
a)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
a)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
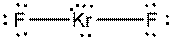
b)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
b)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
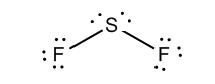
c)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
c)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
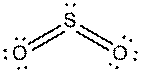
d).
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
d).
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
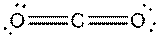
e)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
e)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
f).
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
f).
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
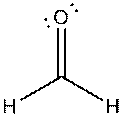
g)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
g)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry, 9th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2 24-Months Printed Access Card
- The reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forwardOne liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forwardHow does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forward
- Draw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forwardDraw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward
- 19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forwardIndicate the product of the reaction OH OH CH3-CC- Ph + H2SO4 a 20°C | CH3 Pharrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





