
Economic rents Taxes are a cost, and, therefore, changes in tax rates can affect consumer prices, project lives, and the value of existing firms. The following problem illustrates this. It also illustrates that tax changes that appear to be “good for business” do not always increase the value of existing firms. Indeed, unless new investment incentives increase consumer demand, they can work only by rendering existing equipment obsolete.
The manufacture of bucolic acid is a competitive business. Demand is steadily expanding, and new plants are constantly being opened. Expected cash flows from an investment in a new plant are as follows:
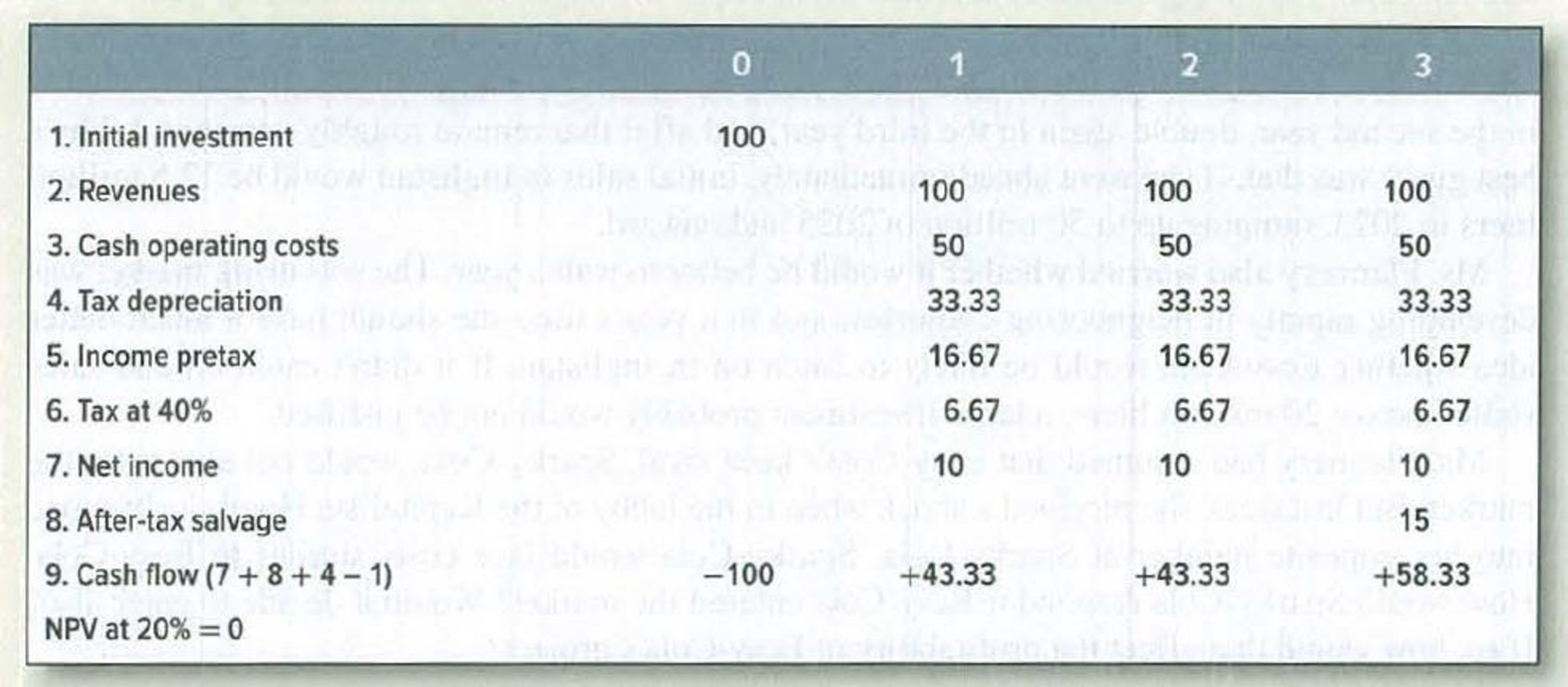
Assumptions:
- 1. Tax depreciation is straight-line over three years.
- 2. Pretax salvage value is 25 in year 3 and 50 if the asset is scrapped in year 2.
- 3. Tax on salvage value is 40% of the difference between salvage value and
depreciated investment. - 4. The cost of capital is 20%.
- a. What is the value of a one-year-old plant? Of a two-year-old plant?
- b. Suppose that the government now changes tax depreciation to allow a 100% writeoff in year 1. How does this affect the value of existing one- and two-year-old plants? Existing plants must continue using the original tax depreciation schedule.
- c. Would it now make sense to scrap existing plants when they are two rather than three years old?
- d. How would your answers change if the corporate income tax were abolished entirely?
a)
To determine: values of one year old plant and two year old plant.
Explanation of Solution
Here, value in the sense, present value.
Calculation of present value of one-year old plant:
Hence, the present value of one-year old plant is $76.62.
Calculation of present value of two-year old plant:
Hence, the present value of two-year old plant is $48.61.
b)
To determine: Effect of government on taxes on one and two year old plant and existing plants should continue using the schedule of original tax depreciation.
Explanation of Solution
Given the industry is competitive, the investments in new plant producing the product must yields zero NPV.
Calculation of Revenues (R) at which the NPV of new plant is zero:
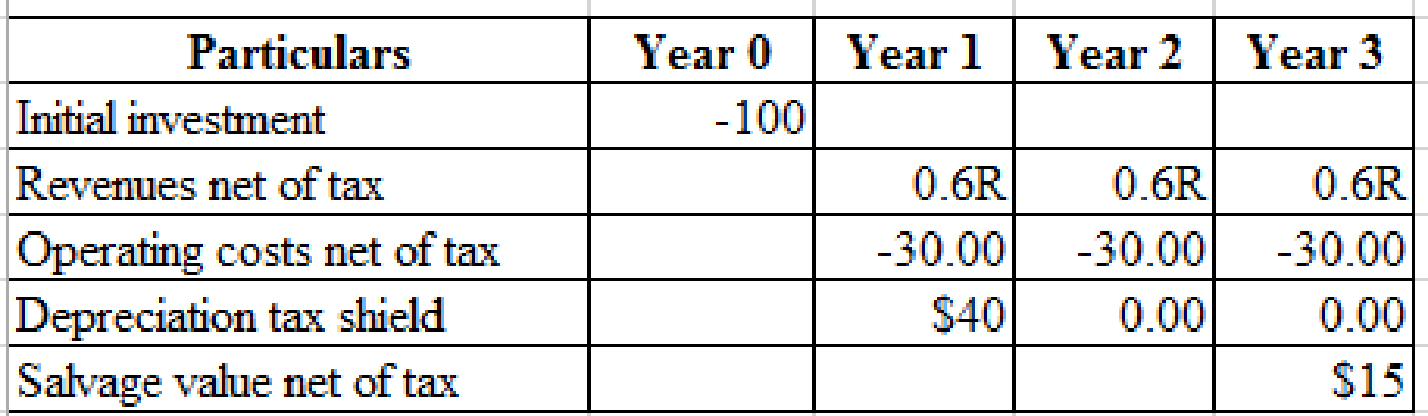
Hence,
By solving this, the value of R= $95.88.
By using the value of R we can calculate the present values of existing one and two years old plants.
Calculation of present value of one and two-year old plants:
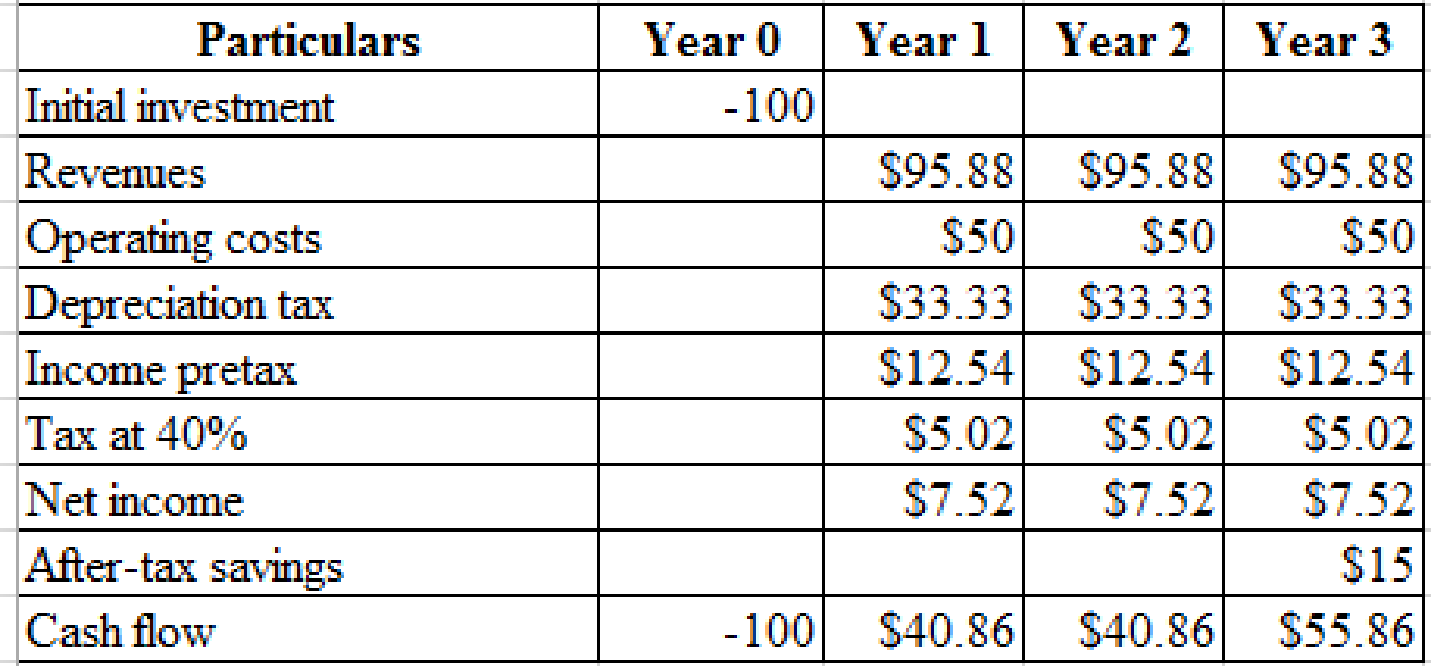
Hence, the present value of one-year old plant is $72.84.
Hence, the present value of two-year old plant is $46.55
c)
To determine: Net salvage value of two year old plant.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of salvage value:
The salvage value is $43.33.
d)
To determine: Values the corporate tax rates are abolished entirely.
Explanation of Solution
Solving for zero NPV:
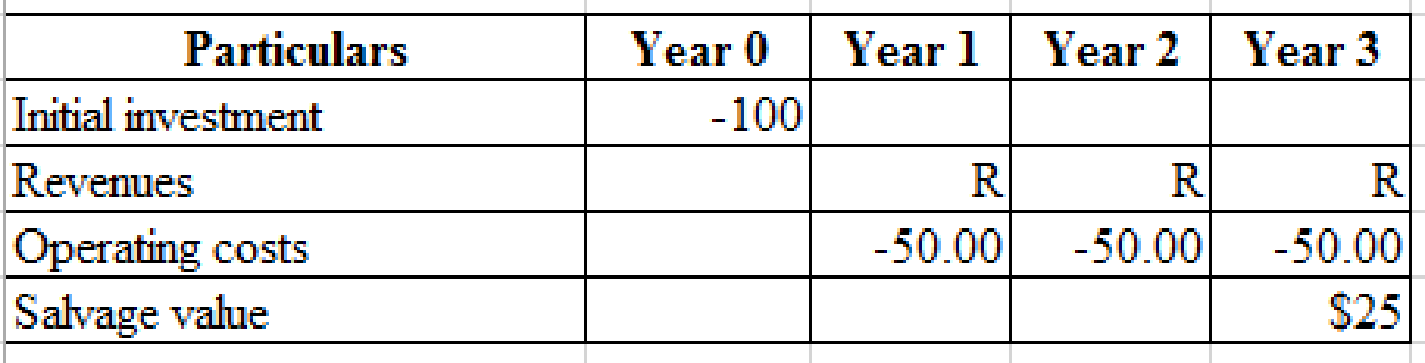
By using the revenues of $90.60
Calculation of present value of one-year old plant:
Hence, the present value of one-year old plant is $79.40.
Calculation of present value of two-year old plant:
Hence, the present value of two-year old plant is $54.67
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Principles of Corporate Finance
- What does a negative net present value (NPV) indicate? a) The project is profitable.b) The project is not viable.c) The project’s return is equal to the discount rate.d) The project has no cash inflows.arrow_forwardI need help in this question. What does a negative net present value (NPV) indicate? a) The project is profitable.b) The project is not viable.c) The project’s return is equal to the discount rate.d) The project has no cash inflows.arrow_forwardI need help!! The time value of money concept is based on the idea that: a) Money loses value over time.b) A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow.c) Future money is worth more than present money.d) Inflation has no effect on money.arrow_forward
- Don't use chatgpt. What does diversification mean in the context of investments?arrow_forwardDon't use chatgpt. The time value of money concept is based on the idea that: a) Money loses value over time.b) A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow.c) Future money is worth more than present money.d) Inflation has no effect on money.arrow_forwardSimilar projects, E and Z, are being considered using the payback method. Each has an initial cost of $100,000. Annual cash flows for each project are provided in the table at the right. a) What is the pay back period in years for E? (round to two decimal places) b) What is the pay back period in years for Z? Determine the cumulative cash flows for each year in the column next to the table (round to two decimal places)arrow_forward
- no ai What is compound interest, and why is it important in personal finance?arrow_forwardNo ai The time value of money concept suggests:A. Money loses value over timeB. Inflation doesn’t matterC. Future money is more valuableD. Money today is worth more than tomorrowarrow_forwardA food processing company is considering replacing essential machinery. Cost and relevant cash flow details are provided in the table at the right. The company requires an 11% return on its capital. a) What is the present value of the yearly cash flows? Use a Time Value of Money function for full credit. (round to nearest dollar) b) What is the net present value of the project? (round to nearest dollar) c) What is the internal rate of return of the project? Use a Time Value of Money function for full credit. (round to two decimal places)arrow_forward
- what is the firms' weighted average cost of capital? please show me weight calculation for each capital source.arrow_forwardA small manufacturer is considering an equipment replacement project. The new equipment would have an installed cost of $125,000 and would replace existing equipment that was purchased 3 years ago at an installed cost of $80,000. If the company moves forward with the replacement, it could sell the old equipment for $25,000. Purchasing the new equipment would result in the company's current assets increasing by $12,000 and current liabilities increasing by $9,000. The company uses the 5-year MACRS table for depreciation, and is taxed at 21%. a) What is the accumulated depreciation of the old equipment? b) What is the current book value of the old equipment? c) What is the amount of depreciation recapture/recovery? d) What is the tax on the sale of the old equipment? e) What are the after-tax proceeds from the sale of the old equipment? f) What is the change in Net Working Capital? g) What is the initial investment for the project?arrow_forwardLast year Lewis Bank paid an annual dividend of $7 per share. The bank expects the growth of its dividends to be stable at 2% per year going forward. a) If investors require an 8% return, what is the current value of Lewis Bank's stock? (round to nearest cent) b) If the stock currently trades at $124.55 per share, what is the dividend growth rate investors expect? (round to nearest percent)arrow_forward
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
