
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and major organic product(s) of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the hydroboration reaction of an alkene, a molecule of water adds to the carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene in an anti-Markovnikov manner. The boron atom in borane is less electronegative than hydrogen and acts as the electron-poor atom. Therefore, the
Answer to Problem 12.52P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
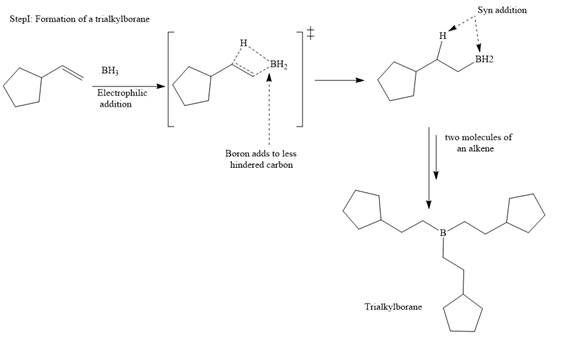
The major product for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
The structure of cyclopentylethene is
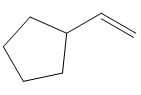
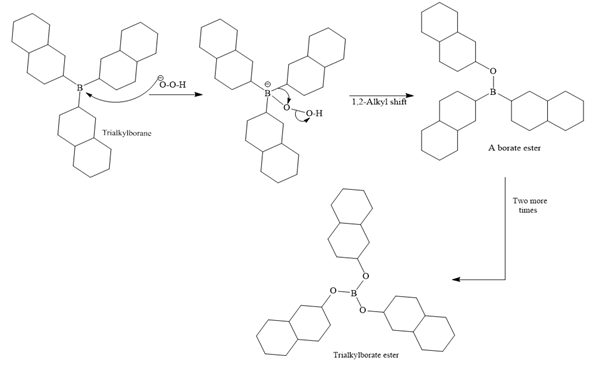
In the first step, borane adds across the carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene via a four-membered cyclic transition state. The addition is anti-Markovnikov as the boron atom adds to the fewer substituted (fewer sterically hindered) carbon, and the hydrogen adds to the most substituted carbon. The remaining two hydrogen atoms from borane are replaced in a similar way by two more alkene molecules to form a trialkylborane.
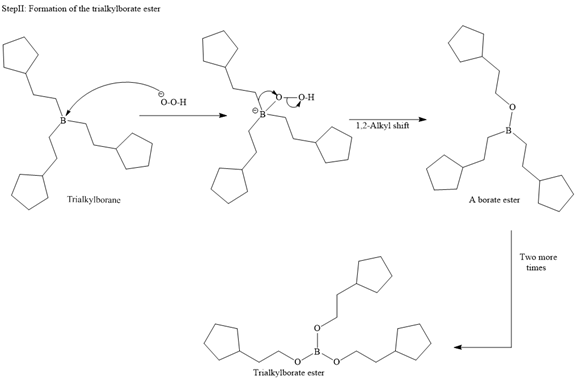
A trialkylborane is then oxidized by the hydroperoxide anion (
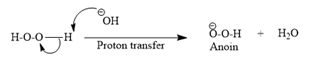
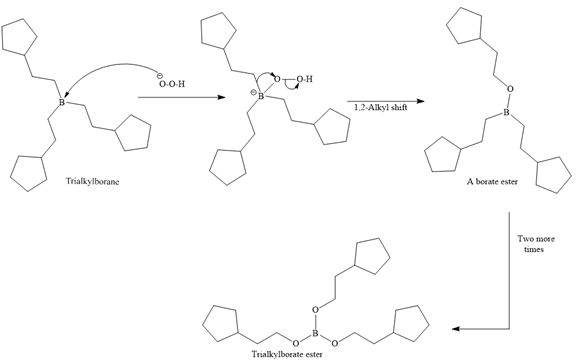
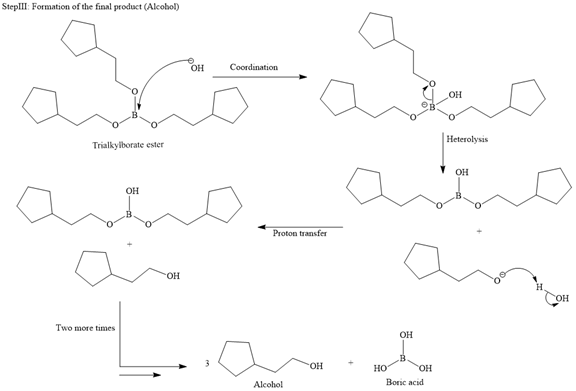
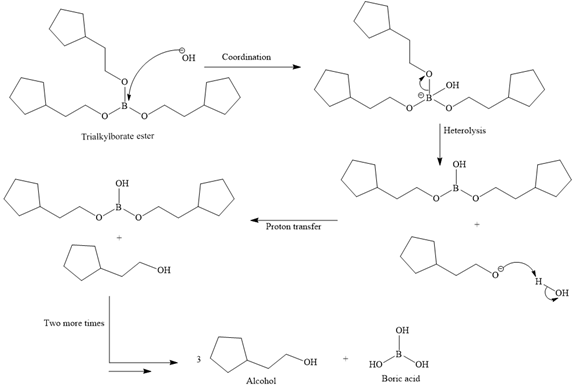
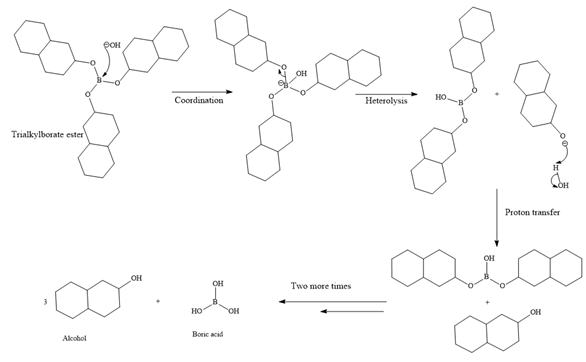
Then the trialkylborate ester undergoes base hydrolysis to three molecules of the alcohol product and boric acid.
The
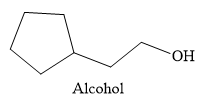
Thus, the major product of the given reaction is

The mechanism and the major organic product(s) for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of an anti-Markovnikov syn addition of borane across the double bond.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product(s) of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the hydroboration reaction of an alkene, a molecule of water adds to the carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene in an anti-Markovnikov manner. The boron atom in borane is less electronegative than hydrogen and acts as the electron-poor atom. Therefore, the
Answer to Problem 12.52P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
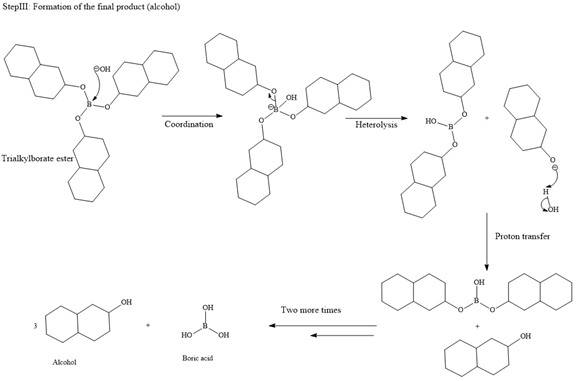
The major product of the given reaction is
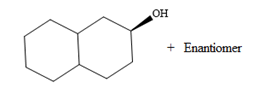
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
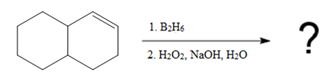
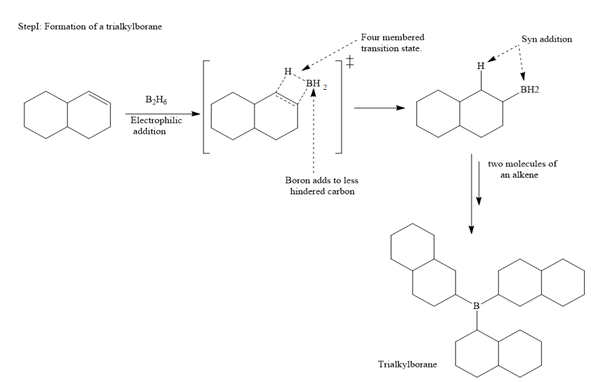
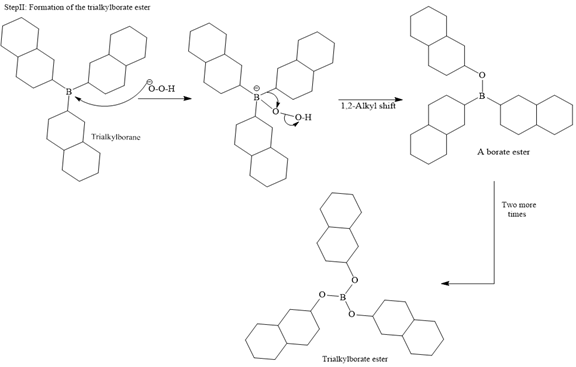
In the first step, borane adds across the carbon-carbon double bond of the alkene via a four-membered cyclic transition state. The addition is anti-Markovnikov as the boron atom adds to the fewer substituted (fewer sterically hindered) carbon, and the hydrogen adds to the most substituted carbon. The remaining two hydrogen atoms from borane are replaced in a similar way by two more alkene molecules to form a trialkylborane.
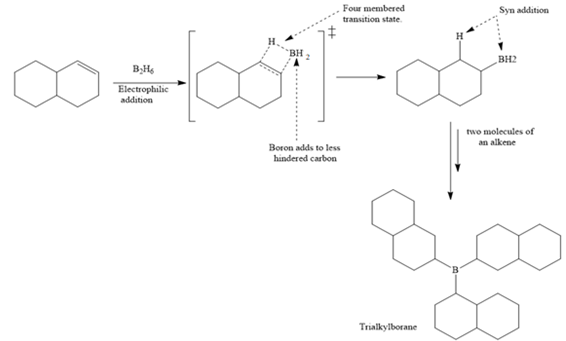
The trialkylborane is then oxidized by the hydroperoxide anion (
Then the trialkylborate ester undergoes base hydrolysis to three molecules of the alcohol product and boric acid.
The
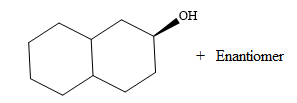
Borane can add across the double bond from either above the plane of the ring or from below the plane of the ring. This will lead to the formation of a racemic mixture as the carbon bonded to the OH group is chiral.
Thus, the major product for the given reaction is
The mechanism and the major organic product(s) for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of an anti-Markovnikov syn addition of borane across the double bond.
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product(s) of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Like alkenes,
The addition of one molecule of borane produces an alkene, and if it is a terminal alkene, another molecule of borane can add to it. This leads to a mixture of products.
This problem can be avoided by the use of a bulky dialkylborane like disiamylborane,
Answer to Problem 12.52P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
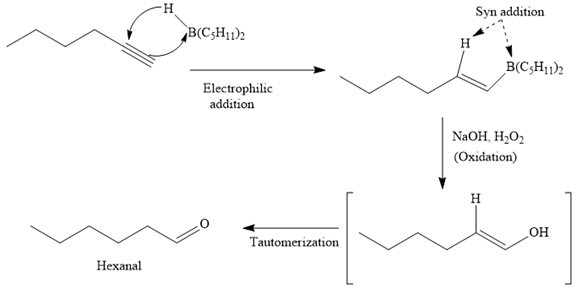
The major product for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
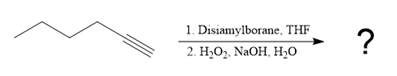
The structure of disiamylborane is
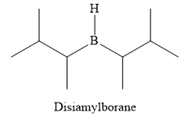
It is a sterically hindered alkyl borane, having only one
So the first step of the above reaction is a syn anti-Markovnikov electrophilic addition of boron and hydrogen to the carbon-carbon triple bond of the substrate.
Oxidation of this adduct by basic

Thus, the major product of the given reaction is
The mechanism and the major organic product(s) of the given reaction are drawn on the basis of the reaction conditions.
(d)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product(s) of the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Like alkenes, alkynes also undergo hydroboration reaction, but the product is different than alcohol. The oxidation of alkynes is carried out by using bulky dialkylborane like disiamylborane
Answer to Problem 12.52P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
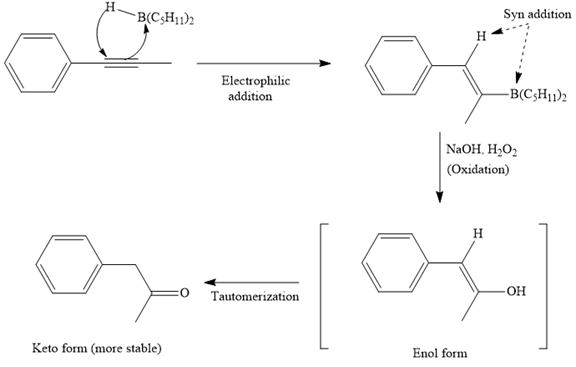
The major product for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
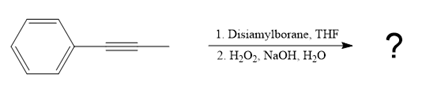
The structure of disiamylborane is
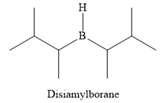
It is a sterically hindered alkyl borane having only one
The first step of the reaction is a syn anti-Markovnikov electrophilic addition of

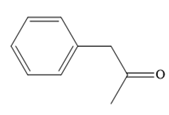
Thus, the major product for the given reaction is
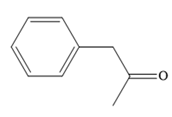
The mechanism and major organic product(s) for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of the reaction conditions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- Part I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward
- Show the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardDraw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forward
- what are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward1) a) Give the dominant Intermolecular Force (IMF) in a sample of each of the following compounds. Please show your work. (8) SF2, CH,OH, C₂H₂ b) Based on your answers given above, list the compounds in order of their Boiling Point from low to high. (8)arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
