
(a)
Interpretation: The reagents that can be used to achieve the following transformation are to be identified.

Concept introduction: The given compound is a terminal
(b)
Interpretation: The reagents that can be used to achieve each of the following transformations are to be identified.
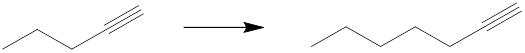
Concept introduction: The starting alkyne is a compound with five carbon atoms, which to be converted into a seven carbon-containing terminal alkyne, needs to undergo a reaction with such reagents which can facilitate this reaction. Reduction using a poisoned catalyst such as Lindlar’s catalyst, followed by bromination and reaction with an alkynide can yield the desired product.
(c)
Interpretation: The reagents that can be used to achieve each of the following transformations are to be identified.
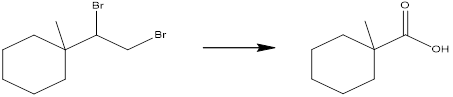
Concept introduction: The starting material has one more carbon atom than the product. This means the synthesis must have an ozonolysis process, to cleave a carbon-carbon bond. Also, since the product is a
(d)
Interpretation: The reagents that can be used to achieve each of the following transformations are to be identified.
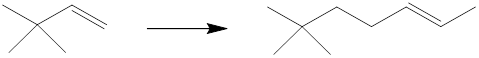
Concept introduction: The starting material has six carbon atoms, and the product has nine carbon atoms. So the synthesis must involve the installation of three carbon atoms and also, the location of the
(e)
Interpretation: The reagents that can be used to achieve each of the following transformations is to be identified.
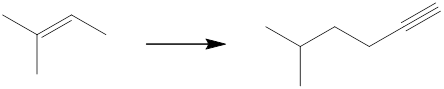
Concept introduction: The product has two more carbon atoms than the starting material, and the location of the functional group has changed. So, bromination followed by dehydrohalogenation can give a terminal alkene, which on further bromination followed by reaction with an alkynide would yield the desired product.
(f)
Interpretation: The reagents that can be used to achieve each of the following transformation is to be identified.
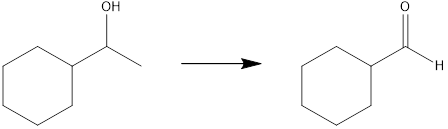
Concept introduction: The starting material has one more carbon atom than the product. Therefore, the synthesis must employ an ozonolysis process, to cleave a carbon-carbon bond. For the formation of an aldehyde product, an alkene is also required. For this alkene to be formed, the alcohol must be converted to a tosylate, and then after the alkene is formed, it can undergo ozonolysis to yield the product.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PRINT MULTI TERM
- When anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forwardDraw the major product in each of the following reaction:arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the following Friedel-Craft reaction. AlBr3 Brarrow_forward(a) Draw the structures of A and B in the following reaction. (i) NaNH2, NH3(1) A + B (ii) H3O+arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Consider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Given the reaction R + Q → P, indicate the rate law with respect to R, with respect to P and with respect to P.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardk₁ Given the reaction A B, indicate k-1 d[A] (A). the rate law with respect to A: (B). the rate law with respect to B: d[B] dt dtarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


