
The velocity of the system just after the collision using Newton’s second law and the comparison of the answer with the result of Example 11.4.
Answer to Problem 32PQ
The velocity of the system just after the collision using Newton’s second law is
Explanation of Solution
The free-body diagram of the system is shown in figure 1.
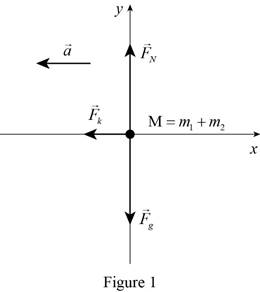
The two-train system only moves in
Write the expression for the Newton’s second law in
Here,
Refer to figure 1. The only force acting in
Write the equation for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (I).
The kinetic friction is proportional to the normal force and the normal force is in turn equal to the weight of the train.
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (III).
Put the above equation in equation (II) and rewrite it for
Initially only the freight train has momentum. Assume that the two trains move together with velocity
Here,
Rewrite the above equation for
Now consider the motion of the system just after the collision to the moment it comes to rest.
Replace
The speed of the two-train system as it comes to rest is zero.
Write the expression for the final speed of the system as it comes to rest.
Here,
Write the constant-acceleration equation of motion.
Here,
Put equations (IV) to (VI) in the above equation and rewrite it for
To find the range of possible initial freight train velocities, the extreme values of the coefficient of kinetic friction must be used.
Write the equation for
Here,
Conclusion:
Given that the value of
Substitute
Substitute
Here,
The system moves in
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Here,
It is given that the train crosses the red signal at a speed of
Since the train passed the red signal with the speed of
Write the expression for the maximum velocity of the system.
Here,
Substitute
The range of the speed of the two-train system is
Therefore, the velocity of the system just after the collision using Newton’s second law is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR KATZ'S PHYSICS FOR SC
- Review Conceptual Example 2 before attempting this problem. Two slits are 0.158 mm apart. A mixture of red light (wavelength = 693 nm) and yellow-green light (wavelength = 567 nm) falls on the slits. A flat observation screen is located 2.42 m away. What is the distance on the screen between the third-order red fringe and the third-order yellow-green fringe? m = 3 m = 3 m = 0 m = 3 m = 3 Fringes on observation screenarrow_forwardA film of oil lies on wet pavement. The refractive index of the oil exceeds that of the water. The film has the minimum nonzero thickness such that it appears dark due to destructive interference when viewed in visible light with wavelength 643 nm in vacuum. Assuming that the visible spectrum extends from 380 to 750 nm, what is the longest visible wavelength (in vacuum) for which the film will appear bright due to constructive interference? Number Unitsarrow_forwardA piece of metal is placed on top of a 2.0 - kg wooden block (mass density = 562 kg/m³) piece. UseArchimedes' principle to calculate the mass (in kg) of copper if the top of the wood surface is exactly at thewater's surface?arrow_forward
- A filmmaker wants to achieve an interesting visual effect by filming a scene through a converging lens with a focal length of 50.0 m. The lens is placed betwen the camera and a horse, which canters toward the camera at a constant speed of 7.9 m/s. The camera starts rolling when the horse is 36.0 m from the lens. Find the average speed of the image of the horse (a) during the first 2.0 s after the camera starts rolling and (b) during the following 2.0 s.arrow_forwardAnswer the question (Physics)arrow_forwardsolve smybolically and plug in numbers and solve at the endarrow_forward
- answer the question symbolically until you have to plug in numbers. show all work please.arrow_forwardWhat is the direction of the magnetic force on a NEGATIVE CHARGE that moves as shown in each of the six cases?arrow_forwardHi! I need help with these calculations for part i and part k for a physics Diffraction Lab. We used a slit width 0.4 mm to measure our pattern.arrow_forward
- Examine the data and % error values in Data Table 3 where the angular displacement of the simple pendulum decreased but the mass of the pendulum bob and the length of the pendulum remained constant. Describe whether or not your data shows that the period of the pendulum depends on the angular displacement of the pendulum bob, to within a reasonable percent error.arrow_forwardIn addition to the anyalysis of the graph, show mathematically that the slope of that line is 2π/√g . Using the slope of your line calculate the value of g and compare it to 9.8.arrow_forwardAn object is placed 24.1 cm to the left of a diverging lens (f = -6.51 cm). A concave mirror (f= 14.8 cm) is placed 30.2 cm to the right of the lens to form an image of the first image formed by the lens. Find the final image distance, measured relative to the mirror. (b) Is the final image real or virtual? (c) Is the final image upright or inverted with respect to the original object?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





