
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
The given transformation can be carried out by oxymercuration-reduction. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
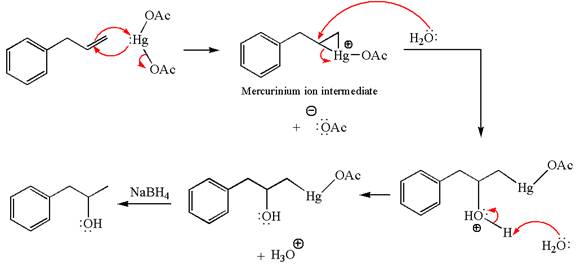
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
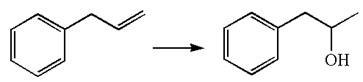
In the substrate, the alkene
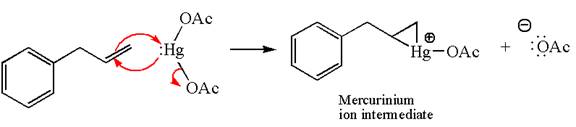
The alkene substrate, on reaction with mercury
In the first step, the electron rich
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
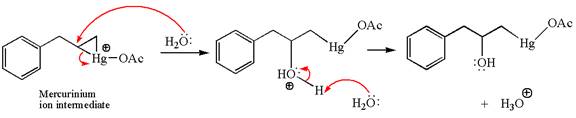
The product formed in the previous step is then subjected to reduction with sodium borohydride,
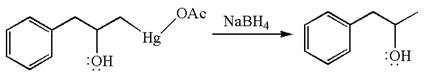
The preparation of the given compound is explained indicating the addition of water across the
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
The given transformation can be carried out by acid-catalyzed hydration. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
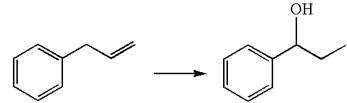
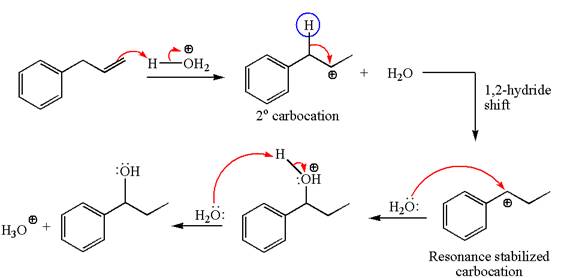
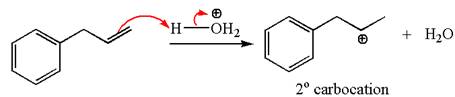
In the substrate, the alkene
The first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted double bonded carbon.
The secondary carbocation can be rearranged to more stable tertiary as well as resonance stabilized carbocation by
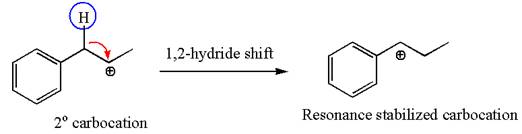
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
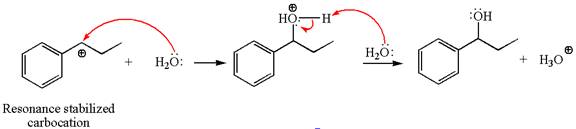
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through carbocation rearrangement.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
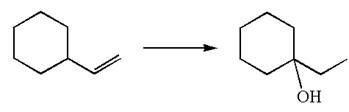
The given transformation can be carried out by acid catalyzed hydration. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
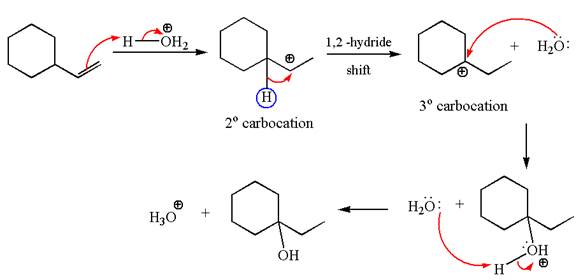
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
In the substrate, the alkene
The first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted double bonded carbon.
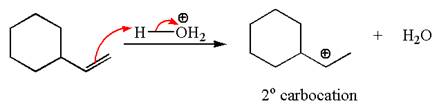
The secondary carbocation can be rearranged to more stable tertiary by
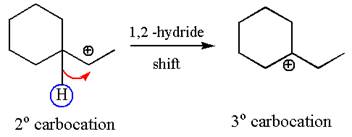
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
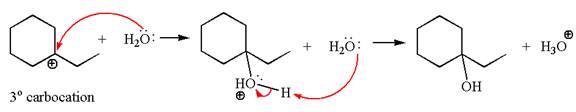
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through carbocation rearrangement.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water across the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
The given transformation can be carried out by oxymercuration-reduction. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
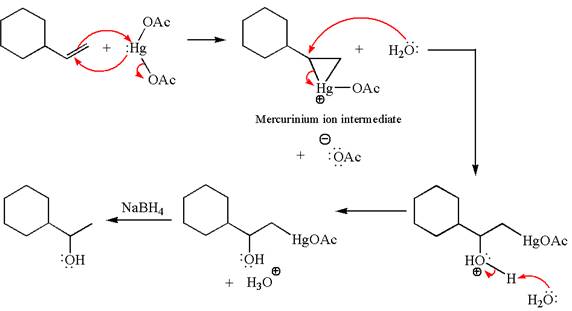
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
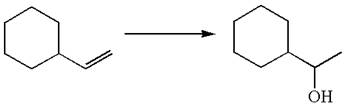
In the substrate, the alkene
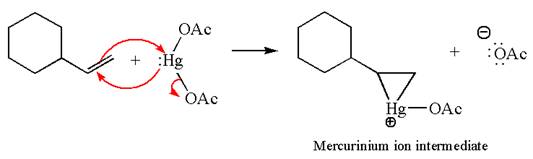
The alkene substrate, on reaction with mercury
In the first step, the electron rich
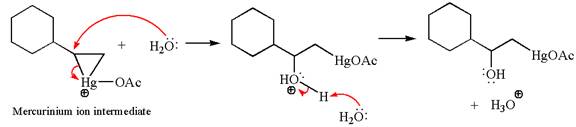
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
The product formed in the previous step is then subjected to reduction with sodium borohydride,
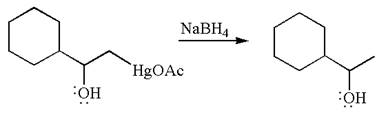
The preparation of the given compound is explained indicating the addition of water across the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Get Ready for Organic Chemistry
- Predict the product of this organic reaction: IZ + HO i P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ :arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: 0 O ----- A + KOH ? CH3-CH2-C-O-CH2-C-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. X ⑤ èarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forward
- What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forwardDE d. Draw an arrow pushing mechanism for the following IN O CI N fo 人 P Polle DELL prt sc home end ins F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: + H₂O H* ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic products of the reaction below and draw them on right side of the arrow. If there will be no significant reaction, check the box below the drawing area instead. C Cl CH, OH There will be no significant reaction. + pyridine G Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? H R+ H2O Δ OH 0= CH3-CH-O-CH3 + CH3-C-OH Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. dyarrow_forwardYou are trying to determine whether the following organic reaction can be done in a single synthesis step. If so, add any missing reagents or conditions in the drawing area below. If it isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step, check the box below the drawing area instead. Note for advanced students: if you have a choice of reagents to add, you should choose the least reactive and most economical reagents possible. Cl It isn't possible to do this reaction in a single synthesis step. + T OHarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole


