
a)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
a)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
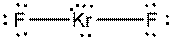
b)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
b)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
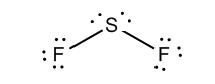
c)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
c)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
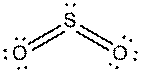
d).
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
d).
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
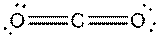
e)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
e)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
f).
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
f).
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
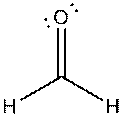
g)
Interpretation: The dissolution of the following in water or
Concept Introduction:
The bonds involving the atoms with various electronegativites having a large dipole moment are called as polar solvents. Example of polar solvent is Water.
The bonds involving the atoms with same electronegativites are called as non polar solvents. Examples of non polar solvents are Gasoline, Carbon tetrachloride etc
Water is a polar solvent as well as dissolves polar solutes and ionic solutes. Carbon tetrachloride
(
g)
Answer to Problem 43E
Answer
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
OWLv2 with MindTap Reader, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for Zumdahl/Zumdahl's Chemistry, 9th
- Draw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forwardWhat is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forwardIndicate the product obtained (formula). F3C. CF3 Br NH2 NH OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forward
- What are the missing intermediates 1, 2, and 3? Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediates and how they occur.arrow_forwardThe following intermediates are to proceed by acetoacetic ester synthesis. What are intermediates 1 and 2 plus the final product 3? Please include a detailed explanation and drawings of the intermediates and how they occurred.arrow_forwardThe chemical formula of "benzimidazole E" is C7H6N2. Draw it.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





