, the absorbances of the external standards are measured against an appropriate blank. Samples are prepared for analysis by taking a portion known to contain approximately 0.1 g of Fe3+, dissolving it in a minimum amount of HNO3, and diluting to…arrow_forwardAbsorbance and transmittance are related by: A = -log(T) A solution has a transmittance of 35% in a 1-cm-pathlength cell at a certain wavelength. Calculate the transmittance if you dilute 25.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL? (A = εbc) What is the transmittance of the original solution if the pathlength is increased to 10 cm?arrow_forwardUnder what conditions will Beer’s Law most likely NO LONGER be linear? When the absorbing species is very dilute. When the absorbing species participates in a concentration-dependent equilibrium. When the solution being studied contains a mixture of ions.arrow_forward
- Compared to incident (exciting) radiation, fluorescence emission will have a: Higher energy Higher frequency Longer wavelengtharrow_forwardLin and Brown described a quantitative method for methanol based on its effect on the visible spectrum of methylene blue. In the absence of methanol, methylene blue has two prominent absorption bands at 610 nm and 663 nm, which correspond to the monomer and the dimer, respectively. In the presence of methanol, the intensity of the dimer’s absorption band decreases, while that for the monomer increases. For concentrations of methanol between 0 and 30% v/v, the ratio of the two absorbance, A663/ A610, is a linear function of the amount of methanol. Use the following standardization data to determine the %v/v methanol in a sample if A610 is 0.75 and A663 is 1.07.arrow_forwardThe crystal field splitting energy, Δ, of a complex is determined to be 2.9 × 10-19 What wavelength of light would this complex absorb? What color of light is this? What color would the compound be in solution?arrow_forward
- A key component of a monochromator is the exit slit. As the exit slit is narrowed, the bandwidth of light (i.e., the range of wavelengths) exiting the slit gets smaller, leading to higher resolution. What is a possible disadvantage of narrowing the exit slit? (Hint: why might a narrower slit lower the sensitivity of the measurement?).arrow_forwardAn x-ray has a frequency of 3.33 × 1018 What is the wavelength of this light?arrow_forwardChoose the Lewis structure for the compound below: H2CCHOCH2CH(CH3)2 HH H :d H H H C. Η H H HH H H H H. H H H HH H H H H H- H H H C-H H H HHHHarrow_forward
- Each of the highlighted carbon atoms is connected to hydrogen atoms.arrow_forwardく Complete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... No reaction. Explanation Check O + G 1. Na O Me Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H + 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility 000 Ar Parrow_forwardDraw a tetramer of this alternating copolymer.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





