
Concept explainers
The pressure in a natural gas pipeline is measured by the manometer shown in Fig. P1–67E with one of the arms open to the atmosphere where the local atmospheric pressure is 14.2 psia. Determine the absolute pressure in the pipeline.
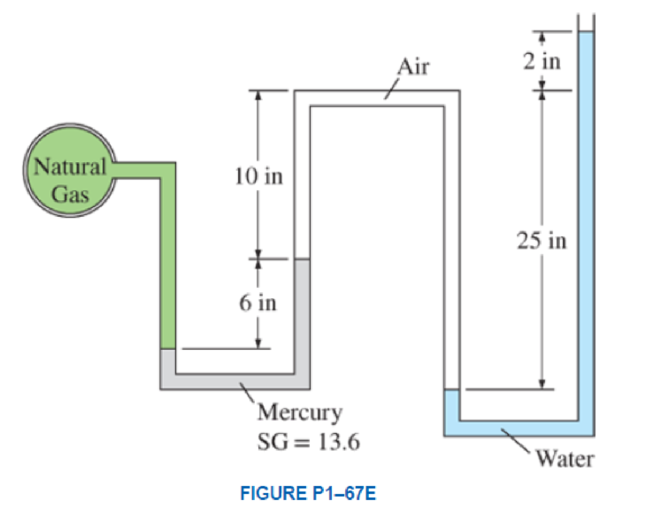
The absolute pressure in the pipeline.
Answer to Problem 67P
The absolute pressure in the pipeline is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the density of mercury.
Here, the specific gravity of the mercury is
Write the expression of pressure in a double U-tube manometer with one arms open to the atmosphere.
Here, the absolute pressure in the pipeline is
Conclusion:
From the Table A-3E (a) “Properties of common liquids, solids, and foods” to obtain the value for density of water as
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the absolute pressure in the pipeline is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
CONNECT FOR THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERI
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Concepts Of Programming Languages
- 2. A single crystal of aluminum is oriented for a tensile test such that its slip plane normal makes an angle of 28.1° with the tensile axis. Three possible slip directions make angles of 62.4°, 72.0°, and 81.1° with the same tensile axis. (a) Which of these three slip directions is most favored? (b) If plastic deformation begins at a tensile stress of σ x = 1.95 MPa (280 psi), determine the critical resolved shear stress for aluminium. (c) If this single crystalspecimen is loaded under the new stress state: σ x =1.2 MPa σ y = -0.8 MPa, and τ xy = 0.6 MPa, howmuch is the resolve the shear stress along the most favored slip direction?arrow_forwardPlease explain how to do each part and tell me if my drawing is correct. thank youarrow_forward4. Determine which of the following flow fields represent a possible incompressible flow? (a) u= x²+2y+z; v=x-2y+z;w= -2xy + y² + 2z a (b) V=U cose U coso 1 (9) [1-9] Usino |1 (4)] [+] V=-Usin 1+1arrow_forward
- 3. Determine the flow rate through the pipe line show in the figure in ft³/s, and determine the pressures at A and C, in psi. 5' B C 12° 20' D 6"d 2nd- Water Aarrow_forward5. A flow is field given by V = x²₁³+xy, and determine 3 ·y³j- (a) Whether this is a one, two- or three-dimensional flow (b) Whether it is a possible incompressible flow (c) Determine the acceleration of a fluid particle at the location (X,Y,Z)=(1,2,3) (d) Whether the flow is rotational or irrotational flow?arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwarddraw the pneumatic circuit to operate a double-acting cylinder with: 1. Extension: Any of two manual conditions plus cylinder fully retracted, → Extension has both meter-in and meter-out, 2. Retraction: one manual conditions plus cylinder fully extended, → Retraction is very fast using quick exhaust valve.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Expert solution plsarrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





