
Concept explainers
Introduction:
Reproductive cells which pass on genetic traits from the parent to child are produced by the process of meiosis. In order to maintain the same number of chromosomes in each generation, an organism produces gametes. Gametes are sex cells and have half the number of chromosomes.
Answer to Problem 3STP
Correct answer :
The correct answer is option C. 3 and 7
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/justification for the correct answer:
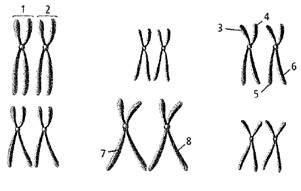
Option C. 3 and 7 −During metaphase of meiosis I, pairs of homologous chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell. During anaphase I the homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. At the end of meiosis I the daughter nuclei have half the number of chromosomes. One chromosome from each pair of homologous chromosomes enters the daughter cell. In anaphase II the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles. At the end of meiosis II, four new cells are formed with nuclei containing only one sister chromatid of the homologous pair. During gamete formation, the sister chromatids separate and they are randomly distributed. So in gametes, the chromosome 3 and 7 are more likely to be found together. Hence, this is the correct option.
Explanation for incorrect answer:
Option A. 1 and 2- Chromosomes 1 and 2 form homologous pair. During gamete formation, they will separate and enter different gametes. Hence, this is not the correct option.
Option B. 3 and 6- Chromosomes 3 and 6 will separately enter different gametes so they will not be found together. Hence, this is not the correct option.
Option D. 5 and 6- Chromosomes 5 and 6 are sister chromatids so they will separate during meiosis II. Hence, this is not the correct option.
Chapter 11 Solutions
EP BIOLOGY 2012-STUDENTWORKS ONLINE
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
- please draw in what the steps are given. Thank you!arrow_forwardplease draw in and fill out the empty slots from image below. thank you!arrow_forwardThere is a species of eagle, which lives in a tropical forest in Brazil. The alula pattern of its wings is determined by a single autosomal gene with four alleles that exhibit an unknown hierarchy of dominance. Genetic testing shows that individuals 1-1, 11-4, 11-7, III-1, and III-4 are each homozygous. How many possible genotypes among checkered eagles in the population?arrow_forward
- students in a science class investiged the conditions under which corn seeds would germinate most successfully. BAsed on the results which of these factors appears most important for successful corn seed germination.arrow_forwardI want to write the given physician orders in the kardex formarrow_forwardAmino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forward
- What is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forwardWhy cells go through various types of cell division and how eukaryotic cells control cell growth through the cell cycle control system?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





