
Concept explainers
A uniform beam of mass m is inclined at an angle θ to the horizontal. Its upper end (point P) produces a 90° bend in a very rough rope tied to a wall, and its lower end rests on a rough floor (Fig. P12.35). Let μs represent the coefficient of static friction between beam and floor. Assume μs is less than the cotangent of θ. (a) Find an expression for the maximum mass M that can be suspended from the top before the beam slips. Determine (b) the magnitude of the reaction force at the floor and (c) the magnitude of the force exerted by the beam on the rope at P in terms of m, M, and μs.
Figure P12.35
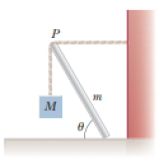
(a)
The expression for the maximum mass that can be suspended from the top surface before the beam starts slip.
Answer to Problem 12.51AP
The expression for the maximum mass that can be suspended from the top surface before the beam starts slip is
Explanation of Solution
The mass of the beam is
The following figure shows the force diagram of the beam.

Figure-(I)
Formula to calculate the frictional force acting on the base of the beam is,
Here,
Formula to calculate the net torque about the point
Here,
Rearrange the above equation to find
Formula to calculate the net vertical forces is,
Rearrange the above equation to find
Formula to calculate the net horizontal force is,
Substitute
Further simplify the above equation to find
Conclusion:
Therefore, the expression for the maximum mass that can be suspended from the top surface before the beam starts slip is
(b)
The magnitude of the reaction force at the floor.
Answer to Problem 12.51AP
The magnitude of the reaction force at the floor is
Explanation of Solution
The mass of the beam is
Formula to calculate the net reaction force acting in the floor is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the reaction force at the floor is
(c)
The magnitude of the force exerted by the beam in the rope at
Answer to Problem 12.51AP
The magnitude of the force exerted by the beam in the rope at
Explanation of Solution
The mass of the beam is
Since the coefficient of static friction of the floor is less than cotangent of the angle
Substitute
Formula to calculate the magnitude of the net force exerted by the beam in the rope at point
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the force exerted by the beam in the rope at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update, Hybrid Edition (with Enhanced WebAssign Multi-Term LOE Printed Access Card for Physics)
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



