
Systematic versus Unsystematic Risk Consider the following information about Stocks I and II:
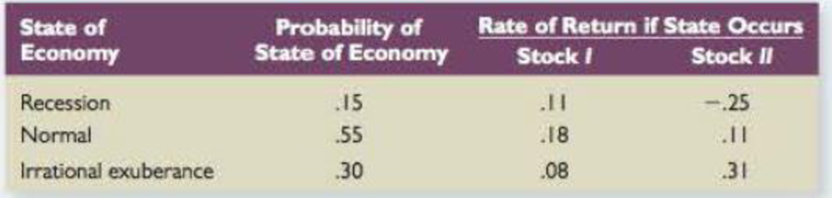
The market risk premium is 7.5 percent, and the risk-free rate is 4 percent. Which stock has the most systematic risk? Which one has the most unsystematic risk? Which stock is “riskier”? Explain.
To determine: The Stock which has more systematic risk, unsystematic risk and stock which is riskier.
Introduction: Systematic Risk is acknowledged as non diversifiable risks or market risk. Such category of risk is not intended to be separated by distinguishing assets. Systematic risk leads on how a particular investment in a distinguished portfolio that support financially to the total or aggregate risk of a business's financial funding.
Unsystematic Risk is acknowledged as diversifiable or residual or particular risk. The proportion of a corporation’s total or aggregate risk which can be barred by holding such risks in a distinguished or as diversified asset portfolio.
Answer to Problem 33QP
Stock I have more systematic risk, Stock II has more unsystematic risk and Stock I is riskier.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Expected Return for Stock I
Therefore the Expected Return for Stock I is 13.95%
Determine the Beta for Stock I
Using CAPM formula we calculate the beta for Stock I as,
Therefore the Beta for Stock I is 1.33
Determine the Variance for Stock I
Therefore the Variance for Stock I is 0.002095
Determine the Standard Deviation for Stock I
Therefore the Standard Deviation for Stock I is 4.58%
Determine the Expected Return for Stock II
Therefore the Expected Return for Stock II is 11.60%
Determine the Beta for Stock II
Using CAPM formula we calculate the beta for Stock II as,
Therefore the Beta for Stock II is 1.01
Determine the Variance for Stock II
Therefore the Variance for Stock II is 0.031404
Determine the Standard Deviation for Stock II
Therefore the Standard Deviation for Stock II is 17.72%
- Stock I have less systematic risk than Stock II since the beta of Stock II is lesser than Stock I and Stock II is said to have more total risk.
- Hence Stock I have more systematic risk and Stock II have more unsystematic risk and greater total risk.
- Stock I is riskier because unsystematic risk can be diversified due to lack of volatility in the stock return.
- Additionally Stock I have higher expected return and higher risk premium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK CORPORATE FINANCE
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT




