
(a)
To draw two cylinders of different sizes.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The volume of a cylinder can be found using the formula
Calculation:
The two cylinders of different sizes are given as below;
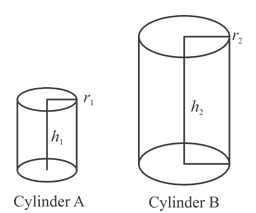
The height of the cylinder A is
(b)
To use a ruler to measure the radius and height of each cylinder.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The volume of a cylinder can be found using the formula
Calculation:
The radius of cylinder is calculated by measuring the distance from the center of the
The height of the cylinder is measured from the center of the circle of the cylinder to the center of the other circle. The height of the cylinder A is
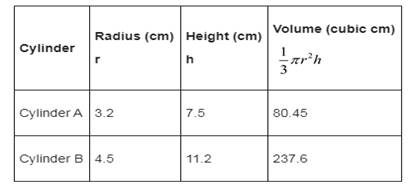
Record of measures in tabular format;
(c)
To write a verbal expression for the difference in volume of the two cylinders
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The volume of a cylinder can be found using the formula
Calculation:
Difference in two cylinders; Cylinder B is more elongated than cylinder as shown in figure. The difference in the radius of the cylinder is slighter but the height of the cylinder B is more than the height of the cylinder A. so, the volume of the cylinder B is approximately more than times the volume of the cylinder A.
(d)
To write and solve an algebraic expression for the difference in volume of the two cylinders.
(d)
Answer to Problem 42PPS
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The volume of a cylinder can be found using the formula
Calculation:
Algebraic expression difference in volume is given as below;
Difference in the volume of cylinder
Chapter 1 Solutions
Glencoe Algebra 2 Student Edition C2014
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Problem #5 Suppose you flip a two sided fair coin ("heads" or "tails") 8 total times. a). How many ways result in 6 tails and 2 heads? b). How many ways result in 2 tails and 6 heads? c). Compare your answers to part (a) and (b) and explain in a few sentences why the comparison makes sense.arrow_forwardA local company has a 6 person management team and 20 employees. The company needs to select 3 people from the management team and 7 employees to attend a regional meeting. How many different possibilities are there for the group that can be sent to the regional meeting?arrow_forwardI have 15 outfits to select from to pack for my business trip. I would like to select three of them to pack in my suitcase. How many packing possibilities are there?arrow_forward
- There are 15 candidates running for any of 5 distinct positions on the local school board. In how many different ways could the 5 positions be filled?arrow_forwardCelina is picking a new frame for a custom piece of artwork. She has to select a frame size, material, and color. There are four different frame sizes, three different frame materials, and six different frame colors. She must chose one option only from each category. How many different possible frames could Celina pick from?arrow_forwardA research study in the year 2009 found that there were 2760 coyotes in a given region. The coyote population declined at a rate of 5.8% each year. How many fewer coyotes were there in 2024 than in 2015? Explain in at least one sentence how you solved the problem. Show your work. Round your answer to the nearest whole number.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





