
(a)
Interpretation:
The normal boiling point of dichlorodimethylsilane has to be determined
Concept Introduction:
Boiling point of a liquid: The temperature at which external pressure and vapour pressure of the liquid become same.
Normal boiling point: When the external pressure is
(a)
Answer to Problem 39IL
The normal boiling point of dichlorodimethylsilane is
The temperatures at which liquid have a vapour pressures of
The molar enthalpy of vaporization of is
Explanation of Solution
The normal boiling point of dichlorodimethylsilane is calculated
Given:
Normal boiling point is the temperature when the external pressure is
From the given data it is clear that the temperature at which the pressure is
Thus the normal boiling point of dichlorodimethylsilane is
(b)
Interpretation:
The graph of
Concept Introduction:
Clausius-Clapeyron equation:
From this relationship we can calculate the molar enthalpy of vaporization by knowing the corresponding temperature and pressure values.
If we have pressures at two different temperatures, then enthalpy of vaporization can be calculated by
(b)
Answer to Problem 39IL
Using the given data we can plot the graph of
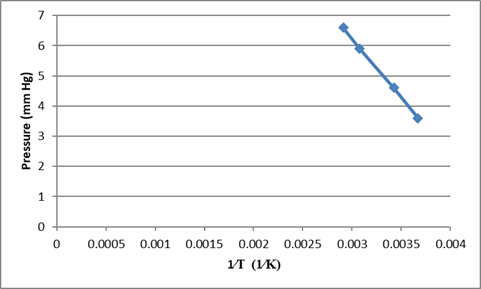
The temperature at which liquid has a vapour pressure of
The temperature at which liquid has a vapour pressure
Explanation of Solution
The temperatures at which liquid have a vapour pressures of
Given:
The values of
Using the given data we can plot the graph of
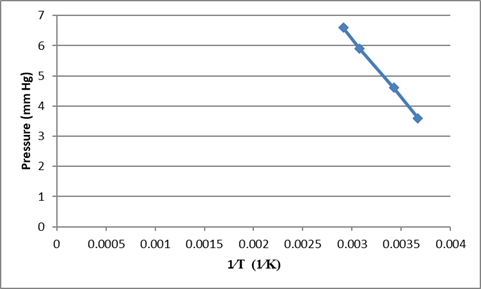
From the slope of the graph we can find the value of
Using the equation for the straight line in the plot
C, the constant value can be calculated by substituting any one of the value of pressure and temperature from the table given in the equation.
Substituting the values
From this equation we can calculate the temperature at which the pressures are
When the pressure is
The temperature at which the pressures is
When the pressure is
The temperature at which the pressures is
(c)
Interpretation:
The molar enthalpy of vaporization has to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Clausius-Clapeyron equation:
From this relationship we can calculate the molar enthalpy of vaporization by knowing the corresponding temperature and pressure values.
If we have pressures at two different temperatures, then enthalpy of vaporization can be calculated by
Boiling point of a liquid: The temperature at which external pressure and vapour pressure of the liquid become same.
Normal boiling point: When the external pressure is
Molar enthalpy of vaporization: The energy required to convert liquid to gas of 1mol of a substance is called molar enthalpy of vaporization
(c)
Answer to Problem 39IL
The molar enthalpy of vaporization of is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The molar enthalpy of vaporization using the given data is calculated.
Substituting the values
The molar enthalpy of vaporization using the given data is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
CHEMISTRY+CHEM...(LL)-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<
- Hello, I am doing a court case analysis in my Analytical Chemistry course. The case is about a dog napping and my role is prosecution of the defendant. I am tasked in the Area of Expertise in Neutron Activation and Isotopic Analysis. Attached is the following case study reading of my area of expertise! The landscaping stone was not particularly distinctive in its decoration but matched both the color and pattern of the Fluential’s landscaping stone as well as the stone in the back of the recovered vehicle. Further analysis of the stone was done using a technique called instrumental neutron activation analysis. (Proceed to Neutron Activation data) Photo Notes: Landscaping stone recovered in vehicle. Stone at Fluential’s home is similar inappearance. Finally, the white paint on the brick was analyzed using stable isotope analysis. The brick recovered at the scene had smeared white paint on it. A couple of pieces of brick in the back of the car had white paint on them. They…arrow_forwardCite the stability criteria of an enamine..arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of a 0.01m solution of acetic acid use pka of 4.75arrow_forward
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forward
- Please answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- Consider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
