
Concept explainers
Tom Sevits is the owner of the Appliance Patch. Recently Tom observed a difference in the dollar value of sales between the men and women he employs as sales associates. A sample of 40 days revealed the men sold a
- (a) State the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis.
- (b) What is the decision rule?
- (c) What is the value of the test statistic?
- (d) What is your decision regarding the null hypothesis?
- (e) What is the p-value?
- (f) Interpret the result.
a.
State the null and the alternative hypothesis.
Answer to Problem 1SR
The null hypothesis is
The alternative hypothesis is
Explanation of Solution
In this context,
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
Alternative hypothesis:
Thus, the null hypothesis is
b.
Determine the decision rule.
Explanation of Solution
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the critical value using MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0 and Standard deviation value as 1
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability and Right Tails for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the probability value as 0.05.
- Click OK.
Output obtained using MINITAB software is given below:
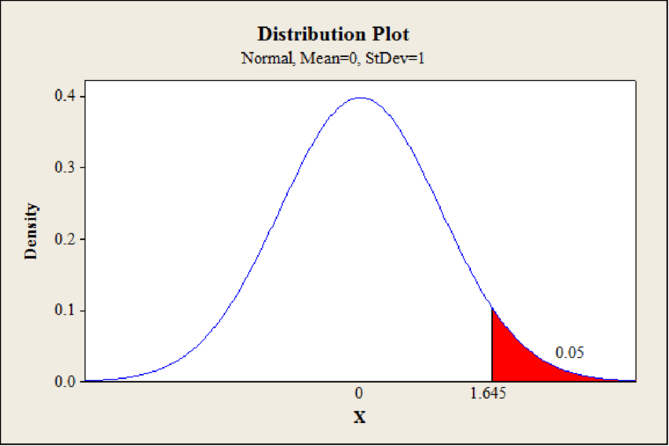
From the MINITAB output, the critical value is 1.645.
The decision rule is as follows:
If
c.
Find the value of the test statistics.
Answer to Problem 1SR
The value of the test statistics is 2.108.
Explanation of Solution
The test statistics is obtained as follows:
Thus, the value of test statistics is 2.108.
d.
Determine the decision regarding
Answer to Problem 1SR
The decision is that reject the null hypothesis
Explanation of Solution
Decision:
The critical value is 1.645 and the value of test statistic is 2.108.
The value of test statistic is greater than the critical value.
That is,
From the decision rule, reject the null hypothesis.
e.
Find the p-value.
Answer to Problem 1SR
The p-value is 0.0175.
Explanation of Solution
p-value:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the p-value using MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Enter the Mean as 0 and Standard deviation value as 1.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose X Value and right tails for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the X value as 2.108.
- Click OK.
Output obtained using MINITAB software is given below:
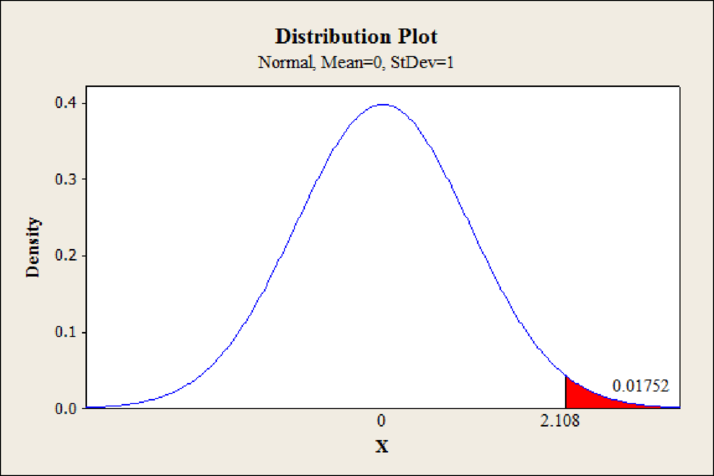
From the MINITAB output, the p-value is 0.0175.
Thus, the p-value is 0.0175.
f.
Interpret the result.
Explanation of Solution
Interpretation:
Here, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Therefore, there is evidence that the mean amount of sales per day by woman is greater than that of women.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
- T1.4: Let ẞ(G) be the minimum size of a vertex cover, a(G) be the maximum size of an independent set and m(G) = |E(G)|. (i) Prove that if G is triangle free (no induced K3) then m(G) ≤ a(G)B(G). Hints - The neighborhood of a vertex in a triangle free graph must be independent; all edges have at least one end in a vertex cover. (ii) Show that all graphs of order n ≥ 3 and size m> [n2/4] contain a triangle. Hints - you may need to use either elementary calculus or the arithmetic-geometric mean inequality.arrow_forwardWe consider the one-period model studied in class as an example. Namely, we assumethat the current stock price is S0 = 10. At time T, the stock has either moved up toSt = 12 (with probability p = 0.6) or down towards St = 8 (with probability 1−p = 0.4).We consider a call option on this stock with maturity T and strike price K = 10. Theinterest rate on the money market is zero.As in class, we assume that you, as a customer, are willing to buy the call option on100 shares of stock for $120. The investor, who sold you the option, can adopt one of thefollowing strategies: Strategy 1: (seen in class) Buy 50 shares of stock and borrow $380. Strategy 2: Buy 55 shares of stock and borrow $430. Strategy 3: Buy 60 shares of stock and borrow $480. Strategy 4: Buy 40 shares of stock and borrow $280.(a) For each of strategies 2-4, describe the value of the investor’s portfolio at time 0,and at time T for each possible movement of the stock.(b) For each of strategies 2-4, does the investor have…arrow_forwardNegate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forward
- Negate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forwardQuestion 6: Negate the following compound statements, using De Morgan's laws. A) If Alberta was under water entirely then there should be no fossil of mammals.arrow_forwardNegate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forward
- Characterize (with proof) all connected graphs that contain no even cycles in terms oftheir blocks.arrow_forwardLet G be a connected graph that does not have P4 or C3 as an induced subgraph (i.e.,G is P4, C3 free). Prove that G is a complete bipartite grapharrow_forwardProve sufficiency of the condition for a graph to be bipartite that is, prove that if G hasno odd cycles then G is bipartite as follows:Assume that the statement is false and that G is an edge minimal counterexample. That is, Gsatisfies the conditions and is not bipartite but G − e is bipartite for any edge e. (Note thatthis is essentially induction, just using different terminology.) What does minimality say aboutconnectivity of G? Can G − e be disconnected? Explain why if there is an edge between twovertices in the same part of a bipartition of G − e then there is an odd cyclearrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill

