
Maxwell Company produces a variety of kitchen appliances, including cooking ranges and dishwashers. Over the past several years, competition has intensified. In order to maintain—and perhaps increase—its market share, Maxwell’s management decided that the overall quality of its products had to be increased. Furthermore, costs needed to be reduced so that the selling prices of its products could be reduced. After some investigation, Maxwell concluded that many of its problems could be traced to the unreliability of the parts that were purchased from outside suppliers. Many of these components failed to work as intended, causing performance problems. Over the years, the company had increased its inspection activity of the final products. If a problem could be detected internally, then it was usually possible to rework the appliance so that the desired performance was achieved. Management also had increased its warranty coverage; warranty work had been increasing over the years.
David Haight, president of Maxwell Company, called a meeting with his executive committee. Lee Linsenmeyer, chief engineer; Kit Applegate, controller; and Jeannie Mitchell, purchasing manager, were all in attendance. How to improve the company’s competitive position was the meeting’s topic. The conversation of the meeting was recorded as seen on the following page:
DAVID: We need to find a way to improve the quality of our products and at the same time reduce costs. Lee, you said that you have done some research in this area. Would you share your findings?
LEE: As you know, a major source of our quality problems relates to the poor quality of the parts we acquire from the outside. We have a lot of different parts, and this adds to the complexity of the problem. What I thought would be helpful would be to redesign our products so that they can use as many interchangeable parts as possible. This will cut down the number of different parts, make it easier to inspect, and cheaper to repair when it comes to warranty work. My engineering staff has already come up with some new designs that will do this for us.
JEANNIE: I like this idea. It will simplify the purchasing activity significantly. With fewer parts, I can envision some significant savings for my area. Lee has shown me the designs so I know exactly what parts would be needed. I also have a suggestion. We need to embark on a supplier evaluation program. We have too many suppliers. By reducing the number of different parts, we will need fewer suppliers. And we really don’t need to use all the suppliers that produce the parts demanded by the new designs. We should pick suppliers that will work with us and provide the quality of parts that we need. I have done some preliminary research and have identified five suppliers that seem willing to work with us and assure us of the quality we need. Lee may need to send some of his engineers into their plants to make sure that they can do what they are claiming.
DAVID: This sounds promising. Kit, can you look over the proposals and their estimates and give us some idea if this approach will save us any money? And if so, how much can we expect to save?
KIT: Actually, I am ahead of the game here. Lee and Jeannie have both been in contact with me and have provided me with some estimates on how these actions would affect different activities. I have prepared a handout that includes an activity table revealing what I think are the key activities affected. I have also assembled some tentative information about activity costs. The table gives the current demand and the expected demand after the changes are implemented. With this information, we should be able to assess the expected cost savings.
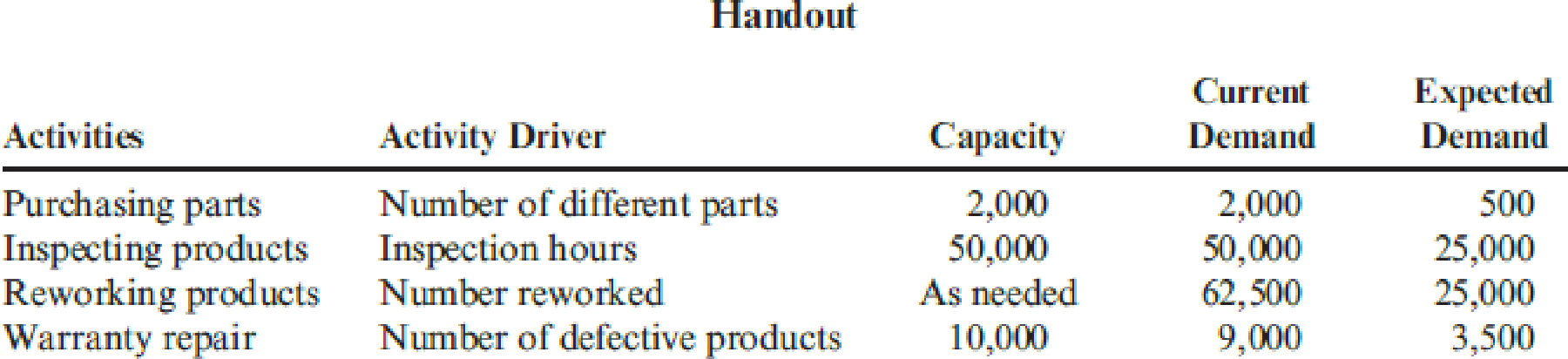
Additionally, the following activity cost data are provided:
Purchasing parts: Variable activity cost: $30 per part number; 20 salaried clerks, each earning a $45,000 annual salary. Each clerk is capable of processing orders associated with 100 part numbers.
Inspecting parts: Twenty-five inspectors, each earning a salary of $40,000 per year. Each inspector is capable of 2,000 hours of inspection.
Reworking products: Variable activity cost: $25 per unit reworked (labor and parts).
Warranty: Twenty repair agents, each paid a salary of $35,000 per year. Each repair agent is capable of repairing 500 units per year. Variable activity costs: $15 per product repaired.
Required:
- 1. Compute the total savings possible as reflected by Kit’s handout. Assume that resource spending is reduced where possible.
- 2. Explain how redesign and supplier evaluation are linked to the savings computed in Requirement 1. Discuss the importance of recognizing and exploiting internal and external linkages.
- 3. Identify the organizational and operational activities involved in the strategy being considered by Maxwell Company. What is the relationship between organizational and operational activities?
1.
Calculate the total savings that are possible by assuming that resource spending can be reduced where ever possible.
Explanation of Solution
Strategic cost management: “Strategic cost management” is the process of managing and understanding the cost relationships among the activities in an “organization's value chain” for the benefit of the firm.
Internal linkages: Internal linkages explain the relationship between activities that are carried out within a company’s section of the “value chain”.
External linkages: External linkages explain the relationship of a company’s value-chain activities that are carried out with its “suppliers and customers”.
Calculate the total savings:
| Savings | Amount |
| Purchasing | $720,000(1) |
| Inspecting | $480,000(3) |
| Reworking | $937,500(5) |
| Warranty | $537,500(6) |
| Total | $2,675,000 |
Table (1)
Therefore, the amount of total savings is $2,675,000.
Working notes:
(1)Calculate the savings for purchasing parts:
Note:
(2)Calculate the number of clerks required for purchasing parts:
(3)Calculate the savings for inspecting:
(4)Calculate the number of inspectors required for inspecting:
Note:
(5)Calculate the savings for reworking:
Note:
(6)Calculate the savings for warranty:
Note:
(7)Calculate the number of agents required for warranty:
(8)Calculate the number of defective units:
2.
Explain the manner in which redesign and supplier evaluation are linked to the savings computed in requirement 1 and state the significance of recognizing and exploiting internal and external linkages.
Explanation of Solution
- The redesign decreases the number of different parts by manufacturing products that use interchangeable parts. This lowers the purchasing activity’s demand and, together, it makes easier for establishing improvements that are related to quality.
- Assessment of suppliers can identify the suppliers who are voluntarily willing and have the ability to produce defect-free parts. The demand for “rework, inspection and warranty” decreases since the number of defect-free parts increases.
- This illustration explains the significance of both “internal and external linkages” by relating the internal activity, redesign, to activities such as “purchasing, inspection, rework, and warranty”.
3.
Identify the organizational and operational activities involved in the strategy and state the relationship between organizational and operational activities.
Explanation of Solution
- The operational activities involve “designing, evaluating suppliers, inspecting, purchasing, rework, and warranty” and other connected organizational activities involve “complexity, providing quality, and designing and producing quality”.
- Organizational activities can identify the “day-to-day business activities” carried out the firm. Conversely, it can imply or specify organizational activities that require improvisation.
- In this illustration, difficulty is reduced by decreasing the number of different parts. Emphasize is given to “total quality and engineering design” for decreasing difficulty. Therefore, it can be said that there exists a circular relationship among “organizational and operational activities”.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Calculate Accounting income after tax?arrow_forwardSummit Enterprises had a pre-tax accounting income of $45 million during the current year. The company's only temporary difference for the year was service fees received in advance for the next year in the amount of $32 million. What would be Summit Enterprises' taxable income for the year?arrow_forwardNot use ai solution please solve things question general Accountingarrow_forward
- What was the sales price per unit?arrow_forwardTutor need step by step answerarrow_forwardEB Accessories is considering the purchase of a land and the construction of a new factory. The land, to be bought immediately, has a cost of $150,000 and the building, to be developed by the end of the first year, would cost $225,000. It is estimated that the firm's after-tax cash flow will be increased by $80,000 starting at the end of the second year, and that this incremental flow would increase at a constant rate of 20% per year over the next 10 years. What is the approximate payback period of this investment? Bella Italia, a famous Italian restaurant, is faced with two independent investment opportunities, i.e., opening of their new outlet in one of two prime locations that restaurant is considering. The company has an investment policy which requires acceptable projects to recover all costs within 4 years. The company uses the discounted payback method to assess potential projects and utilizes a discount rate of 12%. The cash flows for the two projects are as follows:…arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

