
The forces in each member of the truss.
Answer to Problem 12.1P
The forces in each member of the truss are shown below.
The force in member AE is,
The force in member BF is,
The force in member EF is,
The force in member AB is,
The force in member CE is,
The force in member BD is,
The force in member DE is,
The force in member BC is,
The force in member AF is,
The force in member BE is,
The force in member CD is,
Explanation of Solution
Check the determinacy of the truss as shown below.
Here, number of members are
Substitute
Hence, the given truss is statically indeterminate by
The following diagram shows the free body diagram of the truss.
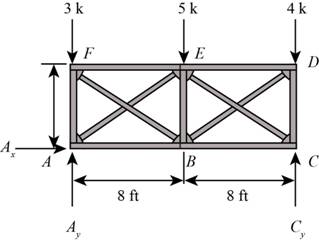
Figure-(1)
Write the equation for moment about A.
Here, vertical reaction at C is
Write the equation for sum of vertical forces.
Here, vertical reaction at A is
Substitute
Consider the force in diagonal members FB is in tension and AE is in compression.
Here, force in member AE and FB are
Use the method of section and cut the section as shown in figure below and calculate the forces in the members.
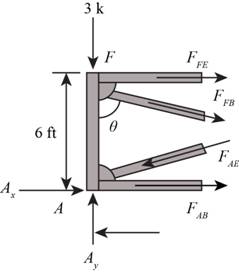
Figure-(2)
Calculate the angles as shown below.
Here, the angle between the members FA and FB is
Consider the joint F.
Write the Equation for sum of vertical forces.
Substitute
Write the equation for the sum of horizontal forces.
Here, force in member FE is
Substitute
Consider joint A.
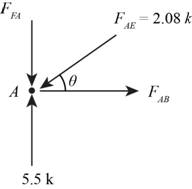
Figure-(3)
Calculate the angles as shown below.
Write the equation for sum of vertical forces.
Substitute
Here, force in member FA is
Write the Equation for sum of horizontal forces.
Substitute
Here, force in member AB is
Consider the force in diagonal members BD is in tension and EC is in compression.
Here, force in member BD and EC are
Use the method of section method and cut the section as shown in figure below and calculate the forces in the members.
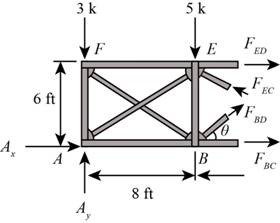
Figure-(4)
Calculate the angles as shown below.
Write the Equation for sum of vertical forces.
Substitute
Here, force in the member BD and CE are
Write the equation for moment about B.
Here, force in the member ED is
Substitute
Write the Equation for moment about E.
Here, force in the member BC is
Substitute
Write the Equation for sum of vertical forces.
Substitute
Here, force in the member BE is
Consider the joint C.
Angles will be same as calculated at joint B.
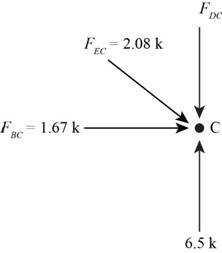
Figure-(5)
Write the Equation for sum of vertical forces.
Here, force in the member CD is
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the forces in each member of the truss are shown below.
The force in member AE is,
The force in member BF is,
The force in member EF is,
The force in member AB is,
The force in member CE is,
The force in member BD is,
The force in member DE is,
The force in member BC is,
The force in member AF is,
The force in member BE is,
The force in member CD is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
STRUCTURAL ANAL.W/MOD MASTERING ACCE
- quantity surveyingarrow_forwardNote: Please accurately answer it!. I'll give it a thumbs up or down based on the answer quality and precision. Question: What is the group name of Sample B in problem 3 from the image?. By also using the ASTM flow chart!. This unit is soil mechanics btwarrow_forwardPick the rural location of a project site in Victoria, and its catchment area-not bigger than 25 sqkm, and given the below information, determine the rainfall intensity for ARI = 5, 50, 100 year storm event. Show all the details of the procedure. Each student must propose different length of streams and elevations. Use fig below as a sample only. Pt. E-ht. 95.0 200m 600m PLD-M. 91.0 300m Pt. C-93.0 300m PL.B-ht. 92.0 PL.F-ht. 96.0 500m Pt. A-M. 91.00 To be deemed satisfactory the solution must include: Q.F1.1.Choice of catchment location Q.F1.2. A sketch displaying length of stream and elevation Q.F1.3. Catchment's IFD obtained from the Buro of Metheorology for specified ARI Q.F1.4.Calculation of the time of concentration-this must include a detailed determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.5.Use must be made of the Bransby-Williams method for the determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.6.The graphical display of the estimation of intensities for ARI 5,50, 100 must be shown.arrow_forward
- QUANTITY SURVEYINGarrow_forward3. (a) Use method of joints to determine forces in all members (all distances are in mm) (b) Find the resultant force at the pin support and state its angle of inclination FIGURE 2 2400 3.3 kN 6 3.6 ky 12 2 + 2400 0.7 kN + 2400 3.3kN + 2400arrow_forwardOK i need help. Please help me work thorought this with autocad. I am not sure where to begin but i need to draw this. Well if you read the question we did it in class and I got suepr confsued.arrow_forward
- A square column foundation has to carry a gross allowable load of 2005 kN (FS = 3). Given: D₤ = 1.7 m, y = 15.9 kN/m³, 0' = 34°, and c' = 0. Use Terzaghi's equation to determine the size of the foundation (B). Assume general shear failure. For o' = 34°, N₁ 36.5 and Ny = 38.04. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) B=2.16 marrow_forwardFor the design of a shallow foundation, given the following: Soil: ' = 20° c=57 kN/m² Unit weight, y=18 kN/m³ Modulus of elasticity, E, = 1400 kN/m² Poisson's ratio, μs = 0.35 Foundation: L=2m B=1m D₁ =1m Calculate the ultimate bearing capacity. Use the equation: 1 qu= c'Ne Fes Fed Fec +qNqFqs FqdFqc + - BNF √s F√d F 2 For d'=20°, N = 14.83, N = 6.4, and N., = 5.39. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) qu kN/m²arrow_forward1.0 m (Eccentricity in one direction only) = 0.15 m Qall = 0 1.5 m x 1.5 m Centerline An eccentrically loaded foundation is shown in the figure above. Use FS of 4 and determine the maximum allowable load that the foundation can carry if y = 16 kN/m³ and ' = 35°. Use Meyerhof's effective area method. For o' = 35°, N₁ = 33.30 and Ny = 48.03. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) Qall kNarrow_forward
- Methyl alcohol at 25°C (ρ = 789 kg/m³, μ = 5.6 × 10-4 kg/m∙s) flows through the system below at a rate of 0.015 m³/s. Fluid enters the suction line from reservoir 1 (left) through a sharp-edged inlet. The suction line is 10 cm commercial steel pipe, 15 m long. Flow passes through a pump with efficiency of 76%. Flow is discharged from the pump into a 5 cm line, through a fully open globe valve and a standard smooth threaded 90° elbow before reaching a long, straight discharge line. The discharge line is 5 cm commercial steel pipe, 200 m long. Flow then passes a second standard smooth threaded 90° elbow before discharging through a sharp-edged exit to reservoir 2 (right). Pipe lengths between the pump and valve, and connecting the second elbow to the exit are negligibly short compared to the suction and discharge lines. Volumes of reservoirs 1 and 2 are large compared to volumes extracted or supplied by the suction and discharge lines. Calculate the power that must be supplied to the…arrow_forwardcan you help me figure out the calculations so that i can input into autocad? Not apart of a graded assinment. Just a problem in class that i missed.arrow_forwardUse method of joints to determine forces in all members (all distances are in mm) Find the resultant force at the pin support and state its angle of inclinationarrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





