
(a)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism with the major product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an
Answer to Problem 12.42P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is
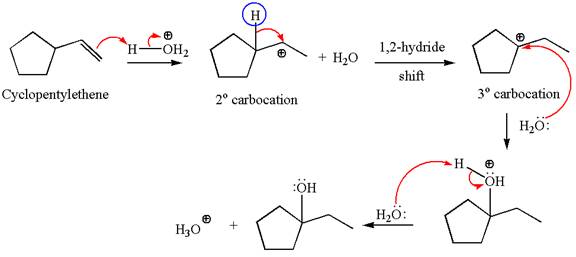
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
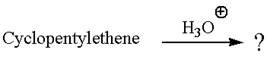
Cyclopentylethene, a terminal alkene, in presence of
The first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted double bonded carbon.
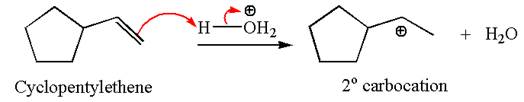
The secondary carbocation can be rearranged to a more stable tertiary carbocation by
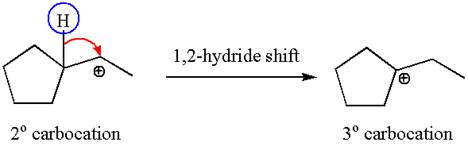
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the tertiary carbocation, forming a tertiary alcohol product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
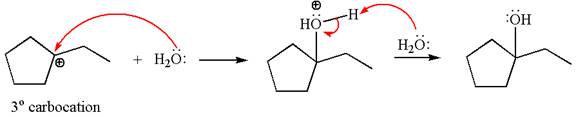
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurs through carbocation rearrangement.
(b)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism with major product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water across the
Answer to Problem 12.42P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
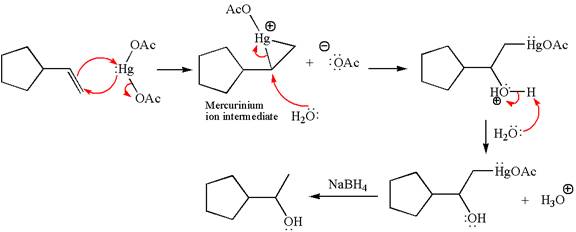
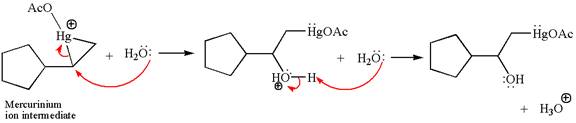
Cyclopentylethene, a terminal alkene, on reaction with mercury
In the first step, the electron rich
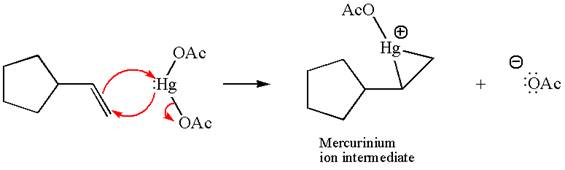
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and, according to Markovnikov rule, attacks the most substituted side to open the three-membered ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
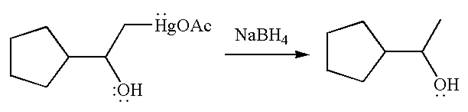
The product formed in the previous step is then subjected to reduction with sodium borohydride,
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through formation of mercurinium ion intermediate without rearrangement.
(c)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism with major product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
Answer to Problem 12.42P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
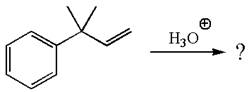
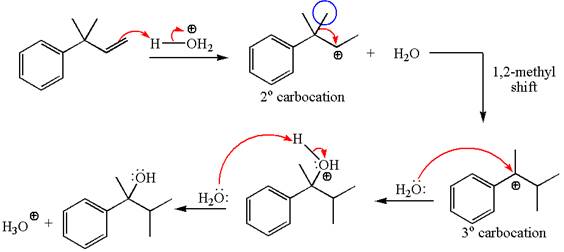
The given substrate, a terminal alkene, in the presence of
The first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted double bonded carbon.
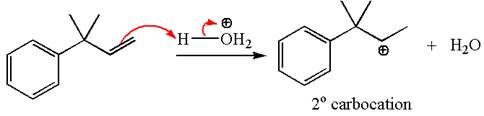
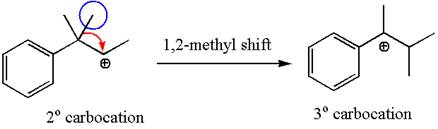
The secondary carbocation can be rearranged to a more stable tertiary as well as resonance stabilized carbocation by
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the tertiary carbocation, forming a tertiary alcohol product, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen.
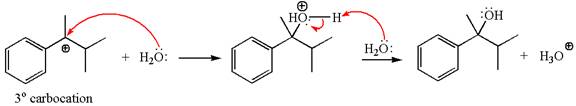
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through carbocation rearrangement.
(d)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism with major product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water across the
Answer to Problem 12.42P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
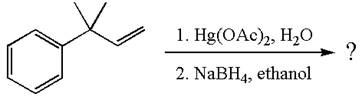
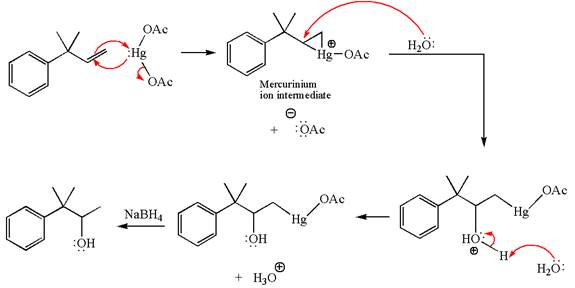
The given substrate, a terminal alkene, on reaction with mercury
In the first step, the electron rich
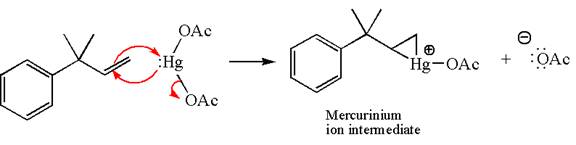
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and, according to Markovnikov rule, attacks the most substituted side to open the three-membered ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
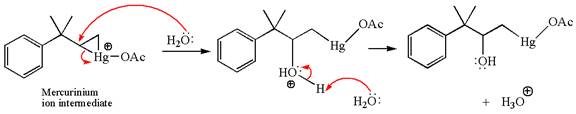
The product formed in the previous step is then subjected to reduction with sodium borohydride,
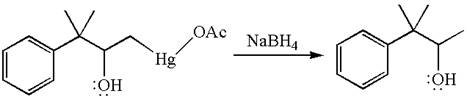
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through formation of mercurinium ion intermediate without rearrangement.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward
- 14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardanswer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
