
Equipment upgrade versus replacement. (A. Spero, adapted) The TechGuide Company produces and sells 7,500 modular computer desks per year at a selling price of $750 each. Its current production equipment, purchased for $1,800,000 and with a five-year useful life, is only two years old. It has a terminal disposal value of $0 and is
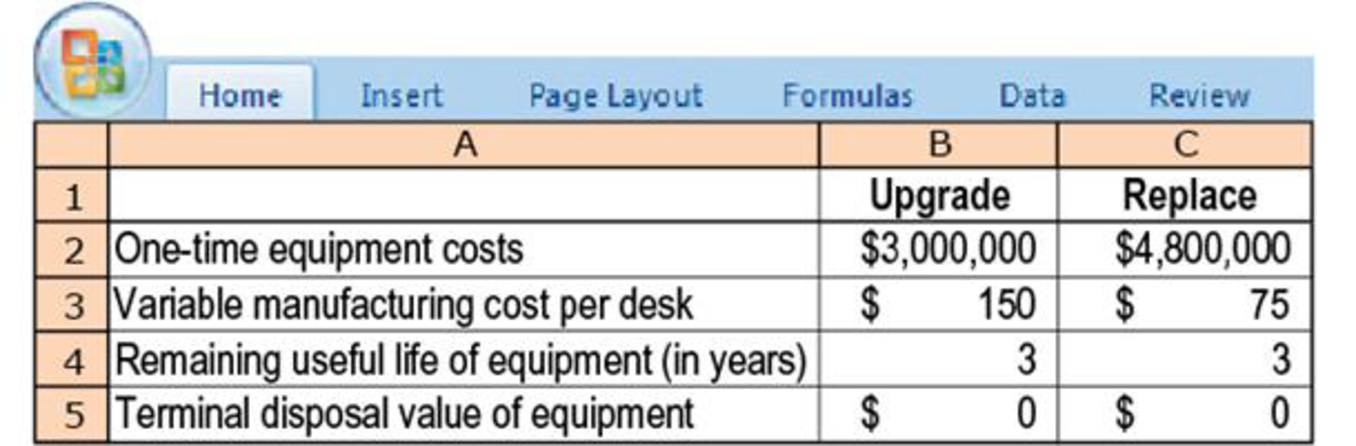
All equipment costs will continue to be depreciated on a straight-line basis. For simplicity, ignore income taxes and the time value of money.
- 1. Should TechGuide upgrade its production line or replace it? Show your calculations.
Required
- 2. Now suppose the one-time equipment cost to replace the production equipment is somewhat negotiable. All other data are as given previously. What is the maximum one-time equipment cost that TechGuide would be willing to pay to replace rather than upgrade the old equipment?
- 3. Assume that the capital expenditures to replace and upgrade the production equipment are as given in the original exercise, but that the production and sales quantity is not known. For what production and sales quantity would TechGuide (i) upgrade the equipment or (ii) replace the equipment?
- 4. Assume that all data are as given in the original exercise. Dan Doria is TechGuide’s manager, and his bonus is based on operating income. Because he is likely to relocate after about a year, his current bonus is his primary concern. Which alternative would Doria choose? Explain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK HORNGREN'S COST ACCOUNTING
- What Is the correct answer A B ?? General Accounting questionarrow_forwardCullumber Company uses a job order cost system and applies overhead to production on the basis of direct labor costs. On January 1, 2025, Job 50 was the only job in process. The costs incurred prior to January 1 on this job were as follows: direct materials $16,800, direct labor $10,080, and manufacturing overhead $13,440. As of January 1, Job 49 had been completed at a cost of $75,600 and was part of finished goods inventory. There was a $12,600 balance in the Raw Materials Inventory account on January 1. During the month of January, Cullumber Company began production on Jobs 51 and 52, and completed Jobs 50 and 51. Jobs 49 and 50 were sold on account during the month for $102,480 and $132,720, respectively. The following additional events occurred during the month. 1. Purchased additional raw materials of $75,600 on account. 2. Incurred factory labor costs of $58,800. 3. Incurred manufacturing overhead costs as follows: depreciation expense on equipment $10,080; and various other…arrow_forwardAccounting questionarrow_forward
- Determine the cost of the patent.arrow_forwardAccounting questionarrow_forwardMs. Sharon Washton was born 26 years ago in Bahn, Germany. She is the daughter of a Canadian High Commissioner serving in that country. However, Ms. Washton is now working in Prague, Czech Republic. The only income that she earns in the year is from her Prague marketing job, $55,000 annually, and is subject to income tax in Czech Republic. She has never visited Canada. Determine the residency status of Sharon Washtonarrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning


