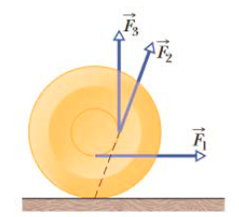
Problem 1Q: Figure 11-23 shows three particles of the same mass and the same constant speed moving as indicated... Problem 2Q: Figure 11-24 shows two particles A and B at xyz coordinates 1 m, 1 m, 0 and 1 m, 0, 1 m. Acting on... Problem 3Q: What happens to the initially stationary yo-yo in Fig. 11-25 if you pull it via its string with a... Problem 4Q: The position vector r of a particle relative to a certain point has a magnitude of 3 m, and the... Problem 5Q: In Fig. 11-26, three forces of the same magnitude are applied to a particle at the origin F1 acts... Problem 6Q: The angular momenta t of a particle in four situations are 1 = 3t 4; 2 = -6t2; 3 = 2; 4 = 4/t.... Problem 7Q: A rhinoceros beetle rides the rim of a horizontal disk rotating counterclockwise like a... Problem 8Q: Figure 11-27 shows an overhead view of a rectangular slab that can spin like a merry-go-round about... Problem 9Q: Figure 11-38 gives the angular momentum magnitude L of a wheel versus time t. Rank the four lettered... Problem 10Q: Figure 11-29 shows a particle moving at constant velocity v and five points with their xy... Problem 11Q: A cannonball and a marble roll smoothly from rest down an incline. Is the cannonballs a time to the... Problem 12Q Problem 1P: A car travels at 80 km/h on a level road in the positive direction of an x axis. Each tire has a... Problem 2P: An automobile traveling at 80.0 km/h has tires of 75.0 cm diameter, a What is the angular speed of... Problem 3P Problem 4P: A uniform solid sphere rolls down an incline. a What must be the incline angle if the linear... Problem 5P: ILW A 1000 kg car has four 10 kg wheels. When the car is moving, what fraction of its total kinetic... Problem 6P: Figure 11-30 gives the speed v versus time t for a 0.500 kg object of radius 6.00 cm that rolls... Problem 7P: ILW In Fig. 11-31, a solid cylinder of radius 10cm and mass 12 kg starts from rest and rolls without... Problem 8P: Figure 11-32 shows the potential energy Ux of a solid ball that can roll along an x axis. The scale... Problem 9P: GO In Fig. 11-33, a solid ball rolls smoothly from rest starling at height H = 6.0 m until it leaves... Problem 10P: A hollow sphere of radius 0.15 m, with rotational inertia I = 0.040 kgm2 about a line through its... Problem 11P: In Fig. 11-34, a constant horizontal force Fapp of magnitude 10 N is applied to a wheel of mass 10... Problem 12P: GO In Fig. 11-35, a solid brass ball of mass 0.280 g will roll smoothly along a loop-the-loop track... Problem 13P: GO Nonuniform ball. In Fig. 11-36, a ball of mass M and radius R rolls smoothly from rest down a... Problem 14P: In Fig. 11-37, a small, solid, uniform ball is to be shot from point P so that it rolls smoothly... Problem 15P: GO A bowler throws a bowling ball of radius R = 11 cm along a lane. The ball Fig. 11-38 slides on... Problem 16P: GO Nonuniform cylindrical object. In Fig. 11-39, a cylindrical object of mass M and radius R rolls... Problem 17P: SSM A yo-yo has a rotational inertia of 950 gcm2 and a mass of 120 g. Its axle radius is 3.2 mm, and... Problem 18P Problem 19P: In unit-vector notation, what is the net torque about the origin on a flea located at coordinates 0,... Problem 20P: A plum is located at coordinates 2.0 m, 0, 4.0 m. In unit-vector notation, what is the torque about... Problem 21P: In unit-vector notation, what is the torque about the origin on a particle located at coordinates 0,... Problem 22P: A particle moves through an xyz coordinate system while a force acts on the particle. When the... Problem 23P: Force F=(2.0N)i(3.0N)k acts on a pebble with position vector r=(0.50m)j(2.0m)k relative to the... Problem 24P: In unit-vector notation, what is the torque about the origin on a jar of jalapeo peppers located at... Problem 25P: SSM Force F=(8.0N)i+(6.0N)j acts on a particle with position vector r=(3.0m)i+(4.0m)j. What are a... Problem 26P: At the instant of Fig. 11-40, a 2.0 kg particle P has a position vector r of magnitude 3.0 m and... Problem 27P: SSM At one instant, force F=4.0N acts on a 0.25 kg object that has position vector r=(2.0i2.0k)m and... Problem 28P: A 2.0 kg particle-like object moves in a plant with velocity components vx = 30m/s and vy = 60 m/s... Problem 29P: ILW In the instant of Fig, 11-41, two particles move in an xy plane. Particle P1 has mass 6.5 kg and... Problem 30P: At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is... Problem 31P: In Fig. 11-42, a 0.400 kg ball is shot directly upward at initial speed 40.0 m/s. What is its... Problem 32P: A particle is acted on by two torques about the origin: 1 has a magnitude of 2.0 Nm and is directed... Problem 33P: SSM WWW ILW At time t = 0, a 3.0 kg particle with velocity v=(5.0m/s)i(6.0m/s)j is at x = 3.0 m, y =... Problem 34P: A particle is to move in an xy plane, clockwise around the origin as seen from the positive side of... Problem 35P: At time t, the vector r=4.0t2i(2.0t+6.0t2)j gives the position of a 3.0 kg particle relative to the... Problem 36P Problem 37P: GO In Fig. 11-44, three particles of mass m = 23 g are fastened to three rods of length d = 12cm and... Problem 38P: A sanding disk with rotational inertia 1.2 103 kgm2 is attached to an electric drill whose motor... Problem 39P: SSM The angular momentum of a flywheel having a rotational inertia of 0.140 kgm2 about its central... Problem 40P: A disk with a rotational inertia of 7.00 kgm2 rotates like a merry-go-round while undergoing a... Problem 41P: GO Figure 11-45 shows a rigid structure consisting of a circular hoop of radius R and mass m, and a... Problem 42P: Figure 11-46 gives the torque that acts on an initially stationary disk that can rotate about its... Problem 43P Problem 44P: A Texas cockroach of mass 0.17 kg runs counterclockwise around the rim of a lazy Susan a circular... Problem 45P: SSM WWW A man stands on a platform that is rotating without friction with an angular speed of 1.2... Problem 46P: The rotational inertia of a collapsing spinning star drops to 13 its initial value. What is the... Problem 47P: SSM A track is mounted on a large wheel that is free to turn with negligible friction about a... Problem 48P: A Texas cockroach walks from the center of a circular disk that rotates like a merry-go-round... Problem 49P: Two disks are mounted like a merry-go-round on low-friction bearings on the same axle and can be... Problem 50P: The rotor of an electric motor has rotational inertia Im = 2.0 103 kgm2 about its central axis. the... Problem 51P: SSM ILW A wheel is rotating freely at angular speed 800 rev/min on a shah whose rotational inertia... Problem 52P: GO A cockroach of mass m lies on the rim of a uniform disk of mass 4.00m that can rotate freely... Problem 53P: GO In Fig. 11-50 an overhead view, a uniform thin rod of length 0.500 m and mass 4.00 kg can rotate... Problem 54P: GO Figure 11-51 shows an overhead view of a ring that can rotate about its center like a... Problem 55P: A horizontal vinyl record of mass 0.10 kg and radius 0.10 m rotates freely about a vertical axis... Problem 56P: In a long jump, an athlete leaves the ground with an initial angular momentum that tends to rotate... Problem 57P: A uniform disk of mass 10m and radius 3.0r can rotate freely about its fixed center like a... Problem 58P: A horizontal platform in the shape of a circular disk rotates on a frictionless bearing about a... Problem 59P: Figure 11-52 is an overhead view of a thin uniform rod of length 0.800 m in and mass M rotating... Problem 60P: In Fig. 11-53, a 1.0 g bullet is tired into a 0.50 kg block attached to the end of a 0.60 m... Problem 61P: The uniform rod length 0.60 m, mass 1.0 kg in Fig. 11-54 rotates in the plane of the figure about an... Problem 62P: GO During a jump to his partner, an aerialist is to make a quadruple somersault lasting a time t =... Problem 63P: GO In Fig. 11-56, a 30 kg child stands on the edge of a stationary merry-go-round of radius 2.0 m.... Problem 64P: A ballerina begins a tour jet Fig. 11-19a with angular speed i and a rotational inertia consisting... Problem 65P: SSM WWW Two 2.00 kg balls are attached to the ends of a thin rod of length 50.0 cm and negligible... Problem 66P Problem 67P Problem 68P Problem 69P: A certain gyroscope consists of a uniform disk with a 50 cm radius mounted at the center of an axle,... Problem 70P: A uniform solid ball rolls smoothly along a floor, then up a ramp inclined at 15.0. It momentarily... Problem 71P: SSM In Fig. 11-60, a constant horizontal force Fapp of magnitude 12 N is applied to a uniform solid... Problem 72P: A thin-walled pipe rolls along the floor. What is the ratio of its translational kinetic energy to... Problem 73P Problem 74P Problem 75P Problem 76P: A uniform block of granite in the shape of a book has face dimensions of 20 cm and 15 cm and a... Problem 77P: SSM Two particles, each of mass 2.90 104 kg and speed 5.46 m/s. travel in opposite directions along... Problem 78P: A wheel of radius 0.250 m, moving initially al 43.0 m/s, rolls to a stop in 225 m. Calculate the... Problem 79P: Wheels A and B in Fig. 11-61 are connected by a belt that does not slip. The radius of B is 3.00... Problem 80P Problem 81P: SSM A uniform wheel of mass 10.0 kg and radius 0.400 m is mounted rigidly on a massless axle through... Problem 82P: A uniform rod rotates in a horizontal plane about a vertical axis through one end. The rod is 6.00 m... Problem 83P: A solid sphere of weight 36.0 N rolls up an incline at an angle of 30.0. At the bottom of the... Problem 84P: Suppose that the yo-yo in Problem 17, instead of rolling from rest, is thrown so that its initial... Problem 85P: A girl of mass M stands on the rim of a frictionless merry-go-round of radius R and rotational... Problem 86P format_list_bulleted

 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




