
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
The given transformation can be carried out by oxymercuration-reduction. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
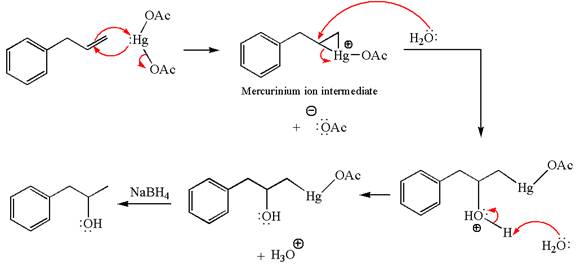
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
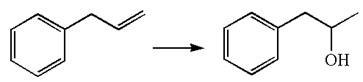
In the substrate, the alkene
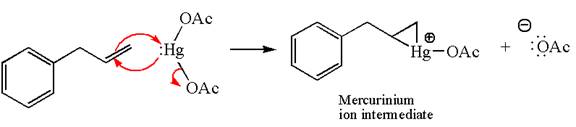
The alkene substrate, on reaction with mercury
In the first step, the electron rich
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
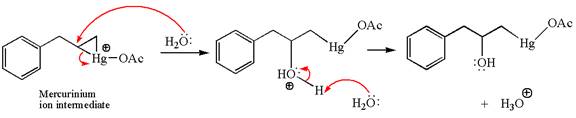
The product formed in the previous step is then subjected to reduction with sodium borohydride,
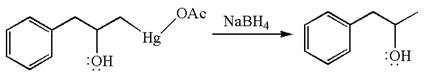
The preparation of the given compound is explained indicating the addition of water across the
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
The given transformation can be carried out by acid-catalyzed hydration. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
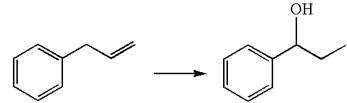
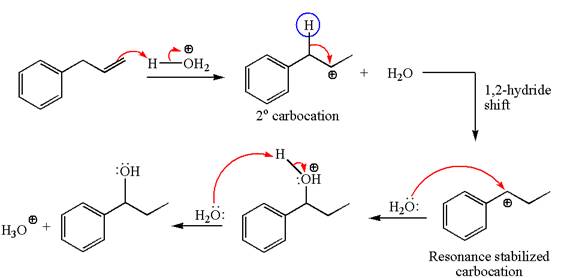
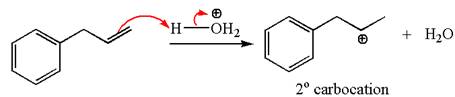
In the substrate, the alkene
The first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted double bonded carbon.
The secondary carbocation can be rearranged to more stable tertiary as well as resonance stabilized carbocation by
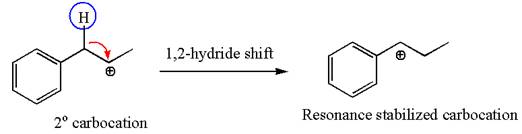
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
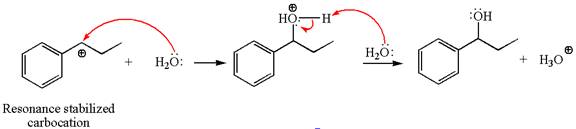
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through carbocation rearrangement.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
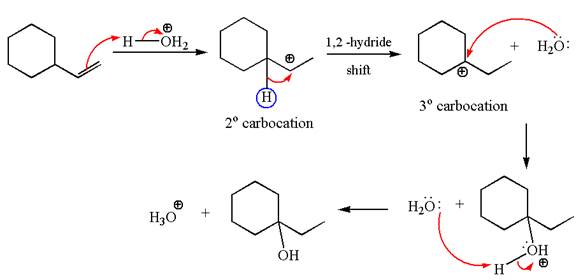
The given transformation can be carried out by acid catalyzed hydration. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
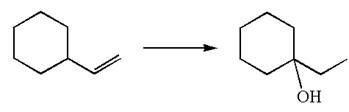
In the substrate, the alkene
The first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted double bonded carbon.
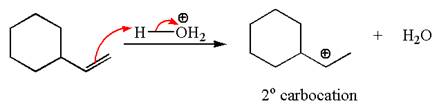
The secondary carbocation can be rearranged to more stable tertiary by
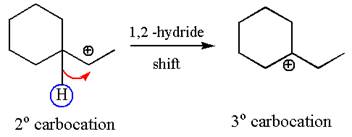
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
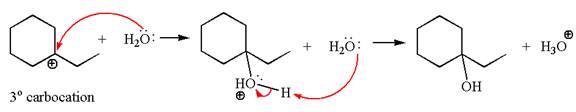
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through carbocation rearrangement.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water across the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
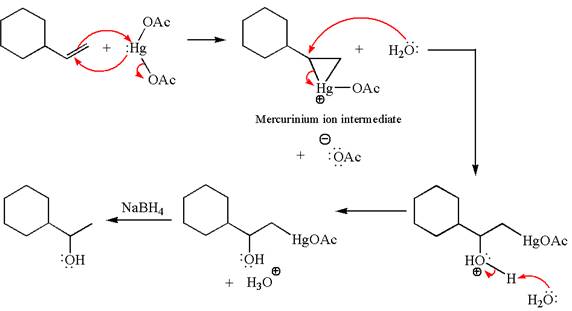
The given transformation can be carried out by oxymercuration-reduction. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
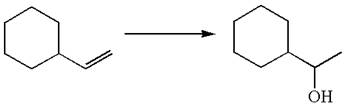
In the substrate, the alkene
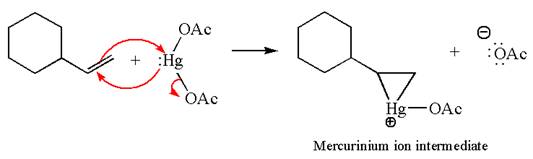
The alkene substrate, on reaction with mercury
In the first step, the electron rich
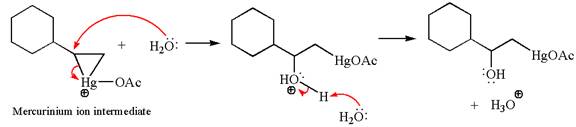
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
The product formed in the previous step is then subjected to reduction with sodium borohydride,
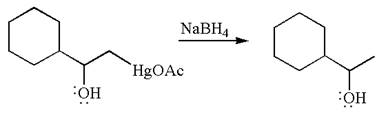
The preparation of the given compound is explained indicating the addition of water across the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- The statements in the tables below are about two different chemical equilibria. The symbols have their usual meaning, for example AG stands for the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction and K stands for the equilibrium constant. In each table, there may be one statement that is faise because it contradicts the other three statements. If you find a false statement, check the box next to t Otherwise, check the "no false statements" box under the table. statement false? AG"1 no false statements: statement false? AG-0 0 InK-0 0 K-1 0 AH-TAS no false statements 2arrow_forwardComplete the following esterification reactions by drawing the line formulas of the carboxylic acid and alcohol required to form the ester shown. catalyst catalyst catalyst apricot fragrancearrow_forwardShow the saponification products of the following ester: You don't need to draw in the Na+ cation. catalyst, A catalyst, A catalyst, Aarrow_forward
- What would happen if the carboxylic acid and alcohol groups were on the same molecule? In essence, the molecule reacts with itself. Draw the structure of the products formed in this manner using the reactants below. If two functional groups interact with one another on the same molecule, this is called an “intramolecular" (within one) rather than "intermolecular" (between two or more) attack. OH OH catalyst OH HO catalyst catalyst HO OHarrow_forwardQ3: Write in the starting alkyl bromide used to form the following products. Include any reactants, reagents, and solvents over the reaction arrow. If more than one step is required, denote separate steps by using 1), 2), 3), etc. H OH racemic OH OH 5 racemicarrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure of the SO3-O(CH3)2 complex shown in the bottom right of slide 2in lecture 3-3 (“Me” means a CH3 group) – include all valence electron pairs and formal charges.From this structure, should the complex be a stable molecule? Explain.arrow_forward
- please add appropriate arrows, and tell me clearly where to add arrows, or draw itarrow_forwardWhat I Have Learned Directions: Given the following reaction and the stress applied in each reaction, answer the question below. A. H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2 HCl(g) Stress applied: Decreasing the pressure 1. What is the Keq expression? 2. What will be the effect in the number of moles of HCl(g)? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? B. Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g) + heat 53 Fe(s) + 4 H₂O(g) Stress applied: Increasing the temperature 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the volume of water vapor collected? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction? C. 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) + heat Stress applied: Increasing the volume of the container 1. What is the Keq expression?. 2. What will be the effect in the amount of H₂O? 3. What will be the Equilibrium Shift or the reaction?arrow_forwardConsider the solubility products (Ksp values) for the following compounds:SrSO4 (Ksp = 7.6 x 10−7), BaSO4 (Ksp = 1.5 x 10−9), SrCO3 (Ksp = 7.0 x 10−10), BaCO3 (Ksp = 1.6 x 10−9)Which anion is the harder base, CO32− or SO42−? Justify your answer.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



