
Concept explainers
(a)
The accelerations of A
(a)
Answer to Problem 11.60P
The accelerations of A
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The relative change in position of block C with respect to block A
The relative velocity of collar B with respect to block A
The displacement of A
The displacement of B
Calculation:
Show the length and position of the cables as in Figure (1).
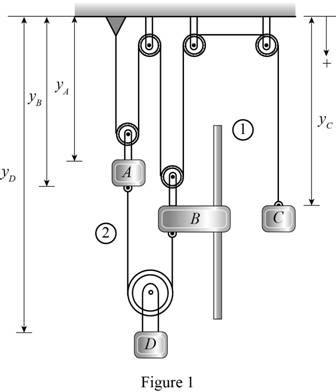
Choose the coordinate downward positive and right side positive.
Write the express for total lengths of cables 1:
Differentiate the above equation with respective to time (t).
Denotes
Differentiate the equation (2) with respective to time (t).
Denotes
Write the express for total lengths of cables 2:
Differentiate the above equation with respective to time (t).
Denotes
Differentiate the equation (3) with respective to time (t).
Denotes
At time (t) 0 sec the velocity (v) is zero.
Then, the initial position of cable A, cable B and cable C is equal.
Calculate the position
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the position
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the position
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Write the expression for relative change in position of block C with respect to block A:
Substitute
Write the equation for acceleration
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of block A:
Substitute
Calculate the velocity
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the velocity
Substitute 0 for
Write the equation for relative velocity of block B with respect to block A
Substitute
Substitute
Modify the equation (5).
Substitute
Modify the equation (7).
Substitute
Calculate the time (t):
Substrate equation (13) and (12).
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration
Substitute 4 sec for t in equation (12).
Therefore, the accelerations of A
(b)
The change in position
(b)
Answer to Problem 11.60P
The change in position
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The relative change in position of block C with respect to block A
The relative velocity of collar B with respect to block A
The displacement of A
The displacement of B
The velocity
Calculation:
Calculate the acceleration
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration
Substitute
Calculate the time (t) using the relation below;
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the change in positon
Here,
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the change in position
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Q | Sign in PDE Lecture W09.pdf PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L9.pdi X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L10.p X PDF MMB241 - Tutorial L11.p X Lecture W12-Work and X + File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Desktop/mmb241/Lecture%20W12%20-%20Work%20and%20Energy.pdf ||! Draw | IA | a | Ask Copilot Class Work + 33 of 34 D Question 1 The engine of a 3500-N car is generating a constant power of 50 hp (horsepower) while the car is traveling up the slope with a constant speed. If the engine is operating with an efficiency of € 0.8, determine the speed of the car. Neglect drag and rolling resistance. Use g 9.81 m/s² and 1 hp = 745.7 W. 10 го Question 2 A man pushes on a 60-N crate with a force F. The force is always directed downward at an angle of 30° from the horizontal, as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the force is gradually increased until the crate begins to slide. Determine the crate's initial acceleration once it starts to move. Assume the coefficient of static friction is μ = 0.6, the coefficient of kinetic…arrow_forwardstate is Derive an expression for the volume expansivity of a substance whose equation of RT P = v-b a v(v + b)TZ where a and b are empirical constants.arrow_forwardFor a gas whose equation of state is P(v-b)=RT, the specified heat difference Cp-Cv is equal to which of the following (show all work): (a) R (b) R-b (c) R+b (d) 0 (e) R(1+v/b)arrow_forward
- of state is Derive an expression for the specific heat difference of a substance whose equation RT P = v-b a v(v + b)TZ where a and b are empirical constants.arrow_forwardTemperature may alternatively be defined as T = ди v Prove that this definition reduces the net entropy change of two constant-volume systems filled with simple compressible substances to zero as the two systems approach thermal equilibrium.arrow_forwardUsing the Maxwell relations, determine a relation for equation of state is (P-a/v²) (v−b) = RT. Os for a gas whose av Tarrow_forward
- (◉ Homework#8arrow_forwardHomework#8arrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^ 2. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A бро Barrow_forwardBox A has a mass of 15 kilograms and is attached to the 20 kilogram Box B using the cord and pulley system shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the boxes and surface is 0.2 and the moment of inertia of the pulley is 0.5 kg * m^2. Both boxes are 0.25 m long and 0.25 m high. The cord is attached to the bottom of Box A and the middle of box B. After 2 seconds, how far do the boxes move? A From бро Barrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY