
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given name has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Ether compounds:
The naming of theorganic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent
Common name: List the alkyl groups bonded to Oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word ‘ether’.
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
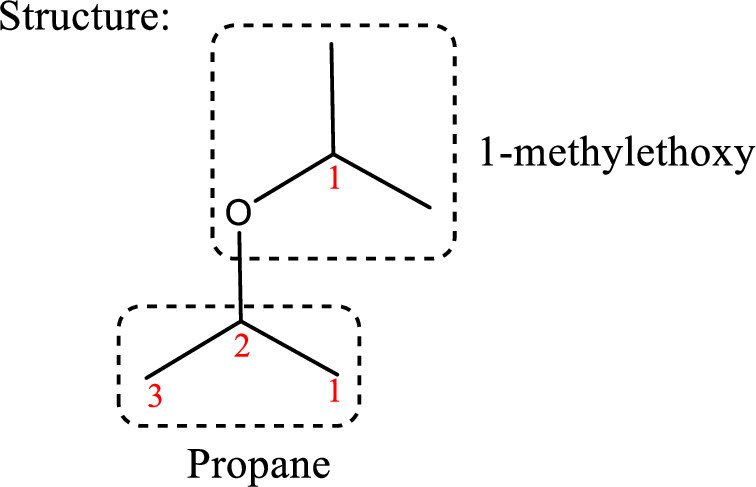
IUPAC name: 2-(1-Methylethoxy)propane
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Using the above principle, the longest carbon chain is propane (contains three carbons) as the parent alkane; naming the –OR group as alkoxy that is ‘2-(1-methylethoxy).
Therefore, the structure obtained is,
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given name has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Ether compounds:
The naming of theorganic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Common name: List the alkyl groups bonded to Oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word ‘ether’.
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
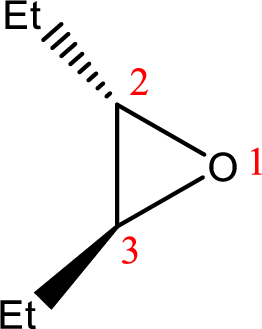
IUPAC name: trans-2,3-Diethyloxirane
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
Using the above principle, the name‘oxirane’ contains two carbons along with one Oxygen atom in a cyclic ringalong with two ‘ethyl’ substituentsin the ring.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given name has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Ether compounds:
The naming of theorganic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Common name: List the alkyl groups bonded to Oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word ‘ether’.
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
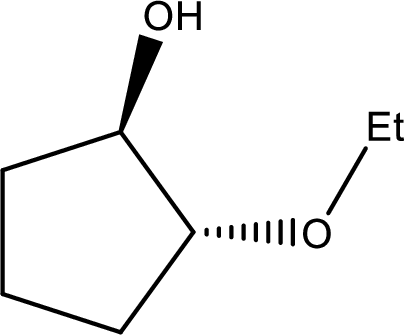
IUPAC name:trans-2-Ethoxycyclopentanol
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Here, the –OH group is preferred as the first priority and the compound is ‘alcohol’.
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain contains five carbons in a cyclic ring; the parent name is CYCLOPETANE and numbering the parent chain begins with carbon attached to the –OH group located at C-1 and the substituent ‘ethoxy’ is located at C-2.
Therefore, the structure is,
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given name has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Ether compounds:
The naming of theorganic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Common name: List the alkyl groups bonded to Oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word ‘ether’.
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
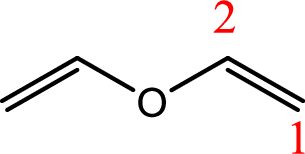
IUPAC name:Ethenyloxyethene.
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Using the above principle, the longest carbon chain isethene (contains two carbons with a double bond) as the parent
(e)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given name has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Ether compounds:
The naming of theorganic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Common name: List the alkyl groups bonded to Oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word ‘ether’.
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
IUPAC name:Cyclohexene oxide:
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
Using the above principle, the longest carbon cyclic ring contains sixcarbon atoms andone Oxygen atom is located at C-1 and 2 as three membered ring.
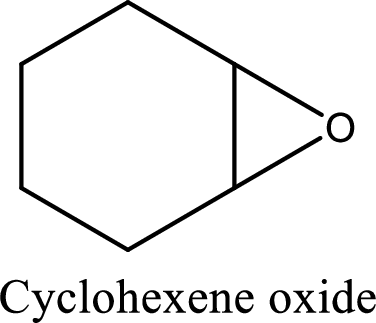
(f)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given name has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Ether compounds:
The naming of theorganic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Common name: List the alkyl groups bonded to Oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word ‘ether’.
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
IUPAC name:3-Cyclopropyloxy-1-propene
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Using the above principle, the longest carbon chain ispropene (contains three carbons with a double bond) as the parent alkene; naming the–OR groups as alkoxy that is 3-Cyclopropyloxy.
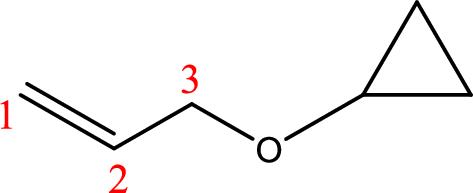
(g)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given name has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Ether compounds:
The naming of theorganic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Common name: List the alkyl groups bonded to Oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word ‘ether’.
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
IUPAC name:(R)-2-Methyloxirane
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
Using the above principle, the longest three membered cyclic ringscontaintwo carbon atoms and one Oxygen atom and the substituent methyl group is located at C-2.
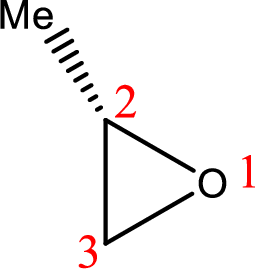
(h)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given name has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Nomenclature of Ether compounds:
The naming of theorganic compound is given by IUPAC (International Union for pure and applied chemistry). In the IUPAC names consist of certain rules for giving chemical names they are,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Common name: List the alkyl groups bonded to Oxygen in alphabetical order and adding the word ‘ether’.
Cyclic ether: The presence of Oxygen atom in a saturated ring is indicated by the prefix ox-, and ring sizes from three to six are indicated by the endings –irane, etane, olane, and –ane, respectively.
Numbering of the atoms of the ring begins with the oxygen atom. These compounds and others in which there is a heteroatom (non-carbon atom) in the ring are called heterocycles.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
IUPAC name:1,1-Dimethyloxycyclohexane,
Ethers are named by selecting the longest carbon chain as the parent alkane and naming the –OR group bonded to it an alkoxy group.
Using the above principle, the longest carbon ringiscyclohexane (contains six carbons) as the parent alkane; naming the two–OR groups as alkoxy that bothmethoxy groups located at C-1.
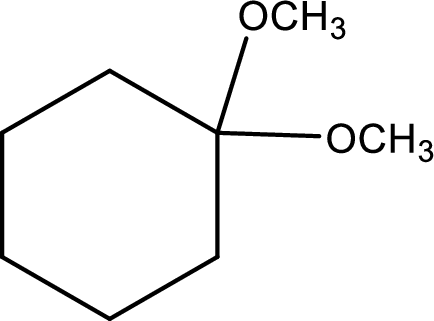
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-OWL V2 ACCESS
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure HO-C-CH2-CH3 O -OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-C-OH CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-C-OH Explanation Check S namearrow_forwardtheres 2 productsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this solvolysis reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + CH3CH2OH Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OCH2CH3 || OEt Charges OH 00-> | Undo Reset | Br Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. CH3CO2Na CH3CO2H Drawing + Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OAC Charges OH ОАс Na ဂ Br Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups entifying positions labeled with Greek letters in acids and derivatives 1/5 ssible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a ce an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. ne of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substi er the drawing area. O H OH Oneither substituent can be added. Check D 1 Accessibility ado na witharrow_forwardDifferentiate between electrophilic and nucleophilic groups. Give examples.arrow_forward
- An aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.arrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H- -OH H- OH H- -OH CH₂OHarrow_forwardAnswer the question in the first photoarrow_forward
- Ggggffg2258555426855 please don't use AI Calculate the positions at which the probability of a particle in a one-dimensional box is maximum if the particle is in the fifth energy level and in the eighth energy level.arrow_forwardExplain the concepts of hemiacetal and acetal.arrow_forwardBriefly describe a nucleophilic addition.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





