
On December 31, 2019, Vail Company owned the following assets:
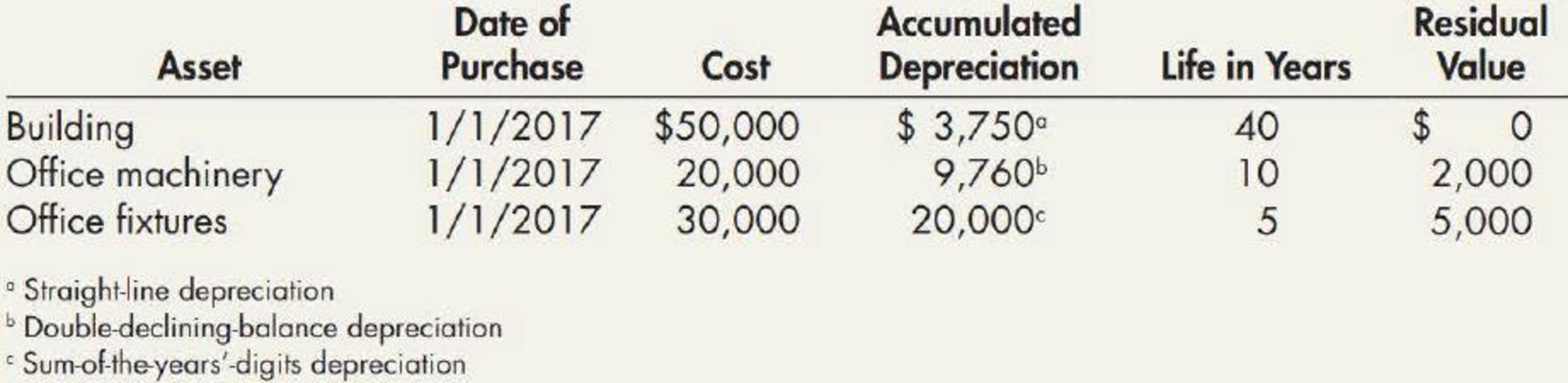
Vail computes depreciation and amortization expense to the nearest whole year. During 2020, Vail engaged in the following transactions:

Required:
- 1. Check the accuracy of the
accumulated depreciation balances at December 31, 2019. Round to the nearest whole dollar in all requirements. - 2. Prepare journal entries to record the preceding events in 2020, as well as the year-end recording of depreciation expense.
- 3. Prepare an Accumulated Depreciation account for each category of assets, enter the beginning balance,
post the journal entries from Requirement 2, and compute the ending balance.
1.
Calculate the accumulated depreciation balance at December 31, 2019 for the given assets, and check it’s ‘accuracy.
Explanation of Solution
Depreciation expense: Depreciation expense is a non-cash expense, which is recorded on the income statement reflecting the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset on account of its wear and tear or obsolesces.
Straight-line depreciation method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset could be distributed equally throughout the useful life of the asset is referred to as straight-line method.
Sum-of- the-years’ digits method: Sum-of-the years’ digits method determines the depreciation by multiplying the depreciable base and declining fraction.
Double-declining-balance method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset is high in the early years but gradually declines towards the end of its useful life is referred to as double-declining-balance method.
Calculate the accumulated depreciation balance at December 31, 2019 for the given assets, and cross check its’ accuracy as follows:
Building:
Office machinery:
| Year | Beginning book value (A) |
Depreciation rate (2) (B) | Depreciation expense |
Ending book value |
| 2017 | 20,000 | 20% | 4,000 | 16,000 |
| 2018 | 16,000 | 20% | 3,200 | 12,800 |
| 2019 | 12,800 | 20% | 2,560 | 10,240 |
| Total | 9,760 |
Table (1)
Note: Ending book value of the prior year is considered as the beginning book value of current year.
Office fixtures:
| Year | Depreciation base (3) (A) |
Faction (4) (B) | Depreciation expense |
Ending book value |
| 2017 | 25,000 | 8,333 | 21,667 | |
| 2018 | 25,000 | 6,667 | 15,000 | |
| 2019 | 25,000 | 5,000 | 10,000 | |
| Total | 20,000 |
Table (2)
Working note (1):
Calculate the annual depreciation expense of building.
Working note (2):
Compute the straight line rate:
Useful life = 10 years
Working note (3):
Calculate the depreciable base of office fixtures.
Working note (4):
Calculate the denominator of the fraction for sum-of-the-year’s digit.
2.
Prepare necessary journal entries for the given transaction for 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare necessary journal entries for the given transaction for 2020 as follows:
| Date | Account Title & Explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| January 3, 2020 | Building | 30,000 | |
| Cash | 30,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of building for cash) | |||
| March 8, 2020 | Cash | 3,000 | |
| Accumulate depreciation-Office machinery | 1,952 | ||
| Office machinery | 4,000 | ||
| Gain on disposal of office machinery (5) | 952 | ||
| (To record a piece of office machinery sold during the year) | |||
| May 17, 2020 | Office fixtures (6) | 5,640 | |
| Office machinery (6) | 3,760 | ||
| Repair expense | 230 | ||
| Cash | 9,630 | ||
| (To record office fixtures and machinery purchased during the year) | |||
| August 10, 2020 | Depreciation expense (7) | 67 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Office fixtures | 67 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred for office fixtures) | |||
| August 10, 2020 | Office fixtures | 900 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Office fixtures (7) | 467 | ||
| Cash | 700 | ||
| Office fixtures | 600 | ||
| Gain on disposal of office fixtures (8) | 67 | ||
| (To record the office fixtures exchanged during the year ) | |||
| October 20, 2020 | Repair expense | 125 | |
| Cash | 125 | ||
| (To record the repair expense incurred during the year) | |||
| December 31, 2020 | Depreciation expense – Building (9) | 2,061 | |
| Depreciation expense - Office machinery (14) | 2,390 | ||
| Depreciation expense - Office fixtures (17) | 5,064 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation-Building | 2,061 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation-Office machinery | 2,390 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation-Office fixtures | 5,064 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense of assets incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (3)
Working note (5):
Calculate the gain on disposal of office machinery.
Working note (6):
Calculate the cost of office fixtures and office machinery.
| Particulars | Appraisal value (A) | Total appraisal value (B) |
Proportion | Total purchase cost (D) |
Cost ($) |
| Office fixtures | $6,000 | $10,000 | 60% |
$9,400 | $5,640 |
| Office machinery | $4,000 | 10,000 | 40% | $9,400 | $3,760 |
| Total | $10,000 | 100% | $9,400 |
Table (4)
Working note (7):
Calculate the depreciation expense of desk.
| Year | Depreciation base |
Faction (4) (B) | Depreciation expense |
| 2017 | 500 | 167 | |
| 2018 | 500 | 133 | |
| 2019 | 500 | 100 | |
| 2020 | 500 | 67 | |
| Total | 467 |
Table (5)
Working note (8):
Calculate the gain on disposal of desk.
Working note (9):
Calculate the depreciation expense of building at the end of the year 2020.
Working note (10):
Calculate the remaining office machinery at 2020.
Working note (11):
Calculate the depreciation expense of office machinery at the end of the year 2020.
Working note (12):
Calculate the depreciation expense for remaining office machinery under double declining balance method.
Working note (13):
Calculate depreciation expense of office machinery purchased during 2020 under double declining balance method.
Working note (14):
Calculate total depreciation expense of office machinery at 2020.
Working note (15):
Calculate the depreciation expense of remaining office fixtures under the sum of the year’s digit method.
Working note (16):
Calculate the depreciation expense of new office fixtures under the sum of the year’s digit method.
Working note (17):
Calculate the total depreciation expense for office fixtures.
3.
Prepare T-account for the accumulated depreciation, and calculate the ending balance of accumulated depreciation for the given assets.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare T-account for the accumulated depreciation, and calculate the ending balance of accumulated depreciation as follows:
| Accumulated depreciation - Building | |||
| December 31, 2019 | 3,750 | ||
| December 31, 2019 | $2,061 | ||
| Clos. Bal. | $5,811 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation – Office machinery | |||
| July 3, 2020 | $1,952 | December 31, 2019 | 9,760 |
| December 31, 2019 | $2,390 | ||
| Clos. Bal. | $10,198 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation – Office mixtures | |||
| October 8, 2020 | 467 | December 31, 2019 | $20,000 |
| October 8, 2020 | $67 | ||
| December 31, 2019 | $5,064 | ||
| Clos. Bal. | $24,664 | ||
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING: REPORTING
- Buffalo Inc. issued $4,200,000 of convertible 5-year bonds on July 1, 2025. The bonds provide for 6% interest payable semiannually on January 1 and July 1. The discount in connection with the issue was $102,000, which is being amortized monthly on a straight-line basis. The bonds are convertible after one year into 15 shares of Buffalo Inc's $1 par value common stock for each $1,000 of bonds. On October 1, 2026, $504,000 of bonds were turned in for conversion into common stock. Interest has been accrued monthly and paid as due. At the time of conversion, any accrued interest on bonds being converted is paid in cash. Prepare the journal entries to record the conversion, amortization, and interest in connection with the bonds as of the following dates. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amounts. List all debit entries before credit entries.arrow_forwardhttps://view.officeapps.live.com/op/view.aspx?src=https%3A%2F%2Flectures.mhhe.com%2Fconnect%2Frichardson_iba_1e_1265454345%2Fdata_files%2Fch2%2FIBA_Lab2-4_Alt_Data.xlsx&wdOrigin=BROWSELINK make a pivot table and pivot chart to assess the sum of raw materials quantity purchased by year. make a slicer to interactively filter the pivot chart by state from which the products were ordered. Adjust the pivot chart to show horizontal bararrow_forwardSolve this following requirementsarrow_forward
- Need help with this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardGary Watson, a graduating business student at a small college, is currently interviewing for a job. Gary was invited by both Tilly Manufacturing Company and Watson Supply Company to travel to a nearby city for an interview. Both companies have offered to pay Gary's expenses. His total expenses for the trip were $96 for mileage on his car and $45 for meals. As he prepares the letters requesting reimbursement, he is considering asking for the total amount of the expenses from both employers. His rationale is that if he had taken separate trips, each employer would have had to pay that amount. Who are the parties that are directly affected by this ethical dilemma? multiple choice 1 Tilly Manufacturing Company Watson Supply Company Both the employers Are the other students at the college potentially affected by Gary's decision? multiple choice 2 Yes No Are the professors at the college potentially affected by Gary's decision? multiple choice 3 Yes No…arrow_forwardSolve with accounting explanationarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning

