
Concept explainers
To label: The components of skeletal muscle fibres in Fig 12.1 (a).
Introduction: A complete skeletal muscle is regarded as one of the organs of the muscular system. Muscles are the largest cylindrical structure that composes of the fascicle, muscle fiber, myofibrils, and filaments.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
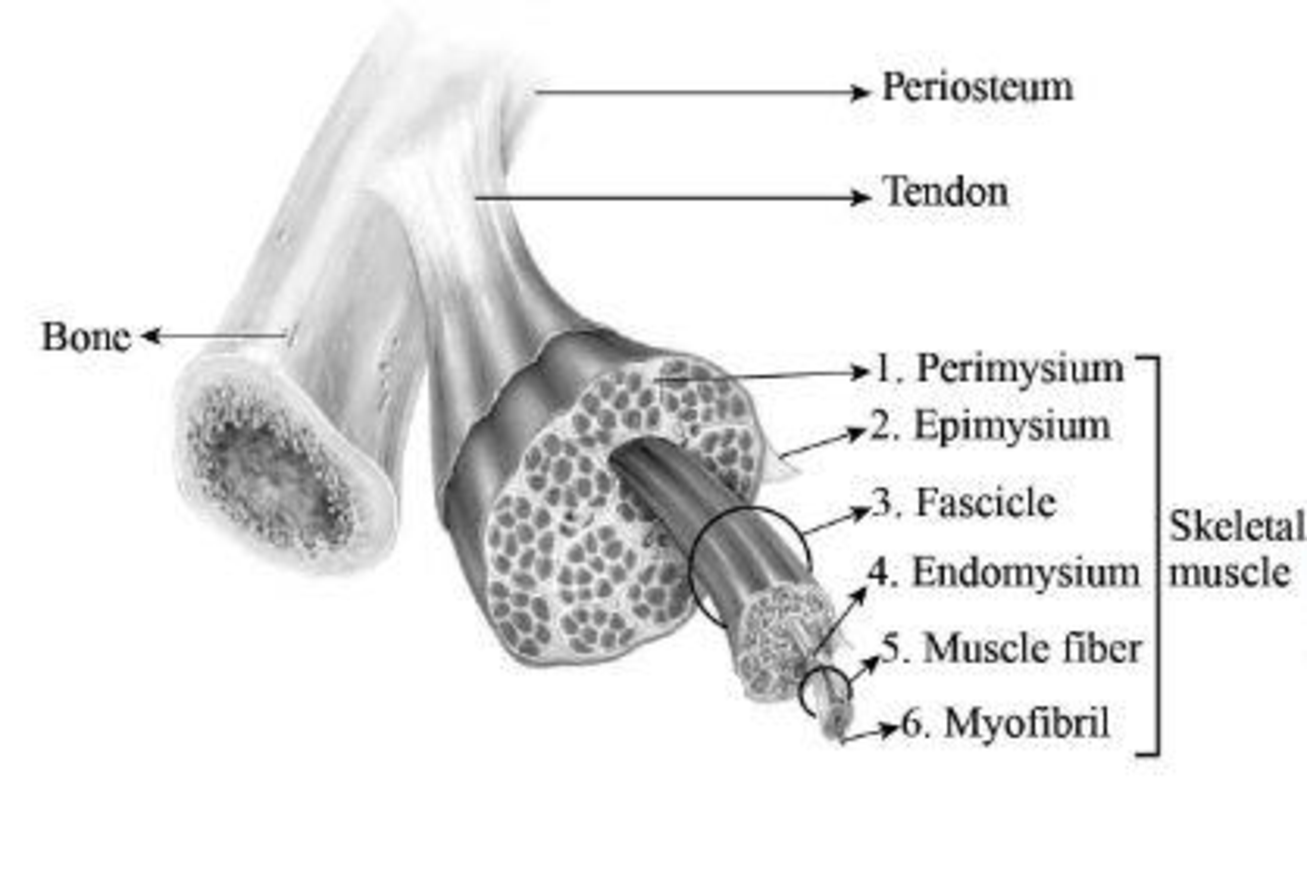
Fig 1: Components of skeletal muscle fibre
Explanation of Solution
The fascicles are bundles of skeletal muscles that are enveloped by connective tissues, which is termed as perimysium. The epimysium is a type of connective tissue that envelops every muscle. The areolar connective tissue that is present inside the muscle is termed as endomysium. This structure composes of nerves as well as capillaries and overlies the sarcolemma. Muscle fibers are smaller in size and they are present inside the fascicle. Myofibrils are rod-like structures and form the basic unit of muscle. They are made of thick and thin filaments.
To label: The components of the fascicle in Fig 12.1 (b).
Introduction: Predominant role played by muscles in the human body is contraction. Muscles that are connected with bones, organs, and blood vessels play a significant role in movements. Muscles are also significant for stability of joints, heat production, and posture.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
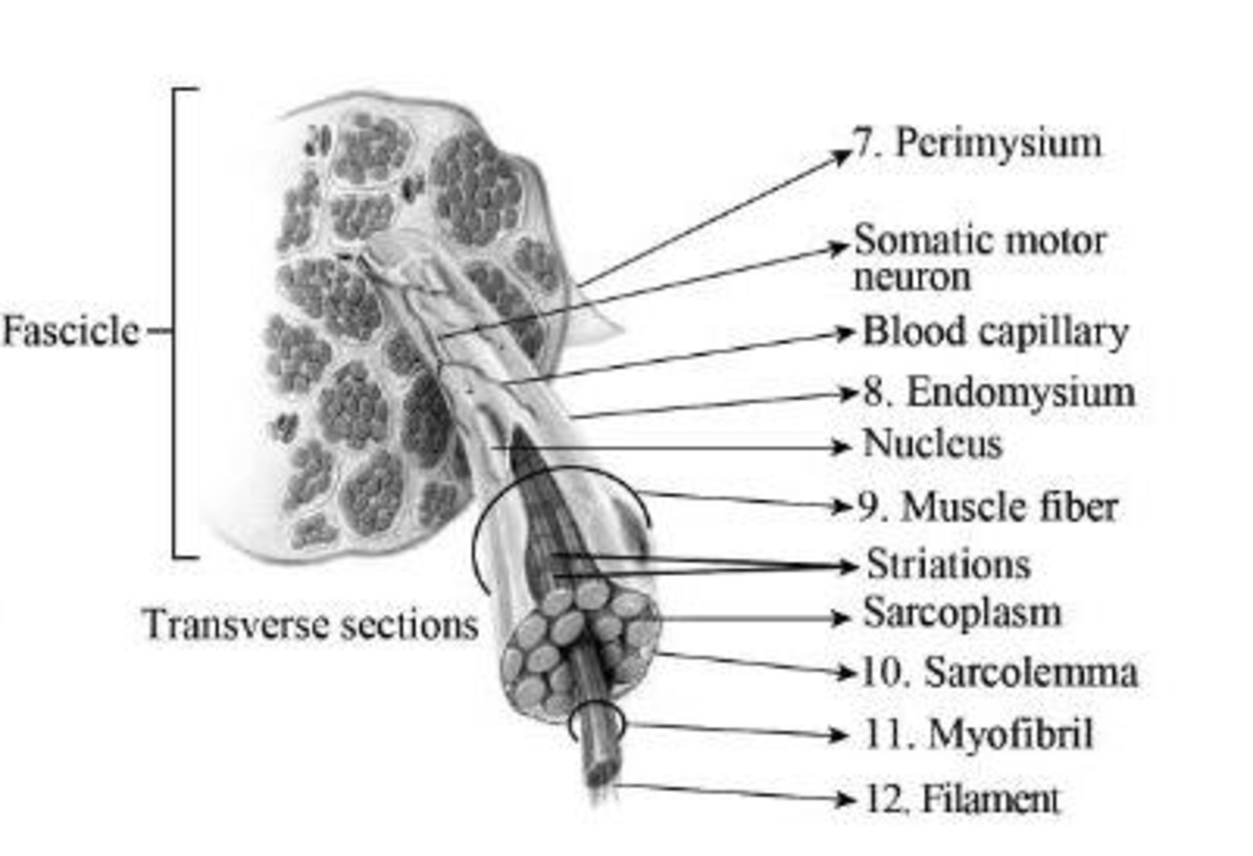
Fig 2: Components of the fascicle
Explanation of Solution
A muscle fascicle is formed of a bunch of skeletal muscle fibers. These fibers are enveloped by connective tissues known as perimysium. The areolar connective tissue that is present inside the muscle is termed as endomysium. Muscle fibers are smaller structures that are present inside the fascicle. The sarcolemma is a fine, tube-like structure that surrounds the fibres in skeletal muscles. Myofibrils are rod-like structures and form the basic unit of muscle. They are made of thick and thin filaments.
To label: The cross-section of a fascicle in a muscle in Fig 12.2 (a).
Introduction: The force that can be generated by a muscle fiber is determined by the muscle fascicle. Tendons are structures that connect the muscle with the bones. This junction is highly prone to injuries.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
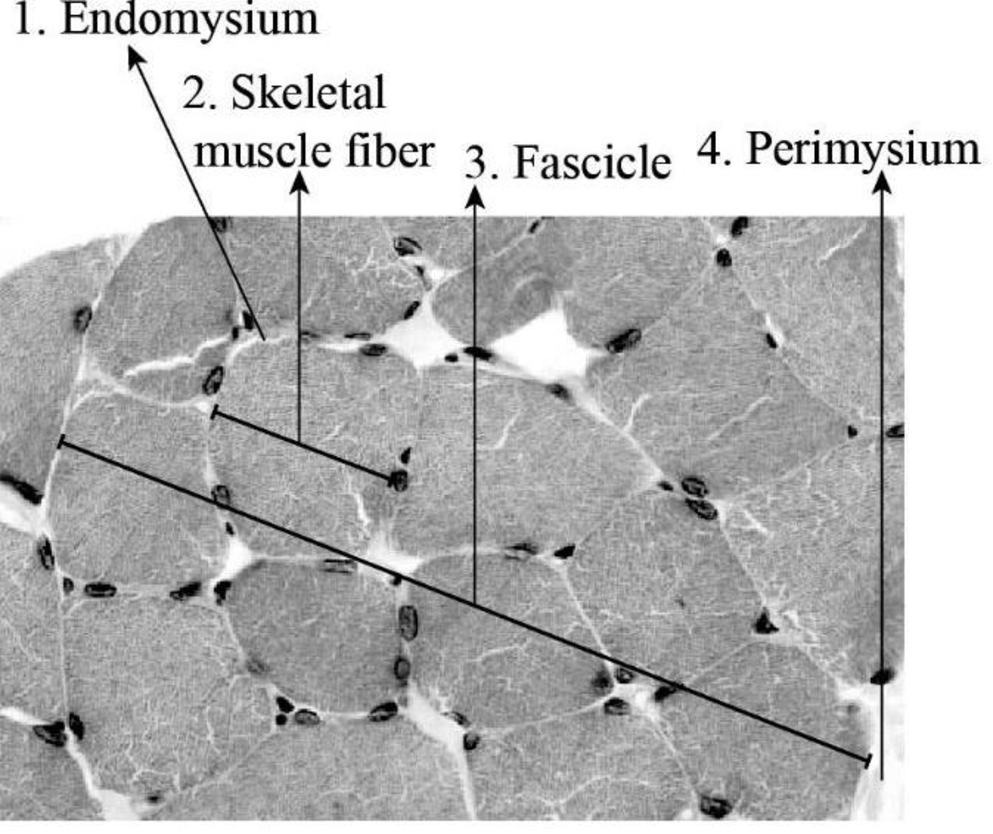
Fig 3: Cross-section of a muscle fascicle
Explanation of Solution
Skeletal muscle cells appear as long, cylindrical structures; therefore, they are generally referred to as muscle fibers. They are structured into a cluster known as fascicles. The epimysium spreads between fascicles internally, forming septa, which are called perimysium. The perimysium further stretches into thinner strands known as endomysium.
To label: The longitudinal section of muscle fibers in Fig 12.2 (b).
Introduction: Skeletal muscle fibers present in humans are large in size. The plasma membrane of the skeletal muscle fiber is known as sarcolemma. This membrane surrounds the sarcoplasm, which is the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
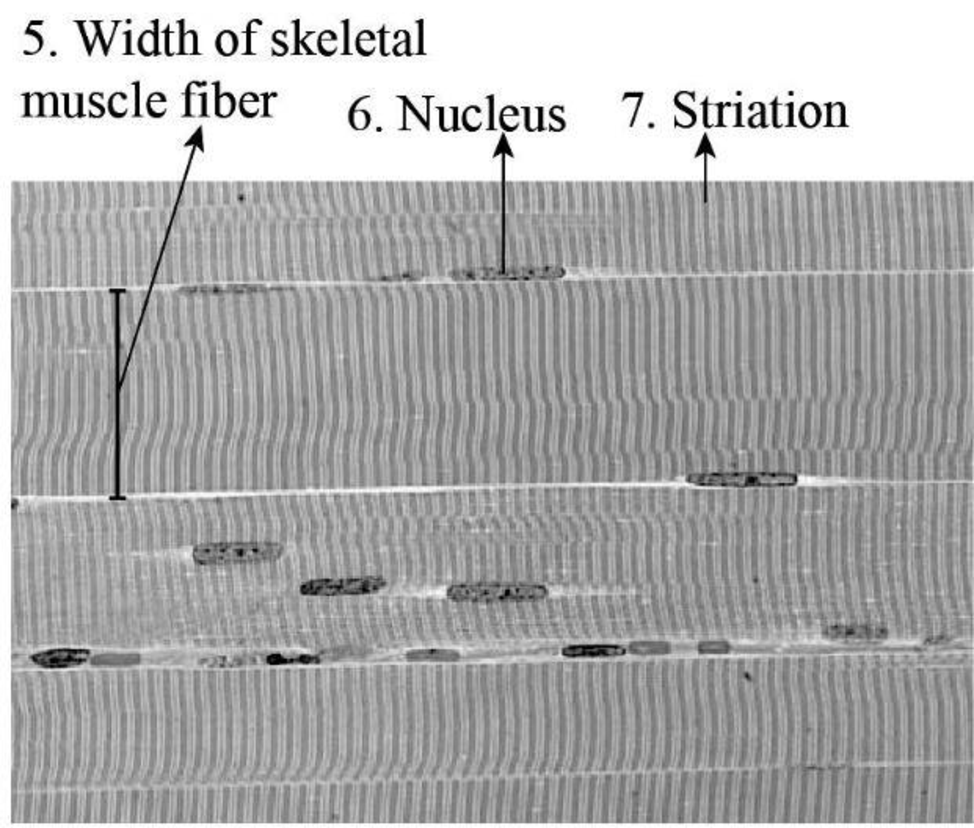
Fig 4: Longitudinal-section of muscle fibers
Explanation of Solution
The skeletal muscle fibers display striated appearance (striation) that is due to the organisation of myofilaments. These fibers are cylindrical shaped and possess more than one nucleus or multinucleated. The width of a typical muscle fiber is 10-50 μm.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
- Neurons and Reflexes 1. Describe the function of the: a) dendrite b) axon c) cell body d) myelin sheath e) nodes of Ranvier f) Schwann cells g) motor neuron, interneuron and sensory neuron 2. List some simple reflexes. Explain why babies are born with simple reflexes. What are they and why are they necessary. 3. Explain why you only feel pain after a few seconds when you touch something very hot but you have already pulled your hand away. 4. What part of the brain receives sensory information? What part of the brain directs you to move your hand away? 5. In your own words describe how the axon fires.arrow_forwardMutations Here is your template DNA strand: CTT TTA TAG TAG ATA CCA CAA AGG 1. Write out the complementary mRNA that matches the DNA above. 2. Write the anticodons and the amino acid sequence. 3. Change the nucleotide in position #15 to C. 4. What type of mutation is this? 5. Repeat steps 1 & 2. 6. How has this change affected the amino acid sequence? 7. Now remove nucleotides 13 through 15. 8. Repeat steps 1 & 2. 9. What type of mutation is this? 0. Do all mutations result in a change in the amino acid sequence? 1. Are all mutations considered bad? 2. The above sequence codes for a genetic disorder called cystic fibrosis (CF). 3. When A is changed to G in position #15, the person does not have CF. When T is changed to C in position #14, the person has the disorder. How could this have originated?arrow_forwardhoose a scientist(s) and research their contribution to our derstanding of DNA structure or replication. Write a one page port and include: their research where they studied and the time period in which they worked their experiments and results the contribution to our understanding of DNA cientists Watson & Crickarrow_forward
- hoose a scientist(s) and research their contribution to our derstanding of DNA structure or replication. Write a one page port and include: their research where they studied and the time period in which they worked their experiments and results the contribution to our understanding of DNA cientists Watson & Crickarrow_forward7. Aerobic respiration of a protein that breaks down into 12 molecules of malic acid. Assume there is no other carbon source and no acetyl-CoA. NADH FADH2 OP ATP SLP ATP Total ATP Show your work using dimensional analysis here: 3arrow_forwardFor each of the following problems calculate the following: (Week 6-3 Video with 6-1 and 6-2) Consult the total catabolic pathways on the last page as a reference for the following questions. A. How much NADH and FADH2 is produced and fed into the electron transport chain (If any)? B. How much ATP is made from oxidative phosphorylation (OP), if any? Feed the NADH and FADH2 into the electron transport chain: 3ATP/NADH, 2ATP/FADH2 C. How much ATP is made by substrate level phosphorylation (SLP)? D. How much total ATP is made? Add the SLP and OP together. 1. Aerobic respiration using 0.5 mole of glucose? NADH FADH2 OP ATP SLP ATP Total ATP Show your work using dimensional analysis here:arrow_forward
- Aerobic respiration of one lipid molecule. The lipid is composed of one glycerol molecule connected to two fatty acid tails. One fatty acid is 12 carbons long and the other fatty acid is 18 carbons long in the figure below. Use the information below to determine how much ATP will be produced from the glycerol part of the lipid. Then, in part B, determine how much ATP is produced from the 2 fatty acids of the lipid. Finally put the NADH and ATP yields together from the glycerol and fatty acids (part A and B) to determine your total number of ATP produced per lipid. Assume no other carbon source is available. 18 carbons fatty acids 12 carbons glycerol . Glycerol is broken down to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, a glycolysis intermediate via the following pathway shown in the figure below. Notice this process costs one ATP but generates one FADH2. Continue generating ATP with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate using the standard pathway and aerobic respiration. glycerol glycerol-3- phosphate…arrow_forwardDon't copy the other answerarrow_forward4. Aerobic respiration of 5 mM acetate solution. Assume no other carbon source and that acetate is equivalent to acetyl-CoA. NADH FADH2 OP ATP SLP ATP Total ATP Show your work using dimensional analysis here: 5. Aerobic respiration of 2 mM alpha-ketoglutaric acid solution. Assume no other carbon source. NADH FADH2 OP ATP Show your work using dimensional analysis here: SLP ATP Total ATParrow_forward
- Biology You’re going to analyze 5 ul of your PCR product(out of 50 ul) on the gel. How much of 6X DNAloading buffer (dye) are you going to mix with yourPCR product to make final 1X concentration ofloading buffer in the PCR product-loading buffermixture?arrow_forwardWrite the assignment on the title "GYMNOSPERMS" focus on the explanation of its important families, characters and reproduction.arrow_forwardAwnser these Discussion Questions Answer these discussion questions and submit them as part of your lab report. Part A: The Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Activity Graph the volume of oxygen produced against the temperature of the solution. How is the oxygen production in 30 seconds related to the rate of the reaction? At what temperature is the rate of reaction the highest? Lowest? Explain. Why might the enzyme activity decrease at very high temperatures? Why might a high fever be dangerous to humans? What is the optimal temperature for enzymes in the human body? Part B: The Effect of pH on Enzyme Activity Graph the volume of oxygen produced against the pH of the solution. At what pH is the rate of reaction the highest? Lowest? Explain. Why does changing the pH affect the enzyme activity? Research the enzyme catalase. What is its function in the human body? What is the optimal pH for the following enzymes found in the human body? Explain. (catalase, lipase (in your stomach),…arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





