
Concept explainers
For each number line in Figure 1.44 (a)-(d), draw three copies of the line. Use your number lines to show three different ways to label the tick marks in the original line. In each case, your labeling should fit with the structure of the base-ten system and the fact that the tick marks at the ends of the number lines are longer than the other tick marks.
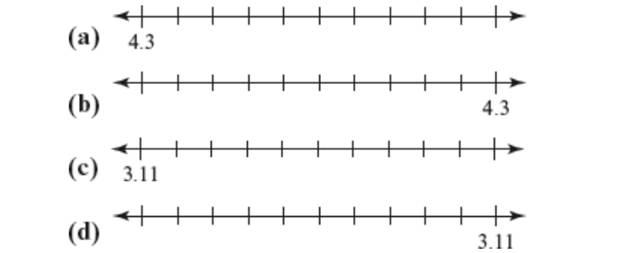
Figure 1.44 How to label the tick marks.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Pearson eText for Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activities -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Elementary Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary & Intermediate Algebra
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- 4. A car travels in a straight line for one hour. Its velocity, v, in miles per hour at six minute intervals is shown in the table. For each problem, approximate the distance the car traveled (in miles) using the given method, on the provided interval, and with the given number of rectangles or trapezoids, n. Time (min) 0 6 12 18|24|30|36|42|48|54|60 Speed (mph) 0 10 20 40 60 50 40 30 40 40 65 a.) Left Rectangles, [0, 30] n=5 b.) Right Rectangles, [24, 42] n=3 c.) Midpoint Rectangles, [24, 60] n=3 d.) Trapezoids, [0, 24] n=4arrow_forwardGiven the functions A and B, can you prove that if B ◦ A is bijective, then A is injective and B is surjectivearrow_forward- + ++ Table 2: Crack Experiment for Exercise 2 A B C D Treatment Combination (1) Replicate I II 7.037 6.376 14.707 15.219 |++++ 1 བྱ॰༤༠སྦྱོ སྦྱོཋཏྟཱུ a b ab 11.635 12.089 17.273 17.815 с ас 10.403 10.151 4.368 4.098 bc abc 9.360 9.253 13.440 12.923 d 8.561 8.951 ad 16.867 17.052 bd 13.876 13.658 abd 19.824 19.639 cd 11.846 12.337 acd 6.125 5.904 bcd 11.190 10.935 abcd 15.653 15.053 Question 3 Continuation of Exercise 2. One of the variables in the experiment described in Exercise 2, heat treatment method (C), is a categorical variable. Assume that the remaining factors are continuous. (a) Write two regression models for predicting crack length, one for each level of the heat treatment method variable. What differences, if any, do you notice in these two equations? (b) Generate appropriate response surface contour plots for the two regression models in part (a). (c) What set of conditions would you recommend for the factors A, B, and D if you use heat treatment method C = +? (d) Repeat…arrow_forward
- Terry has a square plot of land measuring 500 meters by 500 meters. She divided the land into 25 100-m by 100-m plots and created three raster maps showing the type of mineral, fruit tree, and energy available on each plot. Use the maps below to shade the blank maps according to each problem.arrow_forwardThe bracket BCD is hinged at C and attached to a control cable at B. Let F₁ = 275 N and F2 = 275 N. F1 B a=0.18 m C A 0.4 m -0.4 m- 0.24 m Determine the reaction at C. The reaction at C N Z F2 Darrow_forwardQuestion 2 A nickel-titanium alloy is used to make components for jet turbine aircraft engines. Cracking is a potentially serious problem in the final part because it can lead to nonrecoverable failure. A test is run at the parts producer to determine the effect of four factors on cracks. The four factors are: pouring temperature (A), titanium content (B), heat treatment method (C), amount of grain refiner used (D). Two replicates of a 24 design are run, and the length of crack (in mm x10-2) induced in a sample coupon subjected to a standard test is measured. The data are shown in Table 2. 1 (a) Estimate the factor effects. Which factor effects appear to be large? (b) Conduct an analysis of variance. Do any of the factors affect cracking? Use a = 0.05. (c) Write down a regression model that can be used to predict crack length as a function of the significant main effects and interactions you have identified in part (b). (d) Analyze the residuals from this experiment. (e) Is there an…arrow_forward
- Show the stepsarrow_forwardThe correct answer is C,i know that we need to use stokes theorem and parametrize the equations then write the equation F with respect to the curve but i cant seem to find a way to do it, the integral should be from 0 to 2pi but i might be wrongcould you show me the steps to get to 18piarrow_forwardA 10-ft boom is acted upon by the 810-lb force as shown in the figure. D 6 ft 6 ft E B 7 ft C 6 ft 4 ft W Determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at the ball-and-socket joint at A. The tension in cable BD is lb. The tension in cable BE is lb. The reaction at A is ( lb) i + Ib) j. (Include a minus sign if necessary.)arrow_forward
- the correct answer is A could you show me whyarrow_forwardWrite the negation for each of the following statements A. Rory plays basketball and terry plays basketball. B. Rory plays basketball or Jessie plays lacrosse. C. If Tony went to Macdonald’s, then Tony likes hamburgers.arrow_forwardGalena Park ISD Area and Volume → C Delta Math Student Applicat x Delta Math Student Applicat xb Galena Park ISD Area and V x deltamath.com/app/student/3919669/26697249/697de3b5894b134a6f23adadf8d12b31 DeltaMath Question Watch Video Show Examples ← Back to Home Area and Volume Due: February 12 at 4:00 PM Grade: 0% Drag the yellow point until an accurate "height" of the triangle is drawn. Afterwards, fill out the empty boxes below to determine the area of the triangle. Area of a Triangle (Interactive) Area Puzzles (Rectangles/Squares) Volume of Prisms Calculator Estrella Tejada\ Zavaleta Log Out h=4.65 5 6.5 7 C 4 00 10 1 59 USarrow_forward
 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning





