
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given cycloalkane needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: According to the IUPAC rule,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
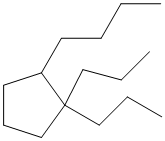
The above structure contains a cycloalkane ring with 5 carbon atoms thus, it is cyclopentane.
Here, numbering will be done according to the number of substituents present of cyclopentane ring. There are 2 substituent at one position and 1 substituent at other.
The numbering can be done as follows:
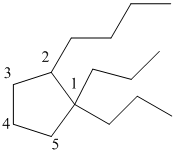
From the above structure, there are 2 propyl groups at 1st position and 1 butyl group at 2nd position of cyclopentane ring.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the molecule will be:
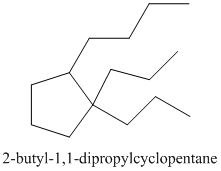
(b)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given
Concept Introduction: According to the IUPAC rule, numbering of atom is done to find the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. After that name of groups attached to the chain are identified. The location of substituent groups is designated by numbers and name. The last step is to assemble the name by listing the groups in alphabetical order. Prefixes such as di, tri, tetra etc. are used to represent groups of same kind.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
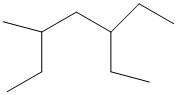
The numbering will be done according to the longest carbon chain in the molecule.
The numbering is done as follows:
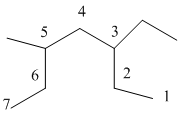
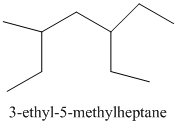
From the above structure, there is 1 ethyl group at 3rd position and 1 methyl group at 5th position of the main chain containing 7 carbon atoms.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of the structure will be:
Thus,
(c)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given alkane needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: According to the IUPAC rule, numbering of atom is done to find the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. After that name of groups attached to the chain are identified. The location of substituent groups is designated by numbers and name. The last step is to assemble the name by listing the groups in alphabetical order. Prefixes such as di, tri, tetra etc. are used to represent groups of same kind.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
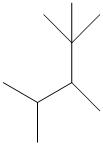
The numbering will be done according to the longest carbon chain in the molecule.
The numbering can be done as follows:
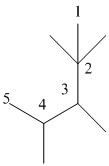
Thus, there are 5 carbon atoms in the parent chain. Also, there are 2 methyl groups at 2nd position, 1 methyl group at 3rd position and 1 methyl group at 4th position. There are total 4 methyl substituents.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of the molecule will be:
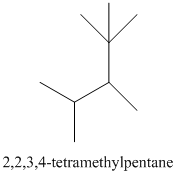
(d)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given cycloalkane needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: According to the IUPAC rule, numbering of atom is done to find the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. After that name of groups attached to the chain are identified. The location of substituent groups is designated by numbers and name. The last step is to assemble the name by listing the groups in alphabetical order. Prefixes such as di, tri, tetra etc. are used to represent groups of same kind.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
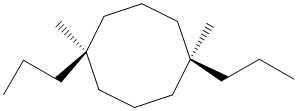
It contains a cycloalkane with 8 carbon atoms. Two substituents are same thus, numbering will start from any one of the substituent side.
The numbering can be represented as follows:
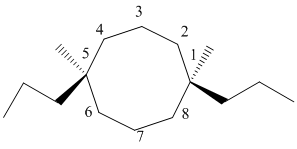
From the above structure, there is 1 methyl and 1 propyl group at 1st and 6th position.
Thus, IUPAC name will be as follows:
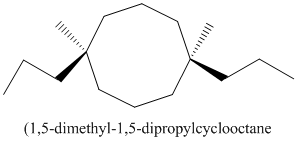
Stereochemistry can also be determined by giving priority to the groups attached.
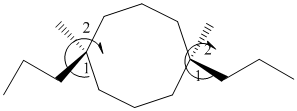
The 1-2 movement is clockwise but the lowest priority group is in front of the curved arrow so assignment will be reversed. Here, clockwise is S and anti or counterclockwise is R. Since, in the above structure the movement is clockwise so the configuration will be S for both sides. The IUPAC name with configuration will be:
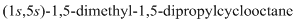
(e)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given cycloalkane needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: According to the IUPAC rule, numbering of atom is done to find the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. After that name of groups attached to the chain are identified. The location of substituent groups is designated by numbers and name. The last step is to assemble the name by listing the groups in alphabetical order. Prefixes such as di, tri, tetra etc. are used to represent groups of same kind.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
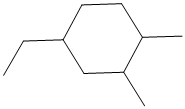
It contains a cycloalkane ring with 6 carbon atoms.
The numbering is represented as follows:
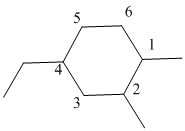
From the above structure, there is 1 methyl group at 1st position, 1 methyl group at 2nd position and 1 ethyl group at 4th position.
Thus, IUPAC name of the molecule will be:
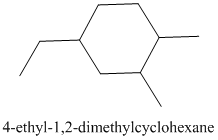
(f)
Interpretation: The IUPAC name for the given alkane needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction: According to the IUPAC rule, numbering of atom is done to find the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. After that name of groups attached to the chain are identified. The location of substituent groups is designated by numbers and name. The last step is to assemble the name by listing the groups in alphabetical order. Prefixes such as di, tri, tetra etc. are used to represent groups of same kind.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
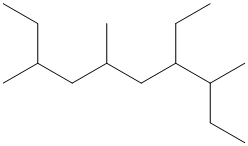
The numbering will be done according to the longest carbon chain in the molecule.
The numbering can be done as follows:
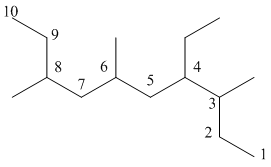
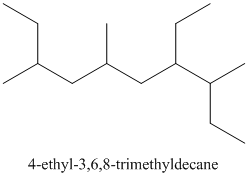
From the above structure, there is 1 ethyl group at 4th position and 1 methyl group each at 3rd, 6th and 8th carbon atom in the chain.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the molecule will be:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
- pressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward
- 6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





