
ENGINEERING MECHANICS: STATICS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780135681879
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.3, Problem 19P
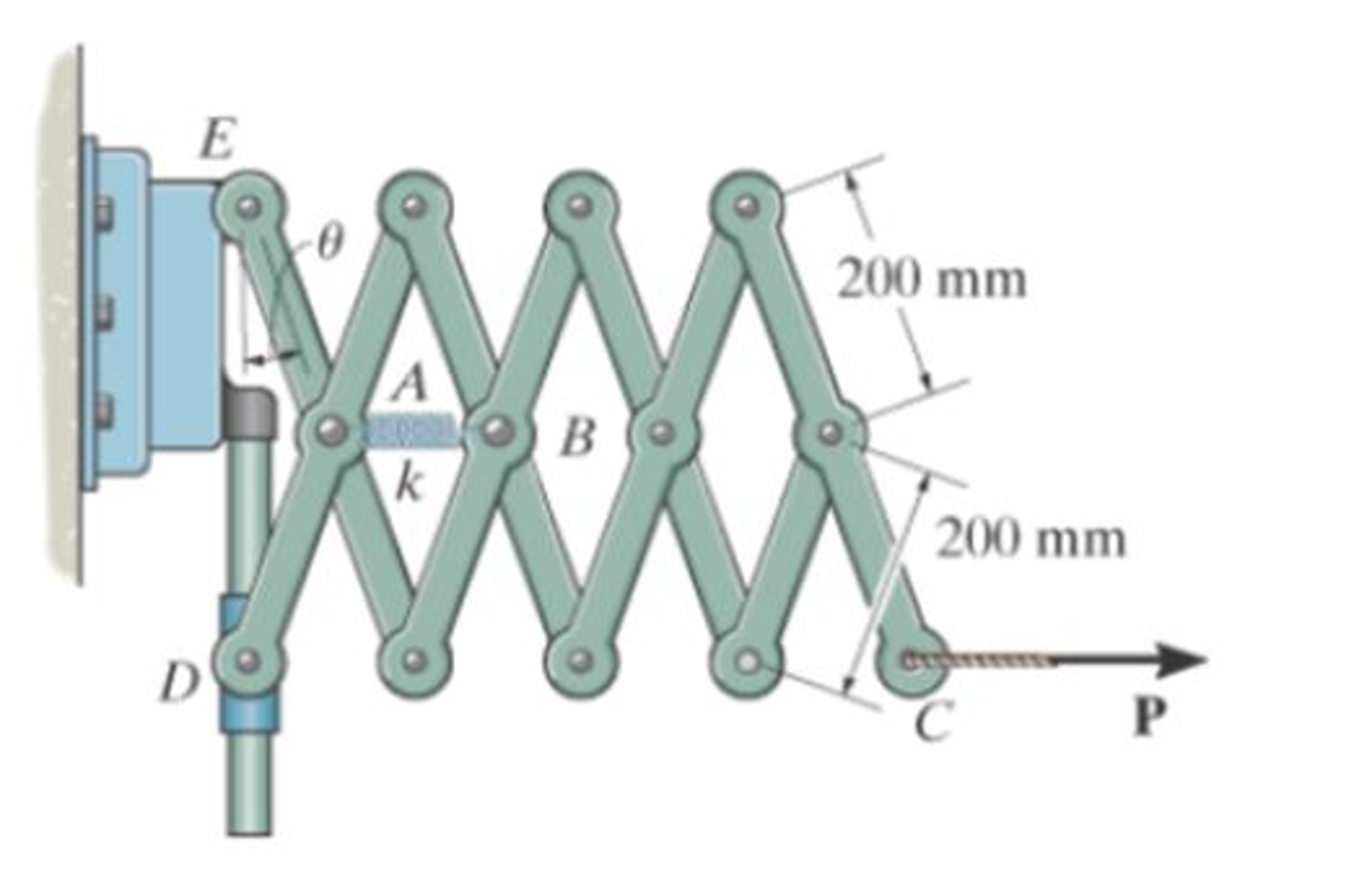
Determine the stillness k of the spring for equilibrium when θ = 60°, spring is unstretched when θ = 15°.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
this is answer to a vibrations question. in the last part it states an assumption of x2, im not sure where this assumption comes from. an answer would be greatly appreciated
Please answer with the sketches.
The beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic material. Determine the shape factor for the cross
section of the beam (Figure Q3). [Take σy = 250 MPa, yNA = 110.94 mm, I = 78.08 x 106 mm²]
y
25 mm
75 mm
I
25 mm
200 mm
25 mm
125
Figure Q3
Chapter 11 Solutions
ENGINEERING MECHANICS: STATICS
Ch. 11.3 - Each link has a mass of 20 kg.Ch. 11.3 - Determine the magnitude of force P required to...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium. The spring...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium. The spring...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 5FPCh. 11.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium. The spring...Ch. 11.3 - The lamp weighs 10 lb.Ch. 11.3 - Each of the four links has a length L and is pin...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the force screw exerts on the cork of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the disks rotation if the end of the...
Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 11.3 - if the uniform inks AB and CD each weigh 10 lb....Ch. 11.3 - If the unstretched length of the spring is I0,...Ch. 11.3 - It vertical forces P1 = P2 = 30 lb act at C and E...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 10PCh. 11.3 - The spring which always remains vertical. Is...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 14PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 15PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 16PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 11.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium. The spring...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the stillness k of the spring for...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the horizontal compressive force F...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 21PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 22PCh. 11.3 - The lever is in balance when the load and block...Ch. 11.3 - If the load F weighs 20 lb and the block G weighs...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder...Ch. 11.7 - Determine the equilibrium positions and...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 27PCh. 11.7 - If the potential function for a conservative...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 29PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 30PCh. 11.7 - The rod BD, having negligible weight, passes...Ch. 11.7 - Determine the angle for equilibrium when a weight...Ch. 11.7 - Determine the angle for equilibrium and...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 34PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 35PCh. 11.7 - The bars each have a mass of 3 Kg one the...Ch. 11.7 - The bars each have a mass of 10 kg and the spring...Ch. 11.7 - Determine the required stiffness k of the spring...Ch. 11.7 - It is unstretched when the rod assembly is in the...Ch. 11.7 - Determine the minimum distance d in order for it...Ch. 11.7 - If the spring is unstretched when = 60. Determine...Ch. 11.7 - The contact at A is smooth, end both are pm...Ch. 11.7 - Determine the steepest grade along which it can...Ch. 11.7 - Determine the weight W2, that is on the pan in...Ch. 11.7 - If the rod is supported by a smooth slider block...Ch. 11.7 - Point C is coincident with B when OA is...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 47PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 48PCh. 11.7 - If the block has three equal sides of length d,...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 1RPCh. 11.7 - Determine the horizontal force P required to hold...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 3RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 4RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 5RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 6RPCh. 11.7 - If both spring DE and BC are unstretched when =...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A beam of the cross section shown in Figure Q3 is made of a steel that is assumed to be elastic- perfectectly plastic material with E = 200 GPa and σy = 240 MPa. Determine: i. The shape factor of the cross section ii. The bending moment at which the plastic zones at the top and bottom of the bar are 30 mm thick. 15 mm 30 mm 15 mm 30 mm 30 mm 30 mmarrow_forwardA torque of magnitude T = 12 kNm is applied to the end of a tank containing compressed air under a pressure of 8 MPa (Figure Q1). The tank has a 180 mm inner diameter and a 12 mm wall thickness. As a result of several tensile tests, it has been found that tensile yeild strength is σy = 250 MPa for thr grade of steel used. Determine the factor of safety with respect to yeild, using: (a) The maximum shearing stress theory (b) The maximum distortion energy theory T Figure Q1arrow_forwardAn external pressure of 12 MPa is applied to a closed-end thick cylinder of internal diameter 150 mm and external diameter 300 mm. If the maximum hoop stress on the inner surface of the cylinder is limited to 30 MPa: (a) What maximum internal pressure can be applied to the cylinder? (b) Sketch the variation of hoop and radial stresses across the cylinder wall. (c) What will be the change in the outside diameter when the above pressure is applied? [Take E = 207 GPa and v = 0.29]arrow_forward
- so A 4 I need a detailed drawing with explanation し i need drawing in solution motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. cam is 50 mm. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the か ---2-125 750 x2.01 98Parrow_forwardFigure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm, BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A 45 B Space Diagram o NTS (Not-to-Scale) C Darrow_forwardI need a detailed drawing with explanation so Solle 4 يكا Pax Pu + 96** motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. cam is 50 mm. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the 55 ---20125 750 X 2.01 1989arrow_forward
- Ashaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180 degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to 20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter. Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of 500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel. 35,000 TNM 20,000 10,000 0 90 270 495 Crank angle 8 degrees 720arrow_forwardchanism shown in figure below, the crank OA rotates at 60 RPM counterclockwise. The velocity diagram is also drawn to scale (take dimensions from space diagram). Knowing that QCD is rigid plate, determine: a. Linear acceleration of slider at B, b. Angular acceleration of the links AC, plate CQD, and BD. D Space Diagram Scale 1:10 A ES a o,p,g b Velocity Diagram Scale 50 mm/(m/s) darrow_forwardA thick closed cylinder, 100 mm inner diameter and 200 mm outer diameter is subjected to an internal pressure of 230 MPa and outer pressure of 70 MPa. Modulus of elasticity, E=200 GPa. and Poisson's ratio is 0.3, determine: i) The maximum hoop stress ii) The maximum shear stress iii) The new dimension of the outer diameter due to these inner and outer pressures.arrow_forward
- A ә レ shaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180 degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to 20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter. Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of 500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel. 35,000 TNm 20,000 10,000 495 Crank angle 8 degrees 270 0 90 か ---20125 750 X 2.01 44 720 sarrow_forwardThe gas tank is made from A-36 steel (σy = 250 MPa) and has an inner diameter of 3.50 m. If the tank is designed to withstand a pressure of 1.2 MPa, determine the required minimum wall thickness to the nearest millimeter using (a) The maximum-shear-stress theory (b) Maximum distortion- energy theory. Apply a factor of safety of 1.5 against yielding.arrow_forwardә レ Figure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm, BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A A B # Space Diagram o NTS (Not-to-Scale) C 10 =--20125 735) 750 x2.01 اهarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License