
1.
Compute the time interest earned for Company E.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Times interest earned ratio:
Times interest earned quantifies the number of times the earnings before interest and taxes can pay the interest expense.
Compute the time interest earned for Company E.
Therefore, time interest earned by Company E is 1.33.
2.
Compute the time interest earned for Company S.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Times interest earned ratio:
Times interest earned quantifies the number of times the earnings before interest and taxes can pay the interest expense.
Compute the time interest earned for Company S.
Therefore, time interest earned by Company S is 2.0.
3.
Identify the effect of increase in sales by 10%, on each company’s net income.
3.
Explanation of Solution
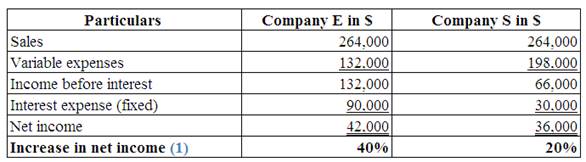
(Table 1)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 1.10
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
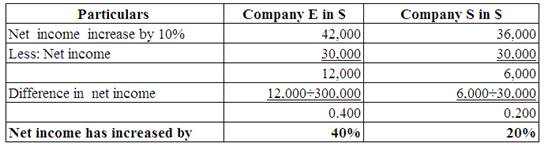
(Table 2)
4.
Identify the effect of increase in sales by 40%, on each company’s net income.
4.
Explanation of Solution
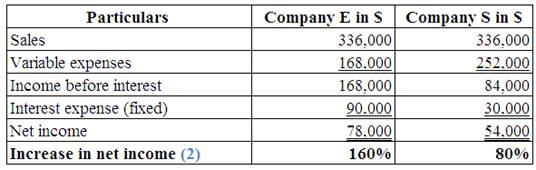
(Table 3)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 1.40
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
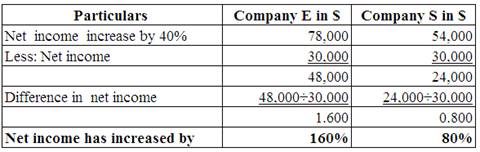
(Table 4)
5.
Identify the effect of increase in sales by 90%, on each company’s net income.
5.
Explanation of Solution
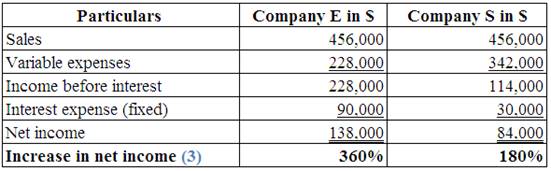
(Table 5)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 1.90
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
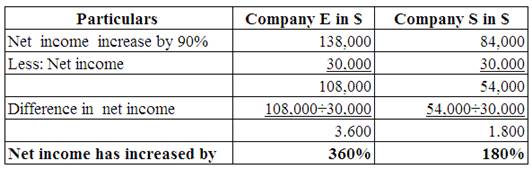
(Table 6)
6.
Identify the effect of decreases in sales by 20%, on each company’s net income.
6.
Explanation of Solution
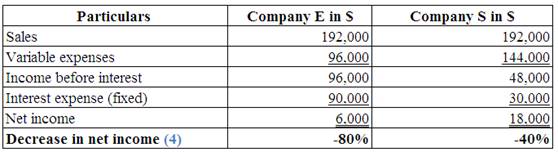
(Table 7)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 0.80
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
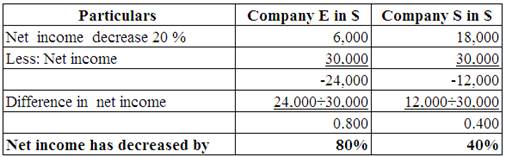
(Table 8)
7.
Identify the effect of decreases in sales by 50%, on each company’s net income.
7.
Explanation of Solution
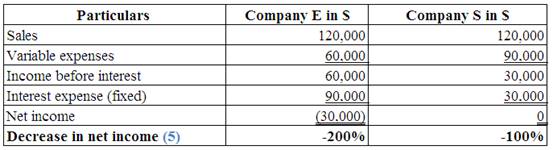
(Table 9)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 0.50
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
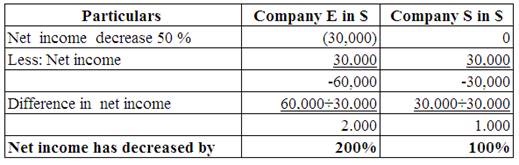
(Table 10)
8.
Identify the effect of decreases in sales by 80%, on each company’s net income.
8.
Explanation of Solution
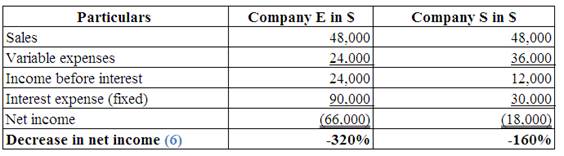
(Table 11)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 0.20
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
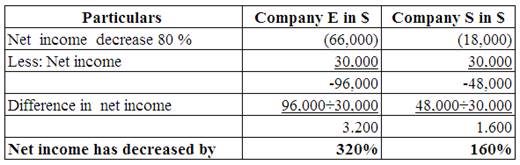
(Table 12)
9.
Comment on the results from requirement 3 through 8 in relation to the fixed-cost strategies of the two companies and the ratio values computed under requirement 1 and 2.
9.
Explanation of Solution
The higher fixed cost strategy of Company E shows the effect of increases and decreases in the value of sales. When sales increase, the value of net income increases. When sales decrease, the value of net income decreases. The higher fixed cost strategy of Company E is indicated by a lower value of the times interest earned ratio.
The higher fixed cost strategy works goods when there is increase in sales. Therefore, Company E enjoys has greater percent increases in the value of its net income. The Company is protected with the lower fixed cost strategy, when there is a decrease in sales level. Company S experiences smaller percent decreases in the value of net income because it has made this choice.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- Can you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forward← Week 1: Homework Question 3 of 4 8.75/10 The project is completed in 2025, and a successful patent is obtained. The R&D costs to complete the project are $113,000. The administrative and legal expenses incurred in obtaining patent number 472-1001-84 in 2025 total $16,000. The patent has an expected useful life of 5 years. Record the costs for 2025 in journal entry form. Also, record patent amortization (full year) in 2025. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amounts. List all debit entries before credit entries.) Account Titles and Explanation Research and Development Expense Cash (To record research and development costs) Patents Cash (To record legal and administrative costs) Amortization Expense Patents (To record one year's amortization expense) Debit 113000 16000 3200 Credit 113000 16000 3200arrow_forward
- Joe transfers land to JH Corporation for 90% of the stock in JH Corporation worth $20,000 plus a note payable to Joe in the amount of $40,000 and the assumption by JH Corporation of a mortgage on the land in the amount of $100,000. The land, which has a basis to Joe of $70,000, is worth $160,000. a. Joe will have a recognized gain on the transfer of $90,000. b. Joe will have a recognized gain on the transfer of $30,000.c. JH Corporation will have a basis in the land transferred by Joe of $70,000. d. JH Corporation will have a basis in the land transferred by Joe of $160,000. e. None of the above.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





