
1.
Calculate the number of additional direct labor hours (DLHs) that will be required each month to fill the Company G’s order.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the number of additional direct labor hours (DLHs):
Note: The standard direct labor hour (DLH) per finished valve is ½ hour.
2.
Prepare an analysis showing the impact on operating income of accepting the Company’s order.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an analysis showing the impact on operating income of accepting the Company’s order.
| Particulars | Per unit | Total for 120,000 units |
| Incremental revenue (a) | $ 21.00 | $ 2,520,000 |
| Incremental costs | ||
| Variable costs: | ||
| Direct materials | 6 | 720000 |
| Direct labor | 8 | 960,000 |
| Variable overhead | 3 | 360,000 |
| Total variable costs | $ 17 | $ 2,040,000 |
| Fixed overhead: | ||
| Supervisory and clerical costs | 48,000 | |
| Total incremental costs (b) | $ 2,088,000 | |
| Incremental operating income (loss) | $ 432,000 |
Table (1)
3.
Calculate the minimum unit price that Company W could accept for the company G’s order without reducing operating income.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The least unit selling price that Company W could accept without decreasing operating income equals a price that covers variable costs plus the additional fixed costs. In this case, there are no opportunity costs. The $30.00 suggested selling price is irrelevant for the special order:
| Particulars | Amounts in ($) |
| Incremental variable costs, per unit: | |
| Direct materials | $ 6.00 |
| Direct labor | $ 8.00 |
| Variable overhead | $ 3.00 |
| Additional fixed cost | 0.4 |
| Minimum selling price per unit | $ 17.40 |
Table (2)
4.
Calculate the minimum unit selling price using the Goal Seek function in Excel for the special sales order and prove the answer of requirement 3.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the minimum unit selling price using the Goal Seek function in Excel for the special sales order and prove the answer of requirement 3:
Step: 1 set up the equation:
| Particulars | Per unit | Total for 120,000 units |
| Four month volume (units) | $ 21.00 | $ 120,000 |
| Selling per unit | ||
| Incremental revenue, special sales order | $ 0 | |
| Incremental costs: | ||
| Variable per unit | 17 | |
| Total Variable | $ 2,040,000 | |
| Total fixed | 48,000 | |
| Opportunity cost | 0 | |
| Total incremental costs full order | $ 2,088,000 | |
| Incremental operating income (loss) | $ -2,088,000 |
Table (3)
Workings:
| Special order characteristics | |
| # of units | 120,000 |
| offer price (per unit) | $ 21 |
| Cost data pressure value: | |
| Direct material (per unit) | $ 6 |
| Direct labor: | |
| Hours per unit | 0.5 |
| DL cost per unit | $ 8 |
| Manufacturing overhead per unit | $ 9 |
| % of overhead that is variable | 33.33% |
| Additional fixed | |
| Per month charge | $ 12,000 |
| Duration (# of months) | 4 |
Table (4)
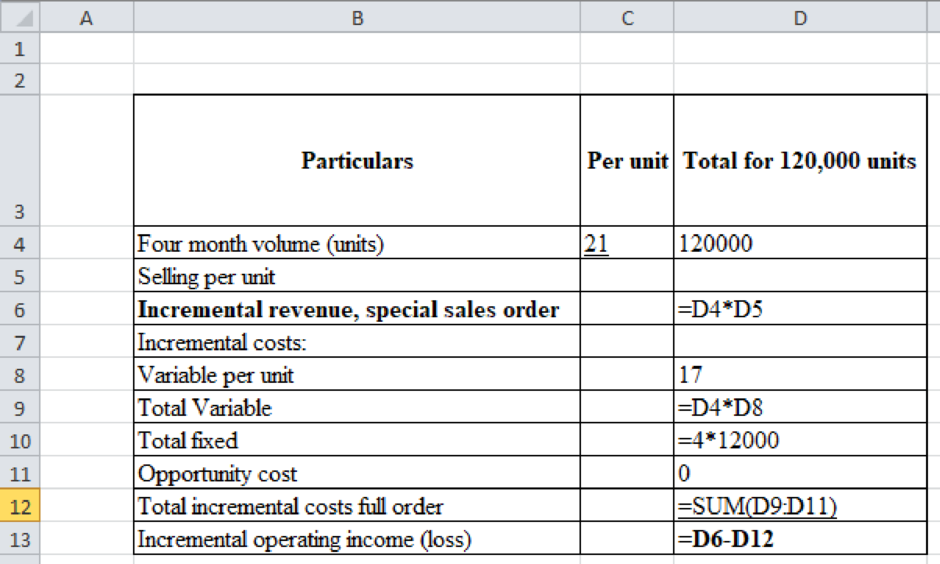
Table (5)
Step 2: Run the goal seek as follows:
In excel go to data tab and select what if analysis, then select Goal seek rom the drop down menu. Then select the respective values as follows:
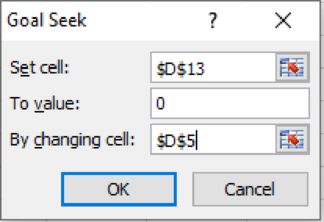
Figure (1)
After selecting click ok.
Figure (2)
Step 2: Result:
Then the result will be as follows:
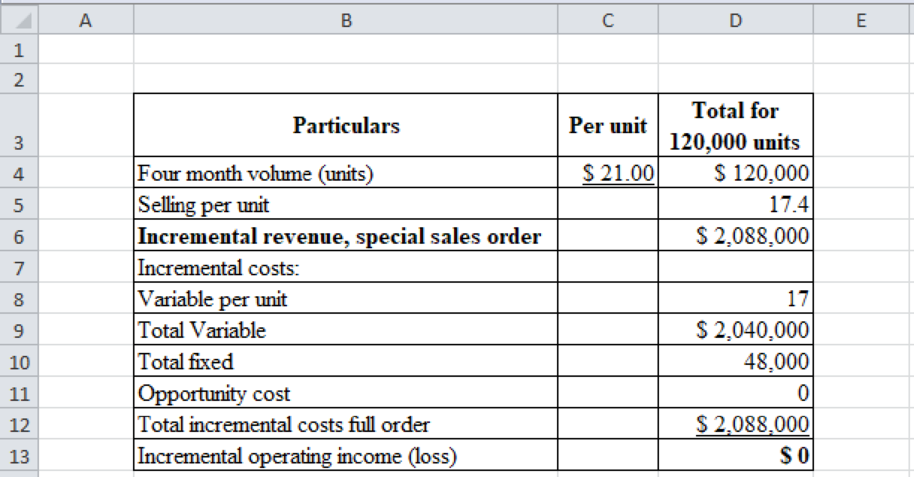
Table (6)
5.
Calculate the revised breakeven selling price per unit for G Company’s special sales order.
5.
Explanation of Solution
The minimum unit price that Company W could accept without reducing operating income must cover all incremental costs: variable, fixed, and opportunity costs.
| Particulars | Per unit | Amounts in ($) |
| Incremental variable cost/unit: | ||
| Direct materials | $ 6.00 | |
| Direct labor | $ 8.00 | |
| Variable overhead | $ 3.00 | $ 17.00 |
| Incremental fixed costs/unit ($48,000 ÷ 120,000 units) | 0.4 | |
| Minimum selling price per unit (a) | $ 17.40 | |
| Opportunity cost, per unit: | ||
| Total lost sales (in units) (4 × 5,000 units) | 20,000 | |
| Regular selling price per unit | $ 30.00 | |
| Less: variable costs (per unit): | ||
| Direct materials | $ 6.00 | |
| Direct labor | $ 8.00 | |
| Variable manufacturing overhead | $ 3.00 | |
| Sales commissions (5% of sales $) | $ 1.50 | |
| Freight charge (per unit) | $ 1.00 | |
| Total variable cost per unit | $ 19.50 | |
| CM per unit, regular sales | $ 10.50 | |
| Total lost CM (20,000 units | $ 210,000 | |
| Divide by: Four month units | 120,000 | |
| Lost CM per unit of special sales order (b) | 1.75 | |
| Minimum selling price per unit | $ 19.15 |
Table (7)
6.
Identify the strategic factors that the company should consider before accepting the order.
6.
Explanation of Solution
The following factors should be considered before accepting the order:
- The special order’seffect on sales at regular prices.
- The impact on local, state, and federal taxes.
- The company's “relevant range” of activity and whether the special order will cause volume to exceed this range.
- The likelihood of future sales and the effects of participating in the international marketplace.
- The effect on machinery.
- The strategic benefit of the long-term commitment from Company G.
- The firm that would handle warranty, repair, and service needs to be analyzed.
7.
Identify the factors related to international business that Company W should consider before accepting the Company G’s order.
7.
Explanation of Solution
- The customs duties and import and export limitations which might affect the special order and future business.
- However the special order will be completed in the relatively short time of a few months, and the foreign exchange rates might change considerably in this period. Hence, the special order agreement regarding the sales price needs to be analyzed.
- If Company W is not now significantly involved in global sales, then the way in which the firm might use this opportunity to increase its exposure in foreign markets needs to be described.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Cost Management
- Can you solve this financial accounting question using valid financial methods?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardMurray Industries applies manufacturing overhead to its cost objects on the basis of 75% of direct material cost. If Job 37A had $96,000 of manufacturing overhead applied to it during July, the direct materials assigned to Job 37A was: A. $72,000 B. $96,000 C. $128,000 D. $144,000arrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forward
- Accurate Answerarrow_forwardAt the beginning of the year, Momentum Corporation estimated its manufacturing overhead to be $425,000. At the end of the year, actual machine-hours were 34,500 hours, actual manufacturing overhead was $408,200, and manufacturing overhead was underapplied by $18,400. If the predetermined overhead rate is based on machine-hours, then the estimated machine-hours at the beginning of the year used in the predetermined overhead rate must have been: (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem using the correct accounting principles.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





