
Computer Science Illuminated
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781284055917
Author: Nell Dale, John Lewis
Publisher: Jones & Bartlett Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 11, Problem 43E
a.
Program Plan Intro
Directories:
- A file system or a directory system is observed as a directory tree.
- A tree structure which shows the directories and files in one more directory is called directory tree.
- A directory system is used to manage the list of files in a computer.
- The directory tree contains directories, files, and subdirectories. They are as follows:
- The topmost level of the directory system is called root directory.
- The directory which contains another directory is called the parent directory.
- The directory which is contained within another directory is called sub directory.
- The directory that is currently active (working) of all other directories is referred to as working directory.
- The directory contains the information such as file name, location of the file, extension of the file, the size of the file, date created, and last modified date.
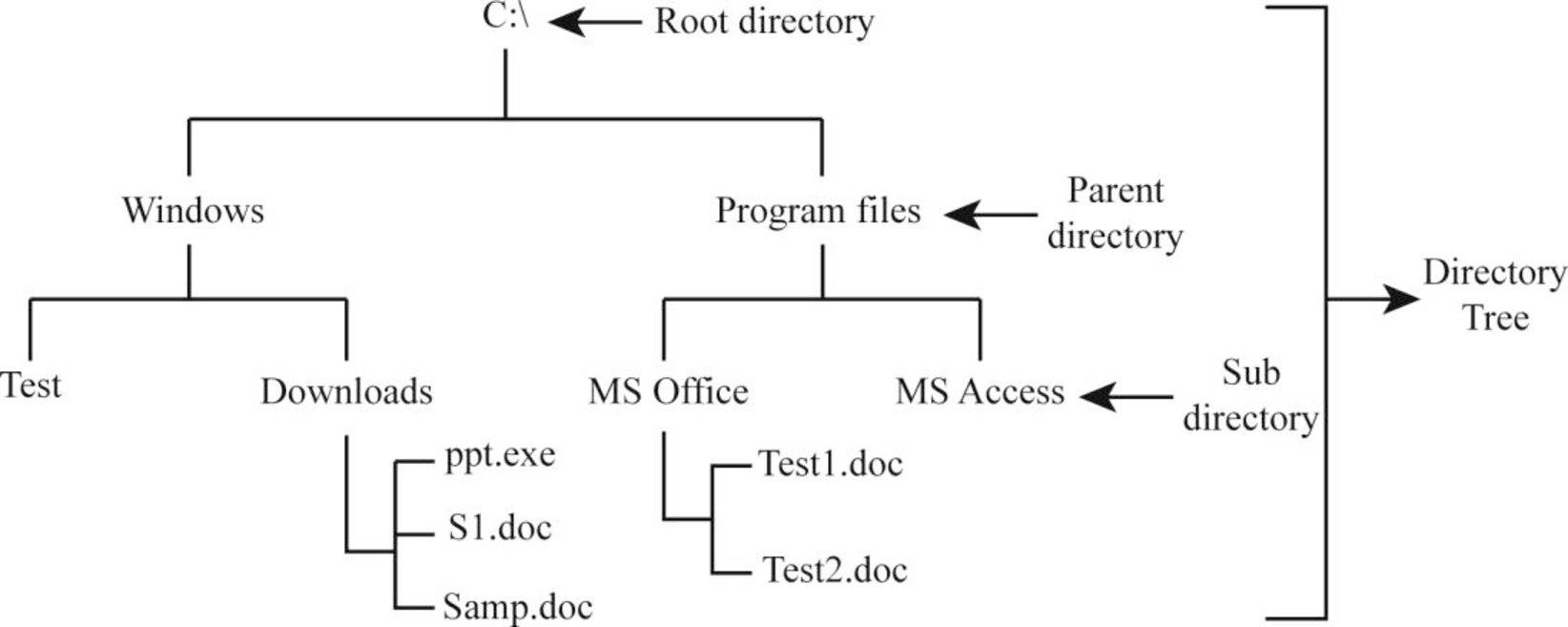
- The diagrammatic representation shows the directory tree structure on windows environment as follows:
Explanation of Solution
b.
Represent the name of the directory which is within another directory:
- From the above directory tree structure, it clearly specifies that under the root directory “C:/”, there are two directories:
- Windows
- Program Files
- The above two directories “Windows” and “Program Files” are called parent directories because they each contain another directory.
- Under the parent directory “Windows”, the directories “Test” and “Downloads” are located...
Explanation of Solution
c.
Represent the name of the directory that is under any other directory:
- From the above directory tree structure, it clearly specifies
- “C:\” is the directory which acts as root for all the files, directories, and subdirectories...
Explanation of Solution
d.
Represent the name that shows the nested directory organization:
- From the above diagram, it clearly specifies that under the root directory “C:/”, there are two directories:
- Windows
- Program Files
- The above two directories “Windows” and “Program Files” are called parent directories because it contains another directory.
- Under the parent directory “Windows”, the directories “Test” and “Downloads” are located. They are called subdirectories. Because it is located within the parent directory.
- Under the subdirectory “Downloads”, the files are located...
Explanation of Solution
e.
Similarities of binary tree and directory tree structure:
- The representation of directory tree and binary tree follows the hierarchical model...
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question D.4: FIFO Page Replacement
Consider the following page reference string:
e, c, b, e, a, g, d, c, e, g, d, a
Considering 4 frames, fill in the following table and then answer how many page faults would occur with the
FIFO page replacement algorithm.
RS: reference string; FO: frame 0, F1: frame 1, etc.
Hint: all frames are initially empty, so your first unique pages will all cost one fault each.
Time
1234567891011
12
RS
e
cb
e agd ce g d
a
FO
F1
F2
F3
Page fault?
b) Total # page faults:
c) Briefly (1-2 sentences) explain Belady's Anomaly that can occur in FIFO Page Replacement.
Consider a system that uses a fixed-partition scheme, with equal partitions of size 2" bytes, and the main
memory has 2¹8 bytes. A process table is maintained with a pointer to the resident partition for each resident
process. How many bits are required for the pointer in the process table? Show all your steps.
Use the same semaphore notation shown above to describe how we can ensure the execution order of the
following process execution graph:
P6
P2
P7
P1
P3
P4
P5
Use all of the following semaphores in your answer:
s1=0; s2=0; s3=0; s4=0; s5=0; s6=0;
Chapter 11 Solutions
Computer Science Illuminated
Ch. 11 - Prob. 1ECh. 11 - Prob. 2ECh. 11 - Prob. 3ECh. 11 - Prob. 4ECh. 11 - Prob. 5ECh. 11 - Prob. 6ECh. 11 - Prob. 7ECh. 11 - Prob. 8ECh. 11 - Prob. 9ECh. 11 - Prob. 10E
Ch. 11 - Prob. 11ECh. 11 - Prob. 12ECh. 11 - Prob. 13ECh. 11 - Prob. 14ECh. 11 - Prob. 15ECh. 11 - Prob. 16ECh. 11 - Prob. 17ECh. 11 - Prob. 18ECh. 11 - Prob. 19ECh. 11 - Prob. 20ECh. 11 - Prob. 21ECh. 11 - Prob. 22ECh. 11 - Prob. 23ECh. 11 - Prob. 24ECh. 11 - Prob. 25ECh. 11 - Prob. 26ECh. 11 - Prob. 27ECh. 11 - Prob. 28ECh. 11 - Prob. 29ECh. 11 - Prob. 30ECh. 11 - Prob. 31ECh. 11 - Prob. 32ECh. 11 - Prob. 33ECh. 11 - Prob. 34ECh. 11 - Prob. 35ECh. 11 - Prob. 36ECh. 11 - Prob. 37ECh. 11 - Prob. 38ECh. 11 - Prob. 39ECh. 11 - Prob. 40ECh. 11 - Prob. 41ECh. 11 - Prob. 42ECh. 11 - Prob. 43ECh. 11 - Prob. 44ECh. 11 - Prob. 45ECh. 11 - Prob. 46ECh. 11 - Prob. 47ECh. 11 - Prob. 48ECh. 11 - Prob. 49ECh. 11 - Prob. 50ECh. 11 - Prob. 51ECh. 11 - Prob. 52ECh. 11 - Prob. 53ECh. 11 - Prob. 54ECh. 11 - Prob. 55ECh. 11 - Prob. 56ECh. 11 - Prob. 57ECh. 11 - Prob. 1TQCh. 11 - Prob. 2TQCh. 11 - Prob. 3TQCh. 11 - Prob. 4TQCh. 11 - Prob. 5TQCh. 11 - Prob. 6TQ
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider the set of process: Process ID Arrival Time Burst Time P1 0 5 P2 0 10 P3 + 15 P4 18 10 P5 22 20 a) Draw the GANTT chart for the Round Robin time quantum -5) scheduling algorithm. Use the same implementation you used for the programming assignmenti.e. the processes should always run in PID order. Assume there is no context-switch overhead. Show your work for partial credit. b) Write your answer to the following performance metrics given your above CANTT charts. Show your work for partial credit. Average Response time: Average Wating time: Average Turnaround time:arrow_forwardConsider a file currently consisting of 10 blocks. Assume that the file control block and the new block information to be added are already in memory. Calculate how many disk I/O operations are required for the linked allocation strategy, if, for one block, the following conditions hold: HINTS: 1) ignore disk I/O associated with the file control block. 2) each read and each write is an explicit disk I/O. 3) assume a pointer to the end of the list for linked allocation a. The block is added at the beginning. b. The block is added in the middle. c. The block is added at the end. d. The block is removed from the beginning. e. The block is removed from the middle. f. The block is removed from the end.arrow_forwardSegment Base (original) Length Base (after compaction) 0 100 300 1 1400 600 2 450 100 3 3200 80 4 2200 500 5 3300 33 1. Given the original base addresses, what are the physical addresses for the following logical addresses? If it's an invalid address, just write "invalid". Note that (X, Y) => segment X, offset Y a) (0,350) b) (1,599) c) (2,50) d) (3,81) e) (4,300) f) (5.0) g) (5,34)arrow_forward
- Process Allocation A Max BCDABC D A Available B C PO 3 0 2 1 4 2 4 2 1 0 0 P1 0 1 0 1 0 2 2 2 P2 1 2 0 0 3 2 1 0 P3 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 P4 0 0 1 1 1 - 0 2 1 a) What is the content of the matrix Need? Process PO P1 P2 P3 P4 A Need BC D D ° b) Is the system in a safe state? If yes, give a safe sequence of processes. If not, explain why the system is not in a safe state. c) If a request from process P4 arrives for (1,0,0,0), can the request be granted immediately? Please state the reason.arrow_forwardConsider N processes sharing the CPU in a round-robin fashion (N>=2). Assume that each context switch takes S ms and that each time quantum is Q ms. For simplicity, assume that processes never block on any event and simply switch between the CPU and the ready queue. Also, assume that a process is still in the ready queue while a context switch is happening. a) What happens if Q is much smaller than S? What happens when Q→→ ∞, i.e. is much larger than the maximum turnaround time of all the processes? Be brief (1-2 sentences max) in your answer. b) If you use RR for scheduling, which of the three performance metrics (waiting, response, turnaround time) is more likely to be improved? Why (1-2 sentences max)?arrow_forwardCompute the jackknife estimate of bias and standard error for the correlation statistics from the law82 data using r languagearrow_forward
- Question D.1: Effective Access Time A computer keeps its page tables in memory. Memory access time is 100 nanoseconds (ns). Answer the following questions about the performance of this setup. Show your work. a) What is the effective access time (i.e. reading a word in memory) with no caching and a two-level page table? b) Consider the above scenario but with a TLB having a cache hit rate of 98%. If the TLB takes 20 ns to access, what is the effective access time of this setup when considering this TLB?arrow_forwardThe data law82 in bootstrap library contains LSAT and GPA for 82 law schools. 1. Write you own R code to estimate the correlation between LSAT and GPA scores, and compute the bootstrap estimate of the standard error and bias of the sample correlation. 2. Use the boot function in boot library to compute the bootstrap estimate of the standard error and bias of the sample correlation. Compare your results in 1 with the function output. using r languagearrow_forwardi would like to get help to resolve the following casearrow_forward
- Challenge: Assume that the assigned network addresses are correct. Can you deduce (guess) what the network subnet masks are? Explain while providing subnet mask bits for each subnet mask. [Hint: Look at the addresses in binary and consider the host ids]arrow_forwardWhat is the main difference between Static routing and Dynamic routing (OSPF)? in terms of either wildcard mask or subnet mask, or especially for increasing the number of networks, explaining the reason while providing a specific example like what command they use in CLIarrow_forwardAdd a new class Checking Account that inherits from the BankAccount class, and has a double instance variable overdraftLimit in addition to the variables inherited from the superclass. Create a constructor for the Checking Account class that takes in the account number, account holder name, initial balance, account type and overdraft limit as input, and uses the super keyword to call the constructor of the superclass, passing in the account number, account holder name and initial balance, account type. Re-write the withdraw() method in the CheckingAccount class so that it first checks if the withdrawal amount is less than the current balance plus the overdraft limit. If it is, the withdrawal is allowed and the balance is updated. If not, the method should return an error message "Insufficient funds". Create a new method displayOverdraft Limit() that returns the overdraft limit of the Checking Account. In the BankAccountTest class, create a new object of type Checking Account with…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education