
Concept explainers
Exercises 21—24 refer to the population of animals in the following table. The population is divided into four groups: mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish.
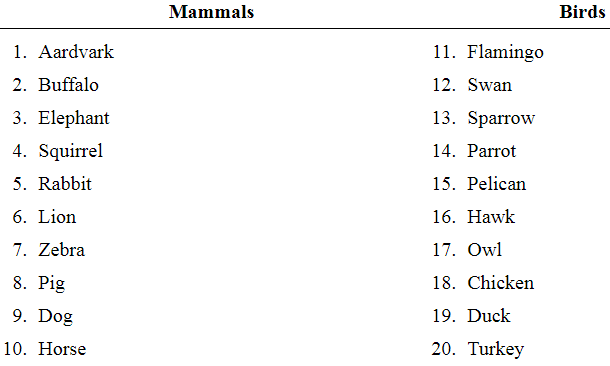

Another sample: Draw a simple random sample of two groups of animals from the four groups, and construct a sample of 20 animals by including all the animals in the sampled groups. What kind of sample is this?
Tofind:The simple random sample of two groups of animal and the type of sample.
Answer to Problem 23E
The simple random sample of two groups of animal is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:The population is divided into four groups: mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish. Refer to the population of animals in the following table.
| Mammals | Birds | Reptiles | Fish |
| Aardvark Buffalo Elephant Squirrel Rabbit Lion Zebra Pig Dog Horse | 11. Flamingo 12. Swan 13. Sparrow 14. Parrot 15. Pelican 16. Hawk 17. Owl 18. Chicken 19. Duck 20. Turkey | 21. Gecko 22. Iguana 23. Chameleon 24. Rattlesnake 25. Boa constrictor 26. Python 27. Turtle 28. Tortoise 29. Alligator 30. Crocodile | 31. Catfish 32. Tuna 33. Cod 34. Salmon 35. Goldfish 36. Shark 37. Trout 38. Perch 39. Guppy 40. Minnow |
Concept Involved:
If a sample is taken from a population and each item is equally like to make the sample then the sample is called simple random sample.
Calculation:
Since, the items are drawn from the population in groups, or clusters.
Thus, the type of sample is cluster sample.
Consider a simple random sample of two groups of animals from the four groups, and construct a sample of 20 animals by including all the animals in the sampled groups.
| Group | Samples | |
| Mammals | 1 | Aardvark, Buffalo, Elephant, Squirrel, Rabbit, Lion, Zebra, Pig, Dog, Horse |
| Birds | 2 | Flamingo, Swan, Sparrow, Parrot, Pelican, Hawk, Owl, Chicken, Duck, Turkey |
| Reptiles | 3 | Gecko, Iguana, Chameleon, Rattlesnake, Boa constrictor, Python, Turtle, Tortoise, Alligator, Crocodile |
| Fish | 4 | Catfish, Tuna, Cod, Salmon, Goldfish, Shark, Trout, Perch, Guppy, Minnow |
The step-by-step procedure is shown below.
Step 1: Enter any nonzero number on the HOME screen as the seed Step 2: Press Step 3: Press Step 4: Press Then enter Step 5: Press |
Therefore, the simple random sample of two groups of animal is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Connect Hosted by ALEKS Online Access for Elementary Statistics
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
Elementary and Intermediate Algebra: Concepts and Applications (7th Edition)
Graphical Approach To College Algebra
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
- A well-known company predominantly makes flat pack furniture for students. Variability with the automated machinery means the wood components are cut with a standard deviation in length of 0.45 mm. After they are cut the components are measured. If their length is more than 1.2 mm from the required length, the components are rejected. a) Calculate the percentage of components that get rejected. b) In a manufacturing run of 1000 units, how many are expected to be rejected? c) The company wishes to install more accurate equipment in order to reduce the rejection rate by one-half, using the same ±1.2mm rejection criterion. Calculate the maximum acceptable standard deviation of the new process.arrow_forward5. Let X and Y be independent random variables and let the superscripts denote symmetrization (recall Sect. 3.6). Show that (X + Y) X+ys.arrow_forward8. Suppose that the moments of the random variable X are constant, that is, suppose that EX" =c for all n ≥ 1, for some constant c. Find the distribution of X.arrow_forward
- 9. The concentration function of a random variable X is defined as Qx(h) = sup P(x ≤ X ≤x+h), h>0. Show that, if X and Y are independent random variables, then Qx+y (h) min{Qx(h). Qr (h)).arrow_forward10. Prove that, if (t)=1+0(12) as asf->> O is a characteristic function, then p = 1.arrow_forward9. The concentration function of a random variable X is defined as Qx(h) sup P(x ≤x≤x+h), h>0. (b) Is it true that Qx(ah) =aQx (h)?arrow_forward
- 3. Let X1, X2,..., X, be independent, Exp(1)-distributed random variables, and set V₁₁ = max Xk and W₁ = X₁+x+x+ Isk≤narrow_forward7. Consider the function (t)=(1+|t|)e, ER. (a) Prove that is a characteristic function. (b) Prove that the corresponding distribution is absolutely continuous. (c) Prove, departing from itself, that the distribution has finite mean and variance. (d) Prove, without computation, that the mean equals 0. (e) Compute the density.arrow_forward1. Show, by using characteristic, or moment generating functions, that if fx(x) = ½ex, -∞0 < x < ∞, then XY₁ - Y2, where Y₁ and Y2 are independent, exponentially distributed random variables.arrow_forward
- 1. Show, by using characteristic, or moment generating functions, that if 1 fx(x): x) = ½exarrow_forward1990) 02-02 50% mesob berceus +7 What's the probability of getting more than 1 head on 10 flips of a fair coin?arrow_forward9. The concentration function of a random variable X is defined as Qx(h) sup P(x≤x≤x+h), h>0. = x (a) Show that Qx+b(h) = Qx(h).arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning




